Lecture
AT 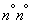 14.1 - 14.4 we considered the tasks associated with the estimates for the numerical characteristics of one random variable with a limited number of experiments and the construction of confidence intervals for these characteristics.
14.1 - 14.4 we considered the tasks associated with the estimates for the numerical characteristics of one random variable with a limited number of experiments and the construction of confidence intervals for these characteristics.
Similar questions arise when processing a limited number of observations on two or more random variables.
Here we confine ourselves to considering only point estimates for the characteristics of the system.
We first consider the case of two random variables.
There are results 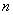 independent experiments on a random variable system
independent experiments on a random variable system 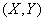 that gave results:
that gave results:
 ;
; 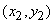 ; ...;
; ...; 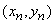 .
.
Required to find estimates for the numerical characteristics of the system: mathematical expectations 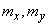 dispersions
dispersions  and the correlation moment
and the correlation moment 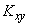 .
.
This question is solved in the same way as we solved it for one random variable. Unbiased estimates for mathematical expectations are arithmetic averages:
 ;
;  , (14.6.1)
, (14.6.1)
and for the elements of the correlation matrix -
 (14.6.2)
(14.6.2)
The proof can be carried out similarly.  14.2.
14.2.
When directly calculating estimates for the variances and the correlation moment, it is often convenient to use the connection between the central and initial statistical moments:
 (14.6.3)
(14.6.3)
Where
 (14.6.4)
(14.6.4)
Having calculated the statistical moments using formulas (14.6.3), one can then find unbiased estimates for the elements of the correlation matrix using the formulas:
 (14.6.5)
(14.6.5)
Example. Made shots from the aircraft on the ground in single shots. The coordinates of the points of impact were recorded and the corresponding values of the angle of the aircraft were recorded simultaneously. Observed values of slip angle 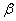 (in thousandths of radians) and abscissas of the point of impact
(in thousandths of radians) and abscissas of the point of impact 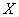 (in meters) are given in table 14.6.1.
(in meters) are given in table 14.6.1.
Table 14.6.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
one | -eight | -ten | eleven | +3 | -one |
2 | +10 | -2 | 12 | -2 | +4 |
3 | +22 | +4 | 13 | +28 | +12 |
four | +55 | +10 | 14 | +62 | +20 |
five | +2 | -one | 15 | -ten | -eleven |
6 | -39 | -1+ | sixteen | -eight | +2 |
7 | -15 | -eight | 17 | +22 | +14 |
eight | +5 | -2 | 18 | +3 | +6 |
9 | +10 | +6 | nineteen | -32 | -12 |
ten | +18 | +8 | 20 | +8 | +1 |
Find estimates for the numerical characteristics of the system 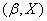 .
.
Decision. For clarity, apply all pairs of values 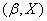 on the chart (Fig. 14.6.1). The location of the points on the graph already indicates the presence of a certain dependence (positive correlation) between
on the chart (Fig. 14.6.1). The location of the points on the graph already indicates the presence of a certain dependence (positive correlation) between 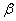
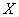 .
.
By the formulas (14.6.1) we calculate the average values of 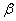 and
and 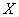 - estimates for mathematical expectations:
- estimates for mathematical expectations:
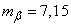 ;
;  .
.
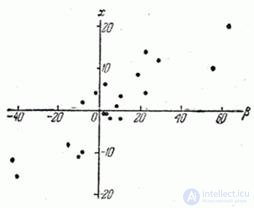
Fig. 14.6.1.
Next we find the statistical second initial moments:
 ;
;
 .
.
According to the formulas (14.6.3) we find the statistical variance:
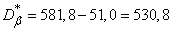 ;
;
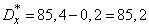 .
.
To find unbiased estimates, multiply the statistical variances by 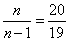 ; we will receive:
; we will receive:
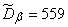 ,
,
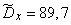 .
.
Accordingly, the standard deviations are equal to:
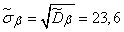 ;
; 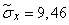 .
.
According to the last formula (14.6.4) we find the statistical initial moment:

and statistical correlation moment:
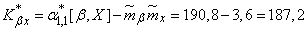 .
.
To determine the unbiased estimate, multiply it by 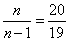 ; we get:
; we get:
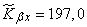 ,
,
whence the score for the correlation coefficient is:
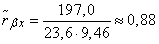 .
.
Obtained relatively large value 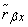 indicates a significant relationship between
indicates a significant relationship between 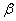 and
and 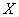 ; on this basis, it can be assumed that the slip is the main cause of lateral deviations of the projectiles.
; on this basis, it can be assumed that the slip is the main cause of lateral deviations of the projectiles.
Let us proceed to the case of processing observations over a system of an arbitrary number of random variables.
There is a system  random variables
random variables
 .
.
Over system produced 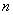 independent observations; the results of these observations are arranged in the form of a table, each row of which contains
independent observations; the results of these observations are arranged in the form of a table, each row of which contains  values taken by random variables
values taken by random variables  in one observation (table. 14.6.2).
in one observation (table. 14.6.2).
Table 14.6.2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The numbers in the table and numbered by two indices are the recorded results of observations; the first index indicates the number of a random variable, the second - the number of observation, so that 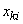 is the value accepted by
is the value accepted by 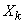 at
at  m observation.
m observation.
Required to find estimates for the numerical characteristics of the system: mathematical expectations 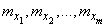 and elements of the correlation matrix:
and elements of the correlation matrix:
 .
.
On the main diagonal of the correlation matrix, obviously, there are variances of random variables.  :
:
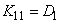 ;
; 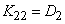 ; ...;
; ...; 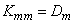 .
.
Estimates for mathematical expectations are found as arithmetic averages:

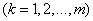 . (14.6.6)
. (14.6.6)
Unbiased estimates for variances are determined by the formulas
 , (14.6.7)
, (14.6.7)
and for the correlation moments - according to the formulas
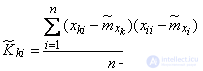 . (14.6.8)
. (14.6.8)
From these data, estimates are determined for the elements of the normalized correlation matrix:
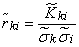 , (14.6.9)
, (14.6.9)
Where
 ;
; 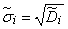 . (14.6.10)
. (14.6.10)
Example. 10 batches of bombs were dropped, 5 bombs each, and hit points were recorded. The results of the experiments are summarized in table 14.6.3. In the table letter  marked series number;
marked series number; 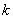 - number of the bomb in the series.
- number of the bomb in the series.
It is required to determine the appropriate values of the numerical characteristics — the expectation value and the elements of the correlation matrices — for a system of five random variables.
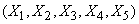
and systems of five random variables
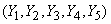 .
.
Decision. Estimates for mathematical expectations are found as arithmetic averages for the columns:
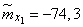 ;
;  ;
; 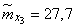 ;
; 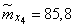 ;
; 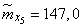 ;
;
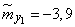 ;
; 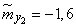 ;
; 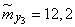 ;
; 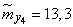 ;
; 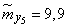 .
.
When calculating the elements of the correlation matrix, we will not, as in the previous examples, use the relations between the initial and central moments; in this case, in view of the strongly varying mathematical expectations, using this technique will not give advantages. We will calculate the estimates for the moments directly using formulas (14.6.2). To do this, subtract from each element of table 14.6.3 the average value of the corresponding column. The results are summarized in table 14.6.4.
Table 14.6.3
Abscissa x | Abscissa y | |||||||||
| one | 2 | 3 | four | five | one | 2 | 3 | four | five |
one | -120 | -20 | 2 | 60 | 180 | -20 | -15 | -eight | -6 | -2 |
2 | -108 | -75 | -20 | 20 | 80 | 40 | 60 | 120 | 125 | 130 |
3 | -200 | -120 | -80 | -20 | ten | -25 | -thirty | -20 | -ten | 2 |
four | -55 | -2 | 40 | 120 | 200 | -100 | -75 | -35 | 2 | 2 |
five | five | 60 | 100 | 165 | 220 | -40 | -thirty | -25 | -thirty | -45 |
6 | -240 | -202 | -140 | -88 | -thirty | 80 | thirty | 25 | ten | 2 |
7 | ten | 65 | 120 | 160 | 205 | 14 | 25 | 25 | thirty | ten |
eight | -40 | 0 | 65 | 103 | 170 | 80 | 75 | 60 | ten | -four |
9 | -100 | -40 | -ten | 55 | 105 | -70 | -60 | -thirty | -ten | 0 |
ten | 105 | 135 | 190 | 280 | 330 | 2 | four | ten | 12 | four |
Table 14.6.4
|
| |||||||||
| one | 2 | 3 | four | five | one | 2 | 3 | four | five |
one | -45,7 | -0,1 | -25,7 | -25,8 | 33.0 | -16,1 | -13,4 | -20,2 | -19,3 | -11,9 |
2 | -33, | -55,1 | -37,7 | -65,8 | -67,0 | 43.9 | 61.6 | 107.8 | 111.7 | 120.1 |
3 | -125.7 | -100,1 | -107.7 | -105,8 | -137.0 | -21,1 | -28,4 | -32,2 | -23,3 | -7.9 |
four | 19.3 | 17.9 | 12.3 | 34.2 | 53.0 | -96,1 | -73,4 | -47,2 | -11,3 | -7.9 |
five | 79.3 | 79.9 | 72.3 | 79.2 | 73.0 | -36,1 | -28,4 | -37,2 | -43,3 | -54.9 |
6 | -165,7 | -182.1 | -167.7 | -173,8 | -177.0 | 83.9 | 31.6 | 12.8 | -3,3 | -7.9 |
7 | 84.3 | 84.9 | 92.3 | 74.2 | 58.0 | 17.9 | 26,6 | 12.8 | 16.7 | 0.1 |
eight | 34.3 | 19.9 | 37.3 | 17.2 | 23.0 | 83.9 | 76.6 | 47.8 | -3,3 | -13,9 |
9 | -25,7 | -20,1 | -37,7 | -30,8 | -42,0 | -66,1 | -58,4 | -42,2 | -23,3 | -9.9 |
ten | 179.3 | 154.9 | 162.3 | 194.2 | 183.0 | 5.9 | 5.6 | -2,2 | -1.3 | -5.9 |
Squaring these numbers, summing up the columns and dividing by 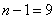 , we obtain estimates for the variances and standard deviations:
, we obtain estimates for the variances and standard deviations:
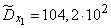 ;
; 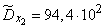 ;
; 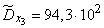 ;
;
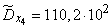 ;
; 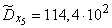 ;
;
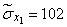 ;
; 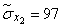 ;
; 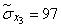 ;
; 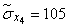 ;
; 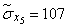 .
.
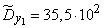 ;
;  ;
;  ;
;
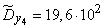 ;
; 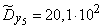 ;
;
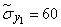 ;
; 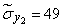 ;
; 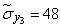 ;
;  ;
; 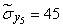 .
.
Чтобы найти оценку для корреляционного момента, например, между величинами 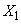 and
and 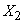 составим столбец попарных произведении чисел, стоящих в первом и втором столбцах таблицы 14.6.4. Сложив все эти произведения и разделив сумму на
составим столбец попарных произведении чисел, стоящих в первом и втором столбцах таблицы 14.6.4. Сложив все эти произведения и разделив сумму на 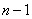 , we get:
, we get:
 .
.
Деля 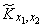 on
on 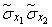 we will receive:
we will receive:
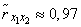 .
.
Аналогично находим все остальные элементы корреляционных матриц. Для удобства умножим все элементы обеих матриц моментов на  . We get:
. We get:

 .
.
(Ввиду симметричности матриц они заполнены только наполовину.)
Нормированные корреляционные матрицы имеют вид:

 .
.
Рассматривая эти матрицы, убеждаемся, что величины 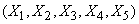 находятся в весьма тесной зависимости, приближающейся к функциональной; magnitudes
находятся в весьма тесной зависимости, приближающейся к функциональной; magnitudes 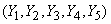 связаны менее тесно, и коэффициенты корреляции между ними убывают по мере удаления от главной диагонали корреляционной матрицы.
связаны менее тесно, и коэффициенты корреляции между ними убывают по мере удаления от главной диагонали корреляционной матрицы.
Comments
To leave a comment
Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis
Terms: Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis