Lecture
Extraction of precious metals from secondary raw materials is part of the problem of using returnable resources, which includes the following aspects:
The problem of using recycled materials containing precious materials from computers, peripheral equipment and other computer equipment (SVT) is relevant in connection with the technical re-equipment of industries.
Precious metals include gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium, iridium, ruthenium, osmium, as well as any chemical compounds and alloys of each of these metals.
Article 2, p. 4 of the Federal Law on Precious Metals and Precious Stones of March 26, 1998 No. 1463 reads: “Scrap and waste of precious metals are subject to collection in all organizations in which the said scrap and waste are generated. Collected scrap and waste are subject to mandatory accounting and can be recycled by collecting organizations for reuse or sold to organizations that have licenses for this type of activity for further production and refining of precious metals. "
The structural model of the work on the extraction of secondary precious metals from spent SVT products includes the following steps:
At the “Information Support” stage , information is collected about a specific facility from which it is planned to dispose of precious metals. At this stage it is necessary to follow the sequence of actions indicated in Figure 85.

As can be seen from the diagram in Figure 85, the main actions in the “Information support” phase are a continuous sequence of actions that prepare the basis for the successful implementation of the “Creation of conditions” phase.
At the stage of "Creating conditions" create conditions for the work of disassembling products SVT. The equipment to be disassembled is purchased and transported, and tools and workplaces are prepared.
At this stage it is necessary to follow the sequence of actions indicated in Figure 86.

As can be seen from the diagram shown in Figure 86, the main actions at the stage of creating the conditions are a continuous sequence of actions that prepare the basis for the successful implementation of the stage of product disassembly.
The sequence of disassembly is determined by the type of SVT product, its design features and equipment.
As a rule, the disassembly process must be performed in the reverse order of the product assembly process. The main activities at the stage "Disassembly of products" are presented in Figure 87.
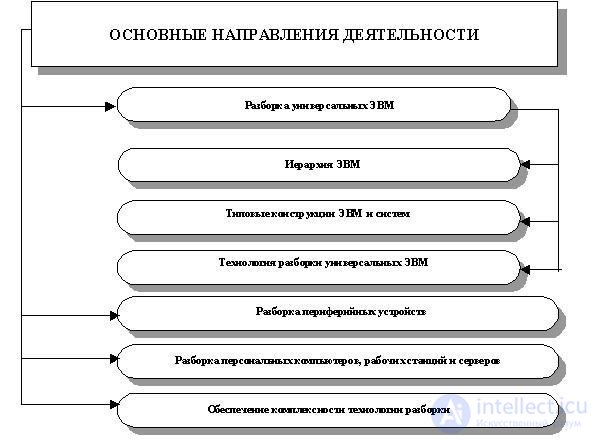
As can be seen from the diagram in Figure 87, the main actions at the “Disassembly” stage are a continuous sequence of actions that prepare the basis for the successful implementation of the “Batch Implementation” stage.
The main activities at the stage of “Implementation of the parties” are presented in Figure 88.

As can be seen from the scheme shown in Figure 88, the main actions at the “Implementation of the batches” stage are a sequence of actions that create the basis for the successful implementation of the procedures for the final stage of utilization of the CTS.
Comments
To leave a comment
Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment
Terms: Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment