Lecture
Flash memory is a type of EEPROM, its full name - Flash Erase EEPROM (Electronically Erasable Programmable ROM) - can be translated as "electrically erasable programmable read-only memory". In other words, flash memory is non-volatile (i.e. not energy consuming when storing data) rewritable (i.e., data can be erased and rewritten with electric current) memory whose contents can be quickly erased (Flash Erase).
Flash memory is semiconductor memory. Its unit cell, in which one bit of information is stored, is not a capacitor, but a field effect transistor with a special electrically isolated region, which is called a floating gate. An electric charge placed in this area can persist for many years. When recording one bit of data, the cell is charged - the charge is placed on the floating gate, when erasing, the charge is removed from the floating gate and the cell is discharged.
The advantages of flash memory compared to other means of transferring and storing data are obvious: high reliability and impact resistance (the result of the absence of moving components and the simplicity of the mechanical design of carriers and drives), low power consumption, compactness. However, it has drawbacks - a limited number of rewriting cycles (from 10 thousand to 1 million) and relatively slow work.
Flash memory has several types of array organization. The most widespread memory types of AND-NOT (NAND), OR-NOT (NOR). By architecture, these two types have significant differences.
The type of OR-NOT (NOR) contains cells connected in parallel to each other and provides relatively fast random access to data, the possibility of recording information byte. However, this type of architecture has cells of relatively large size because it does not scale well. The erase or write time is much longer than other types of flash memory.
Ideal for storing programs (BIOS, ROM cell phones, etc.), as well as to replace the EEPROM chips.
Type AND-NOT (NAND), contains cells, connected in series (garland), between two sample lines. Groups of cells are combined into pages. Pages in blocks. The drains of different transistors such a garland are on different pages. Therefore, random access to cells is not possible. Reading, writing are carried out simultaneously only within one page, and erasing, are carried out simultaneously only within one or several blocks. However, it is faster than the type of OR-NOT. Erasing / writing a block is also quite fast.
Device
The main elements of FLASH are mounted on a multilayer PCB board (see Figure 81):
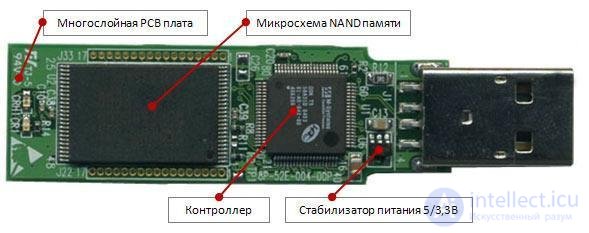
Figure 82 - The location of the main elements of the flash drive

Figure 83 - Block diagram of flash drive
Elements of flash memory appointment and symptoms of their failure
PCB is a multi-layer printed circuit board on which all flash elements are mounted. Typical faults: poor-quality soldering, internal breakages of conductors during mechanical damage, impact, bending. Symptoms: unstable flash work.
USB connector - poor soldering contacts. Symptoms: flash periodically undefined.
Stabilizer - converts and stabilizes the voltage coming from the computer in the voltage required for the controller and flash memory. Symptoms: Flash is not detected at all, or can be seen in the system as an unidentified device. Often fails when reversing the USB connector.
NAND IC - non-volatile memory. Symptoms: damage to individual memory blocks (trouble blocks) due to aging or for other reasons, the inability to write or read, is treated by reformatting proprietary utility with a decrease in the total size of the flash.
Controller - control chip NAND memory and data transfer. It contains information about the type of NAND chip, the manufacturer and other service information necessary for the operation of the flash drive. Symptoms: Flash is defined as an unknown device, zero or underestimated amount of flash memory. Often fails with hot flash extraction. Usually helps flashing the controller proprietary utilities.
Quartz resonator - forms the reference frequency for the operation of the logic controller and flash memory. In case of failure (which is extremely rare), flash is not detected in the system.
All malfunctions of flash drives are divided into two groups:
The most common malfunctions associated with mechanical or electrical damage caused by violation of the rules of operation of the device. By installing a flash drive in the slot on the system unit, the user, by carelessness, hooking it with his hand breaks the connector, often together with the printed circuit board on which the controller chips and the memory itself are soldered. Printed circuit board, despite its miniature, four-layer and restore the damaged tracks in the inner layers is impossible.

Figure 84 - Appearance of a flash drive with a broken connector

Figure 85 - Appearance of flash drive with a burning stabilizer
Software failures or so-called "soft" problems. This is when there is no visible mechanical or electrical damage on the drive, but the flash is defined as an unknown device, the computer freezes when accessing the disk, the volume is incorrectly determined. Here again, first of all, it is necessary to decide what is more important.
- the health of the drive or the data on it. If the system identifies the drive as a USB Storage device, but shows that its volume is zero or the disk is not formatted, or instead of a list of files you see a jumble of characters, it makes sense to first use the data recovery programs that are used for hard drives. Such as R-Studio, Get Data Back or similar. As a rule, if the trouble is related to an incorrect partition table or file system errors, these programs allow you to copy the information. If this method did not produce results, and the data are vital, then it makes sense to think about transferring the memory chip to another working medium. Incorrect recording (logical violations) occurs due to computer failures, improper extraction of the device or the exhaustion of the resource for recording flash chips.
Comments
To leave a comment
Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment
Terms: Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment