Lecture
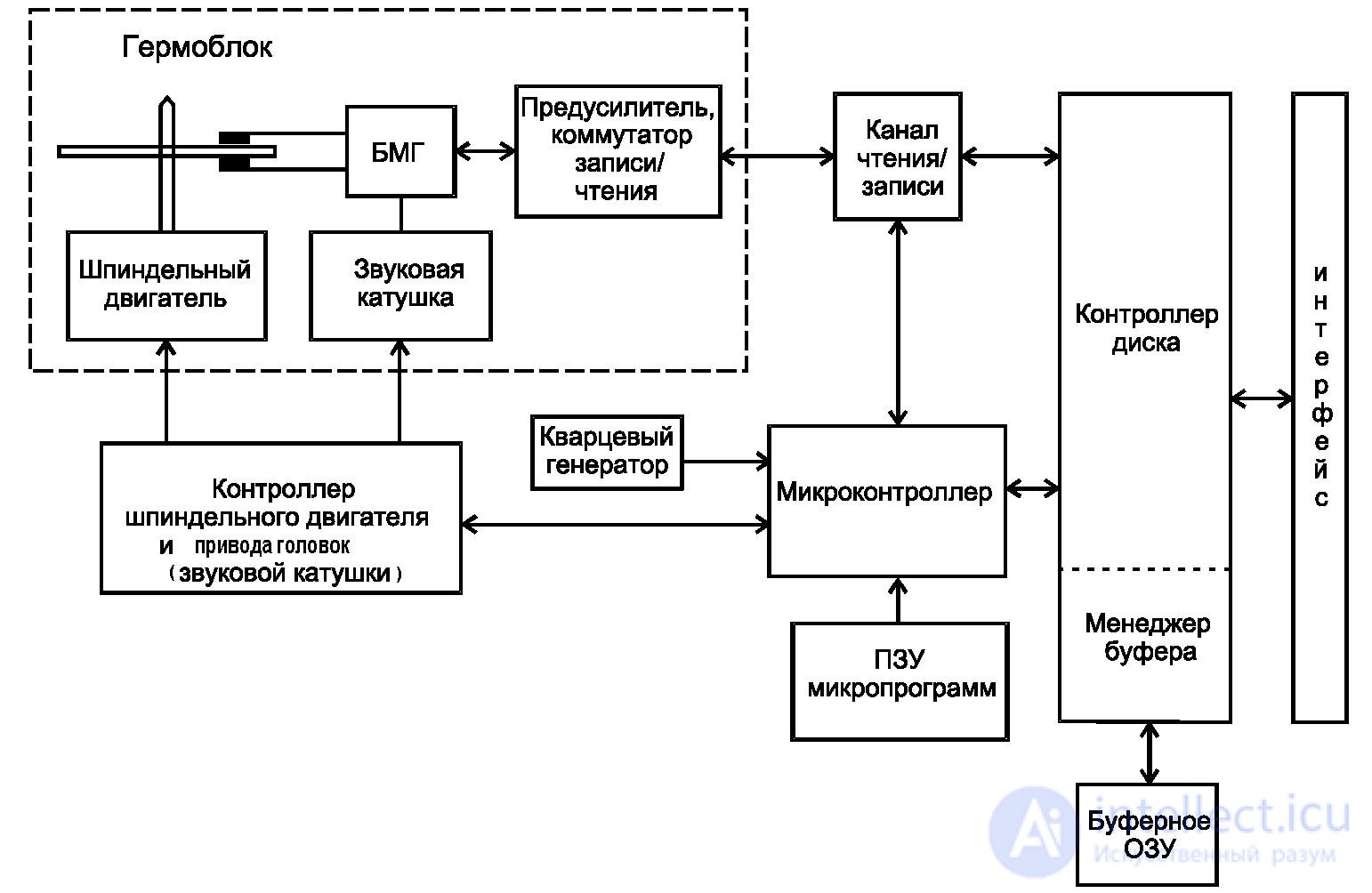
Modern hard disk drive (HDD) is a complex electronic-mechanical device. The elements of the accumulator are placed on the electronic board and the HDA (see Figure 36). The main element placed on the electronic board is a microcontroller (specialized microcomputer), which controls the operation of all storage devices and organizes communication with the CPU. All data to be stored are stored on a magnetic disk, which has the following logical organization (see Figure 37):
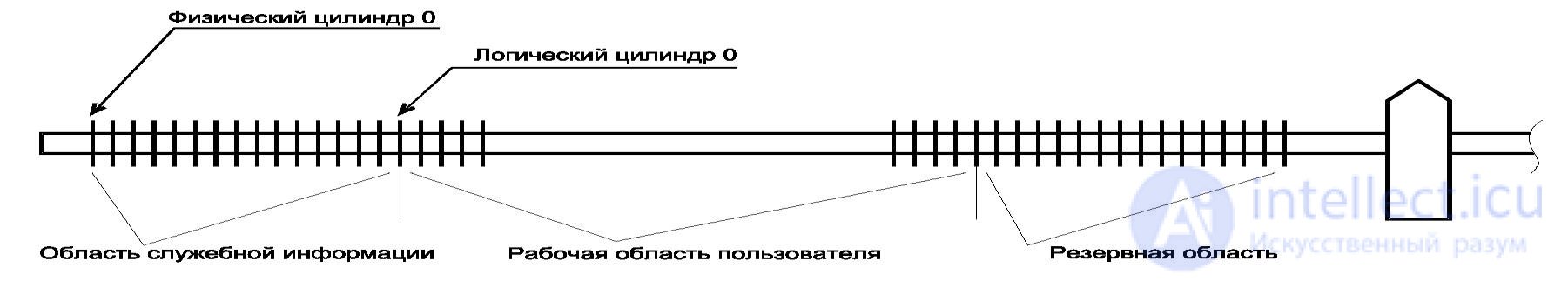
Service information
Service information is necessary for the functioning of the HDD itself and is hidden from the user. Service information can be divided into four main types:
Servo marking is necessary for the operation of the magnetic drive servo system.
heads of HDD. It is by servo marking that they are positioned and held on the track. The service marking is written to the disk during the production process through special technological windows in the housing of the assembled HDA. Recording is carried out by the drive’s own heads with the help of a special high-precision instrument - servoiler. The positioner of the heads is moved by a special servo-timer pusher in calibrated steps that are much smaller than the inter-track intervals.
The work programs (microcode) of the control microcontroller are a set of programs necessary for the operation of the HDD. These include programs for initial diagnostics, engine rotation control, head positioning, information exchange with a disk controller, buffer RAM, etc.
Hard disk manufacturers place a portion of the firmware on magnetic media not only to save the amount of ROM, but also for possible prompt correction of the code if errors are detected during production or operation. It is much easier to rewrite the firmware on a disk than to rewrite the “stitched” microcontrollers.
The configuration tables and drive settings contain information on the logical and physical organization of disk space. They are necessary for self-tuning of the electronic part of the disk, which is the same for all models of the family.
Defect Tables. (defect list) contains information about identified bad sectors
Modern hard drives usually have two main defect lists:
In addition, some HDDs have
Manufacturing technology of magnetic disks is very complex, control
The state of the disk surface is carried out at all stages of manufacturing, but even this does not allow to obtain the surface of a magnetic disk without defects. During the operation of the disk, the number of defects increases. Therefore, manufacturers of drives have provided special methods for hiding defects, which allow you to hide defects both in production and in operation.
Methods of hiding defective sectors (in the manufacture of disks). AT
At present, in the production of disks, several main methods of hiding defects are used.
The first is to reassign the address of damaged sectors to the address of the backup sector (Figure 38).
The method causes a loss of performance of the HDD, since every time it detects a sector marked as unusable, it will be forced to move the heads to a spare area, which may be far from the location of the defect.
This method of hiding defects was called the “replacement method” or REMAP (from the English “re-map”: restructuring of the sector map). Currently, the production does not apply.
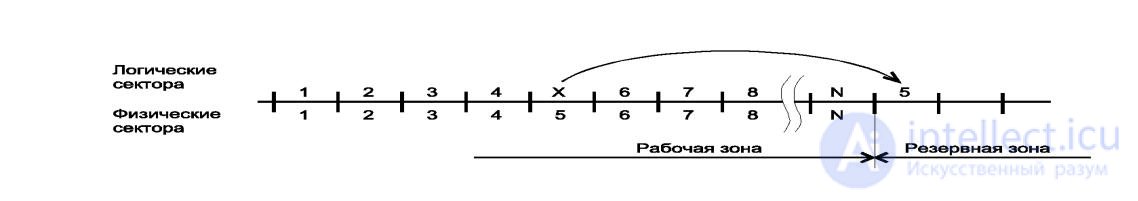
The second (main) method uses the following algorithm: after identifying all defects, addresses of all serviceable sectors are rewritten again, so that their numbers go in order. Bad sectors are simply ignored and are not involved in further work. The reserve area also remains uninterrupted and its part joins the end of the working area - to equalize the volume. This, the second main type of defect hiding, is called the “sector skipping method”. The new disk does not have bad sectors, but
reserve area is continuous!

Methods of hiding defective sectors during disk exploitation To hide defects in domestic conditions, the “method
replacement ”Remup Replacement is performed in automatic mode, this technology has received
the name is automatic defect reassignment (automatic reassignment of defects), and the process itself is reassign.
REMAP works as follows:
if an error occurs while trying to access the sector, the controller understands that the sector is faulty, and marks it on the fly as BAD.
His address is immediately recorded in the table of defects (G-list).
During operation, the controller constantly compares current sector addresses with addresses from a table and does not refer to defective sectors. Instead, he moves the heads to the backup area and reads a sector from there. On the characteristic of the disk V readings = F (N dor), as small dips on the graph of reading. The same thing will happen when recording.
HDD operational monitoring system - SMART
Almost all hard drives released after the 95th year, have a system of operational monitoring of their condition - SMART (Self Monitoring And Reporting Technology).
There is some relationship between SMART attributes and the surface state. Some are directly related to bad-blocks:
Reallocated sector count and Reallocated event count: the number of reassigned sectors . These attributes show the number of sectors reassigned by REMAP to the G-list defect list. For new screws, they must be zero! If their value is different from zero, then this means that the screw has already been in use.
Raw read error rate: the number of read errors. it "Soft" mistakes successfully corrected by the electronics of the drive and not causing data distortion. It is dangerous when this parameter drops sharply in a short period of time, turning into the yellow zone. This indicates serious problems in the drive.
Current Pending Sector: This attribute reflects the content. "Temporary" defect list present on all modern drives, i.e. current number of unstable sectors. These sectors screw could not read the first time. The constant value of this attribute above zero indicates a problem in the drive.
Uncorrectable Sector: shows the number of sectors errors in which failed to correct the ECC-code. If its value is above zero, it means that it is time for the screw to do REMAP.
Types of magnetic disk defects HDD
Defects on the HDD surface are divided into the following groups:
Surface defects . Occur with mechanical damage to the magnetic coating inside the sector space, for example due to scratches caused by dust, aging of pancakes or careless handling of the screw. Such a sector should be marked as invalid and excluded from circulation.
Servo errors . Servo speed stabilization occurs rotation of the engine and keeping the head on a given track, regardless of external influences and thermal deformation of the elements.However, during the operation of the disc, some servos may be destroyed. If there are too many bad servos, failures will occur in this place when accessing the information track: the head, instead of taking the position it needs and reading the data, will begin to shy from side to side. The presence of such errors is often accompanied by a bang of heads, a hovering drive and the inability to fix it with regular utilities. Elimination of such defects is possible only by special programs, by disabling defective tracks, and sometimes the entire disk surface.
Independently HDD cannot restore the servo format, this is done only at the factory.
Hardware BADs Occur due to faulty mechanics or drive electronics. These problems include:
Errors of this type are usually catastrophic and cannot be corrected programmatically.
Correctable logical defects (soft beds): appear, if a The sector checksum does not match the checksum of the data written to it.
Occurs due to interference or power failure during recording, when the HDD has already written data to the sector, but did not have time to write the checksum.
Upon subsequent reading of this “unfinished” sector, a failure will occur: first, the screw will read the data field, then calculate their checksum and compare it with the recorded one. If they do not match, the drive controller will decide that an error has occurred and make several attempts to re-read the sector. If this does not help (and it does not help, because the checksum is obviously wrong), then using the redundancy of the code, it will try to correct the error, and if this fails, the screw will generate an error to the external device. On the part of the operating system, it will look like BAD.
Uncorrectable logical errors. These are errors in the internal format of the hard drive, leading to the same effect as surface defects. Occur when the destruction of the sector headers, for example, due to the effect on the screw of a strong magnetic field. But unlike physical defects, they are amenable to correction programmatically. And they are called incorrigible only because for their correction it is necessary to do the "right"
low-level formatting, which is difficult for ordinary users due to the lack of specialized utilities.
"Adaptive" bedy. Despite, that the screws are very precise devices, their mass production inevitably causes a variation in the parameters of mechanics, radio components, magnetic coatings and heads.
Therefore, all modern screws in the manufacture are individually customized, in the process which selects the parameters of electrical signals in which the device works better.
This setting is carried out by a special program for technological surface scanning. At the same time, so-called adaptive variables are generated, which contain information about the features of a specific HM unit. Adaptives are stored on disks in the service area, and sometimes in flash memory on the controller board.
During operation of the screw adaptive can be destroyed destroyed
"Adaptive" bedy differ from the usual in that they are "floating". Cut adaptive bedy run selfscan'a - internal program
testing, similar to that used at the factory in the manufacture of screws. This creates new adaptive, and the screw returns to normal. This is done in the conditions of branded service centers.
Comments
To leave a comment
Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment
Terms: Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment