GOST 18322-78 "System maintenance and repair of equipment" (service stations and P) defines a system of maintenance and repair of equipment, as a set of interrelated tools, documentation of maintenance and repair and performers needed to maintain and restore the quality of the product included in this system.
The analysis of the task of maintenance and repair of PST allows us to single out the following areas of work for the PTA:
- Ensuring the performance of computer equipment . With It is necessary to understand that this task consists in monitoring the working capacity and forecasting the needs for updating the CBT fleet. When solving this problem, it is necessary to use the analysis and forecasting of the state of the hardware, software and existing tasks, which will allow to solve existing problems in a planned way
- Ensuring the performance of operating systems and application software . It is necessary to understand what is this The challenge is:
- correct selection of drivers, solving problems of their interaction with each other and other hardware - software,
- the need to monitor the performance of installed software and predict the need for its updating;
- Ensuring the integrity, integrity and operability of information arrays . This task is reduced to back-up archiving of data, ensuring their protection against viruses and other distorting actions;
- Ensuring the operability of peripheral, network and communication equipment.
The maintenance and repair system for the CBT must meet the following requirements:
- ensuring the specified levels of operational reliability of the SVT fleet with rational material and labor costs;
- its planned and normative character, which allows planning and organizing maintenance and repair at all levels;
- compulsory for all organizations and enterprises that own SVT, regardless of their departmental subordination;
- concreteness, accessibility and suitability for management and decision-making by all links of the engineering (service) service;
- the stability of the basic principles and the flexibility of specific standards, taking into account changes in operating conditions, design, quality and reliability of SVT; consideration of the diversity of operating conditions of the SVT.
Methods of formation of the system maintenance and repair
The principal basis for building a maintenance and repair system are:
- the goal that is set for the CBT;
- the level of reliability and quality of SVT;
- organizational and technical limitations.
Each node, mechanism, SVT can have its optimum frequency of maintenance. If these periodicities are followed, then the CTS as a whole should almost continuously be sent for maintenance, which will cause great difficulties with the organization of work and additional loss of working time, especially in preparatory and final operations.
Therefore, after selecting from the totality of the effects of those that should be carried out during maintenance and determining the optimal frequency of each operation, the operations are grouped into types of maintenance. This makes it possible to reduce the number of SVT outputs for maintenance and downtime in maintenance and repair. However, it should be borne in mind that the grouping of operations is inevitably associated with the deviation of the frequency of maintenance of a given type from the optimum frequency of maintenance of individual operations. When determining the frequency of maintenance operations of a group (“group” frequency), the following methods are used:
- technical and economic method;
- grouping for core operations
With the techno-economic method determine such a group
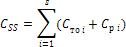
frequency, which corresponds to the minimum cost of maintenance and repair of SVT
where Css is the total unit cost of maintenance and repair of objects;
STOi - specific costs for maintenance of the i-ro facility; СРi - unit costs for repairing an i-ro facility;
S - the number of operations in the group (as maintenance). The optimal frequency will be when Css = Cmin, 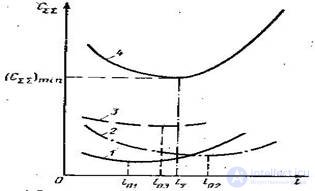
Figure 5-Scheme of application of techniques - an economic method for determining to determine the group optimality THEN.
1,2,3 - the total unit cost of maintenance and P for individual objects.
4- the same for a group of objects.
Grouping for core operations THAT is based on what the implementation of a group of operations maintenance is timed to the optimal frequency, the so-called core operations, which have the following features:
- affect the performance of SVT;
- their non-compliance reduces the reliability and cost-effectiveness of the operation of the SVT;
- characterized by high labor intensity, require special equipment and tools;
- regularly repeated.
Thus, according to this method, the frequency of maintenance of a core operation is taken as the frequency of the type of maintenance or group of operations.
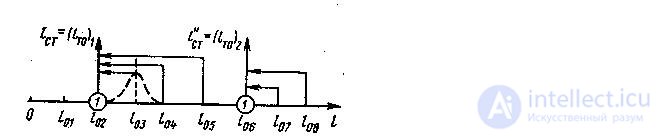
Figure 6-Scheme of grouping for core operations
All activities carried out in the framework of maintenance, are divided into three groups:
-control technical condition;
- preventive maintenance;
-The current maintenance.
Control of the technical state of the CBT serves to control the work SVT, localization of malfunction sites, eliminating the effect of random failures on the results of calculations. In modern CBT, such control is mainly carried out using the CBT itself.
Preventive maintenance is a series of activities aimed at maintaining a given technical state of the CW for a certain period of time and extending its technical resource. Preventive activities conducted at the BAS can be divided into two groups.
There are two types of preventive measures:
- active
- passive.
- are performed
- operations, the main purpose of which is to prolong the time-free service of the computer. They come down mainly to periodic cleaning of the entire system, as well as its individual components.
- usually involve measures to protect the computer from external adverse effects. It is about installing protection devices in the power supply network, maintaining
cleanliness and acceptable temperature in the room where the computer is installed, reducing the level of vibration, etc.
Active Preventive Maintenance Methods System Backup
One of the main stages of preventive maintenance is backing up the system. This operation allows you to restore the system in case of a fatal hardware failure. For backup, you must purchase a high-capacity storage device.
Cleaning
One of the most important elements of preventive maintenance is regular and thorough cleaning. Dust accumulating inside the computer can cause many troubles.
Firstly, it is a heat insulator that impairs the cooling system.
Secondly, dust must contain conductive particles, which can lead to leaks and even short circuits between electrical circuits.
And finally, some substances contained in the dust can accelerate the process of oxidation of contacts, which will eventually lead to disruptions in electrical connections.
Installing chips into place
With preventive maintenance it is very important to eliminate the effects of thermal displacement of the microcircuits. Since the computer heats up and cools when turned on and off (therefore, its components expand and contract), the chips installed in the slots gradually "creep out" of them. Therefore it is necessary to find all the components installed in the sockets, and put them in place.
Cleaning connector pins
Wipe the pins of the connectors is necessary to ensure that the connections between nodes and components of the system were reliable. Attention should be paid to the expansion, power supply, keyboard and speaker connections located on the system board. As for the adapter cards, they need to wipe the printed connectors inserted into the slots on the system board, and all other connectors (for example, installed on the external panel of the adapter).
Cleaning the keyboard and mouse
The keyboard and mouse seem to be designed to draw in dust and dirt. If you ever open the old keyboard, you will be amazed at its resemblance to the trash can.
Therefore, I advise you to periodically clean the keyboard with a vacuum cleaner.
Preventive maintenance of hard drives
To ensure data integrity and improve the efficiency of the hard disk, it is necessary to perform some maintenance procedures from time to time. There are also a few simple programs with which you can to some extent insure yourself against data loss. These programs create backup copies (and, if necessary, restore them) of those critical areas of the hard disk, if they are damaged, access to files becomes impossible.
File defragmentation
As you write files to the hard disk and delete them, many of them fragment, i.e. broken into many parts scattered around the disk. Periodically performing file defragmentation, you solve two problems at once. First, if the files occupy continuous areas on the disk, then the movement of the heads as they are read and written becomes minimal, which reduces the wear of the actuator and the disk itself. In addition, significantly increases the speed of reading files from disk.
Secondly, in case of serious damage to the file allocation tables (File Allocation Table - FAT) and the root directory, it is easier to recover the data on the disk if the files are recorded as a whole.
Antivirus software
Viruses are dangerous for any operating system.
Passive preventive maintenance methods
Under passive prophylaxis means the creation of a common external environment suitable for the operation of a computer.
Workplace
The ultimate goal of any prevention is the safety of the equipment (and the money invested in it). Computers work quite reliably in human-friendly conditions.
Computer heating and cooling
Temperature fluctuations adversely affect the state of the computer. Therefore, in order for the computer to work reliably, the temperature in the office or apartment must be constant.
For any electronic devices, including computers, the allowed temperature range is indicated. Most manufacturers give this data in the product documentation. It should indicate two temperature ranges: during operation and during storage. For example, for most IBM computers, these ranges are:
- during operation: from +15 to + 32 ° C;
- storage: +10 to + 43 ° C.
On and off cycles
To ensure the failure-free operation of the SVT, it is necessary as little as possible
turn on and off. There are two obvious ways to minimize temperature fluctuations in the system: either leave the computer turned on forever or never turn it on.
It is unlikely that the user will be satisfied with the second option. Therefore, if your main and only goal is to extend the life of the system, you should keep your computer constantly turned on. Of course, in real life, other circumstances have to be taken into account, such as the cost of electricity, fire safety, etc.
Electrostatic charges
Electrostatic charges pose a serious threat to computer components. They are most dangerous in winter, with low air humidity, as well as in areas with a dry climate. Under these conditions, special precautions must be taken when working with a computer.
Electrostatic phenomena outside the system case rarely lead to serious consequences, but a strong discharge on the chassis, keyboard, or just next to a computer can lead to violations in parity checking (in memory) or computer hang.
Interference in the power supply
In order for the computer to work normally, the supply voltage must be sufficiently stable, and the level of interference in it should not exceed the maximum permissible value.


Comments
To leave a comment
Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment
Terms: Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment