Lecture
Since we started talking about the semantic core of queries, let's continue this direction and move on to promoting sites on low-frequency queries. “Long tail search” is otherwise called this component. Let us touch on a few points to consider.
First of all, let's see why we need to take into account low-frequency queries. We will bind here both foreign experience, and in relation to the search engine Yandex.
The concept of "long tail search" exists from the very beginning of the development of Internet marketing, and from the very beginning Internet marketers are looking for ways to reach as large an audience as possible with the help of a large amount of content to cover the maximum possible length of the "tail".
The other day I read a wonderful article on the site of the well-known company "Hitwise" (despite the fact that the article was written a year ago, it is still very relevant) in this article, using real examples from the study, it is shown how long this so-called search tail can be requests. In his article, Bill Tancer points out some numbers from his research:
... the most popular keywords make up only 3.25% of all search traffic!
Moreover, even the remaining requests that we can attribute to the top do not have a significant advantage in all search traffic:
What comes out of it. Well, for example, if you somehow miraculously gained control over the first thousand search queries on the most popular search engines (Google, Yahoo !, Bing, Ask, etc.), then all the same you will not be able to receive all the search traffic, even most of it.
Therefore, the tail of the unpopular low-frequency queries is very important, because most of the search traffic is distributed along it. Moreover, the scale in which the ratio of the “tail” to the “head” is expressed is simply amazing.
Take a look at the graph I took from the above article:
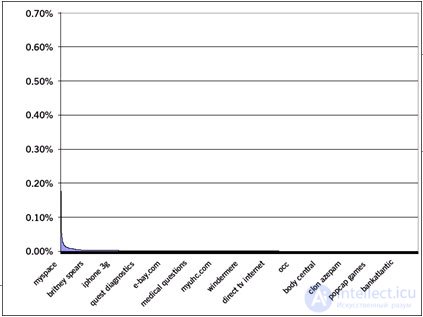
Even this graph does not really reflect the whole situation related to the search tail, it is limited by the following factors:
Despite the fact that it does not look legible on the chart, the Y-axis is shown correctly, and it stretches along the entire list of keywords. Do not forget that these are only 10,000 words that are at the top of the list of 14 million positions.
In order to make you understand better, I made my own schedule, in which the same statistics are shown, but somewhat in a more "artistic" form:
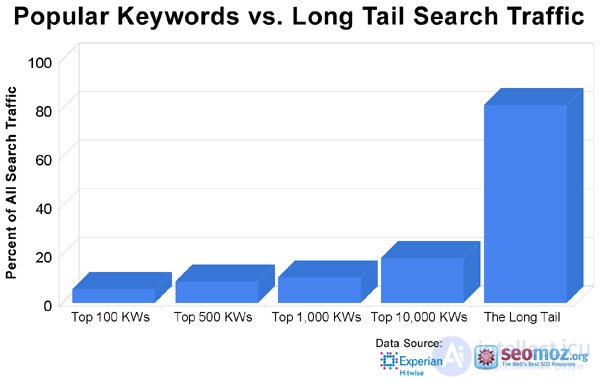
And now the replica at first, the original schedule. I tried to make it as simple and intelligible as possible, I think now it should be clear to you what this “long” search tail is.
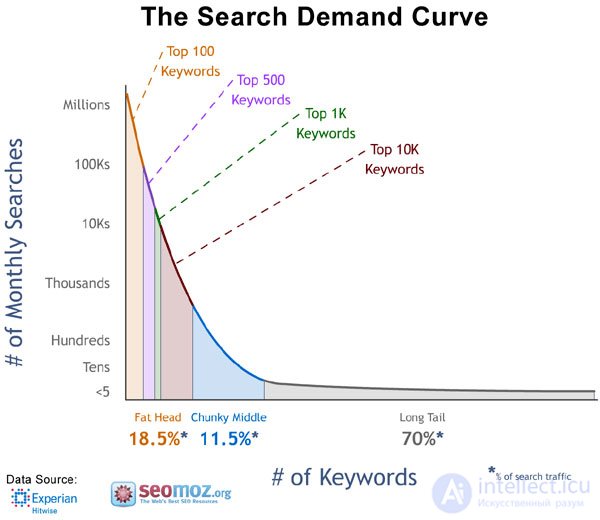
On the graph you see the curve of the popularity of search queries, colored zones marked areas with different levels of popularity.
I draw your attention to the fact that although Bill in his article referred part of the first 9000 of all the 10,000 most popular search queries to the “neck”, I would say that after all this is a head. This is my opinion.
In conclusion, I want to say that the phenomenon of the “long” tail of search is true, but according to the information we have, the “head” and the “body” are simply microscopic compared to the “tail”.
So, we heard the opinion of foreign marketers and optimizers, and now we come to our reality and our search engine Yandex.
There is nothing special to talk about, the main factor is the timing of website promotion. For competitive requests. To demonstrate this factor, let's look at the dynamics of the promotion of competitive inquiries from the subject of real estate:
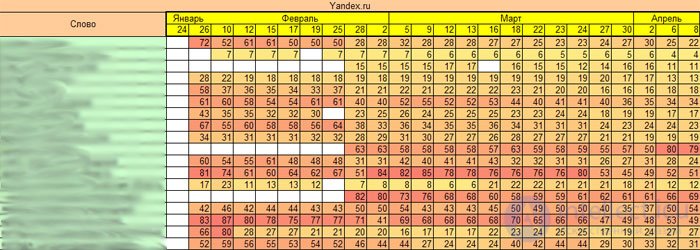
As we can see, the dynamics, although positive, are in their majority, but this is only the tip of the iceberg, and in the period of promotion of these requests, the customer should receive traffic, should receive calls and orders. Promotion of competitive requests for the old site can last 5-8 months, and for a new one from 1 year, you can even predict.
I will make a small digression, the dynamics of advancement should always be investigated, you can immediately tell exactly what happened at one time or another with a part of the requests, let's say on the chart below I noted the implementation of the “you are spam” filter from Yandex to the site selling equipment.
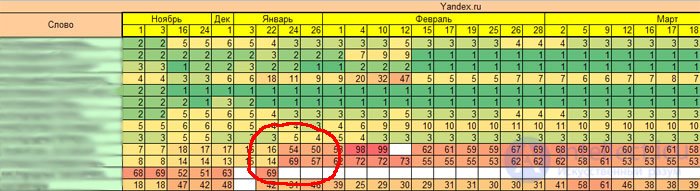
Even if you were not aware that a filter appeared or a change occurred, you will be able to restore the order of your actions according to the dynamics of the project and understand where mistakes were made.
Also on the dynamics you can see how correctly the search engine determines the relevance of the request to the page being promoted. Let us now look at the low-frequency component of the project, I cited the schedule for HF just above, the subject of real estate:
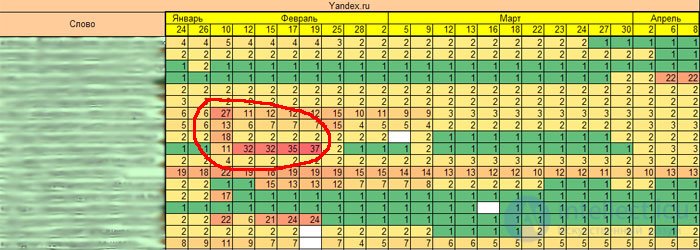
Circled in red especially to show exactly in the perspective of the overall development of the project. What are these "bursts" in the positions? This search engine could not determine the most relevant page for this query during this period. That is why it is desirable to distribute keywords - one request, one page. After such a distribution, as we see on the dynamics, the positions “settled down” on one, necessary, landing page.
The more low-frequency queries, the more difficult it is to keep track of them all, although it’s not the “by position” mechanism that is activated, but the “by traffic” mechanism. On the graph below, just a project that moves only along the low-frequency component, several thousand pages, there is no sense in monitoring positions, and it will take 1 pickup positions for several days ![]()
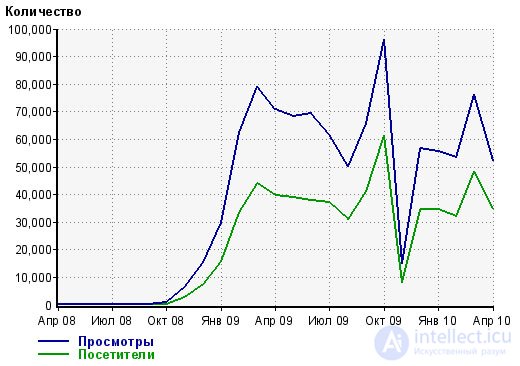
If you monitor 200-300 requests on a commercial site - it's a usual thing, since customers are not always ready to work on traffic, then working with a semantic core of 500 requests is already more difficult.
And any information portal or site with a large amount of content should work just on the low-frequency component. Take for review blog SEOM.info, because here I can tell more detailed than on commercial projects, the data of which is better to hide ![]()
After the new year, the project began a more active stage of promotion, at the moment there are 600 requests in progress, for which 100% of the positions are taken, as well as part of the requests from the low-frequency component that are not monitored.
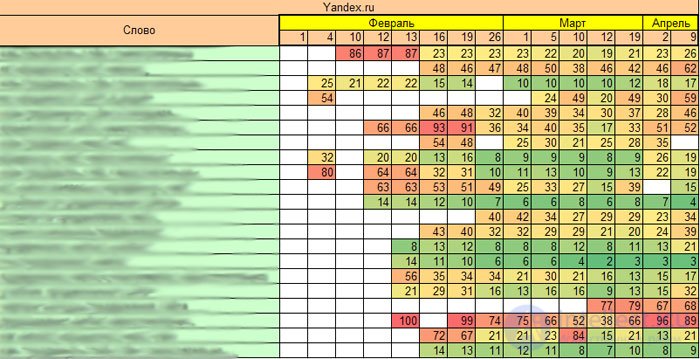
There are competitive low-frequency queries, there are not competitive ones, but each of them brings 10-20 visitors per month, in the end. Here is an example of statistics for several such requests.
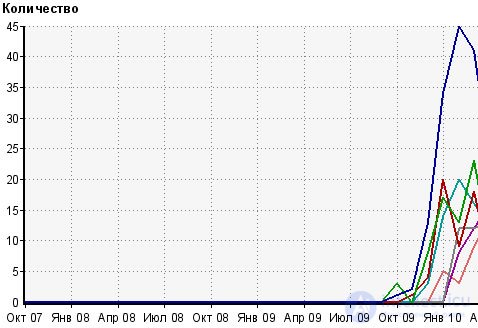
Naturally, when the full semantic core is in the TOP, it will have an effect not on hundreds of visitors from search engines, but on thousands and tens of thousands. At the moment, the core is in a small stage of development, due to the recent start of work on it and the project has low attendance from search engines, although the dynamics pleases with each new day more and more.
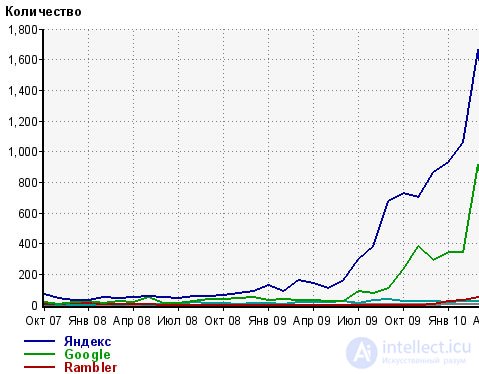
Of course, I will not once again make calculations for a blog on search engine traffic. A blog, like any information project, must be correctly oriented - this is a very important moment when working with traffic. Just above, I wrote how important it is for each keyword to determine its own landing page.
But there is one more important note - for information projects. It is not only about defining keywords, but also about defining key topics for promotion. These topics will be the one, often low-frequency component, which must be properly segmented.
For a blog, the correct “directions” are tag pages. Suppose there are translations of SEO moz articles on SEOM.info, which means there is a request for this direction, what should the user see in the search results and what does he see?
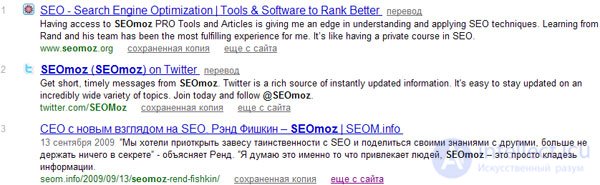
Only one article is visible in the search results, but not the entire spectrum, which is on the pagehttps://intellect.icu/tag/seo-moz/
This is a typical mistake when working with low-frequency queries - not the correct definition of "direction", which has a selection of materials. Although applied to my blog, this is not an error, but an intentional action related to the graphs in the Yandex Webmaster panel.
After the correspondence with the support, I decided to return the tag pages back to the index, since It will be more useful for users coming from search engines - to see a selection of materials , and not one material on a topic. Only the return should be careful, I need in the index the main page with the tag, not additional pages with numbering, so it is important to correctly compile the robots.txt file so that the extra materials do not interfere with the issue.
Why many optimizers exclude pages with tags from the index - because you can get sanctions from the search engine. But the problem is not in the pages themselves, but in the content that is located on them. If there are no problem variations with content about which I wrote and even gave an example, then the tagged pages will not be harmful.
I already wrote about the correct choice of keywords, but it is worth going deeper and analyzing the statistics of search engines, as well as researching materials provided by the analytical department of search engines.
Suppose at the moment I was promoted to the site of the clinic, which deals with treatment for drug addiction, alcoholism, obesity and other problems of the current population of the earth.
What requests immediately come to mind? Naturally competitive and " addiction treatment ", " alcoholism treatment ", " tobacco smoking treatment ", " effective weight loss ", etc. But to move them is time, and by some requests, for a new project - tangible time costs.
And now let's take a look at the Yandex data in order to understand in which direction it is necessary to move when developing a semantic query core.
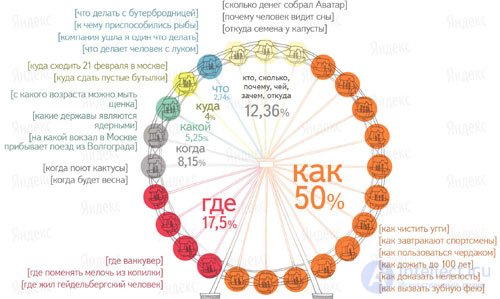
The most constant questions to the search - [how to lose weight], [how to download music from a contact] and [what is love]. They are asked every day an average of 6000 times. In half of all cases, users are interested in "how" and only in 1.6% of cases - "why"
So we will make the core of requests with such a variation of keywords that will allow us to get the most number of target transitions from search engines, and it will include: “ how to lose weight ”, “ how to stop drinking ”, “ how to stop smoking ”, “an easy way to stop smoke "etc.
If we take the complete development of the semantic core for this project, the number of requests for receiving targeted traffic will exceed 300 requests. What will be enough, with investments of $ 200-400, to get traffic of 40-80 thousand visitors per month!
In this article I gave not so much data on the low-frequency promotion of the site, but quite important data. To uncover the whole topic of advancement on low-frequency queries - it takes a lot of time, it is a separate, very important topic worthy of a separate consideration.
Comments
To leave a comment
seo, smo, monetization, basics of internet marketing
Terms: seo, smo, monetization, basics of internet marketing