Lecture
A semiconductor device with one electrical junction, whose job it is to convert one electrical value to another, is called a diode. The design of this product provides two outputs for installation.

Semiconductor diodes
On circuit diagrams, semiconductor diodes are depicted as a triangle and a segment located on one of its vertices and located parallel to the opposite side.
 rectifier, pulsed and universal
rectifier, pulsed and universal zener diodes and stabistory
zener diodes and stabistory tunnel
tunnel converts
converts varicaps
varicapsDepending on the design of the diode, its designation may include additional symbols. In any case, the apex of the triangle, adjacent to the center line of the diode, indicates the direction of current flow.
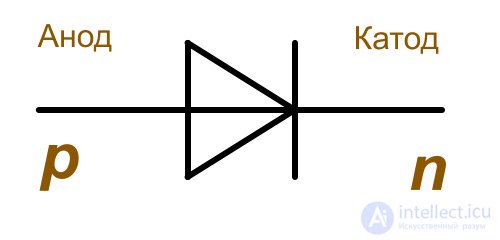
In the part of the designation where the triangle is located, there is a p region, which is also called the anode or emitter, and from the side where the segment is adjacent to the triangle, there is an n region, which is respectively called the cathode, or base.
Semiconductor diodes, the purpose of which is to convert AC to DC, are called rectifier. AC rectification using a semiconductor diode is based on its one-sided electrical conductivity, which is that the diode creates a very small resistance to the current flowing in the forward direction, and a sufficiently large resistance to reverse current.
In order to rectify the current of high power without fear of thermal breakdown, the design of the diodes should provide a significant area of p - n - junction. In this connection, with what in rectifying semiconductor diodes involve special p - n -transitions corresponding to the latest science and technology.
The technology of creating the p n junction is obtained by introducing a p -or n -type impurity into the semiconductor, which creates an area with the opposite conductivity in it. Impurities can be added by fusion or diffusion.
Diodes produced by the fusion method are called “ alloy ”, and those produced by the diffusion method are called “ diffusion ”.
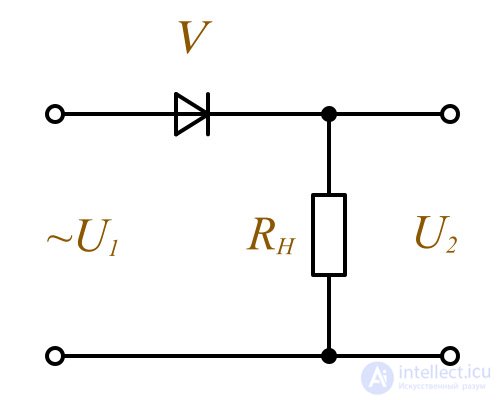
Simplest rectifier
During the positive half-period of the input voltage U 1 diode V working in the forward direction, its resistance is small and at the load R H voltage U 2 almost equal to the incoming voltage.

Graph of voltage at the input and output of the simplest half-wave rectifier
With a negative half-period of this input voltage, the diode is turned in the opposite direction, where its resistance is formed much more than the resistance on the load, and almost all the incoming voltage drops on the diode, and the voltage on the load approaches zero. In such a scheme, only one half-cycle of the incoming voltage is used to obtain the rectified voltage, so this type of rectifier is called half-wave.
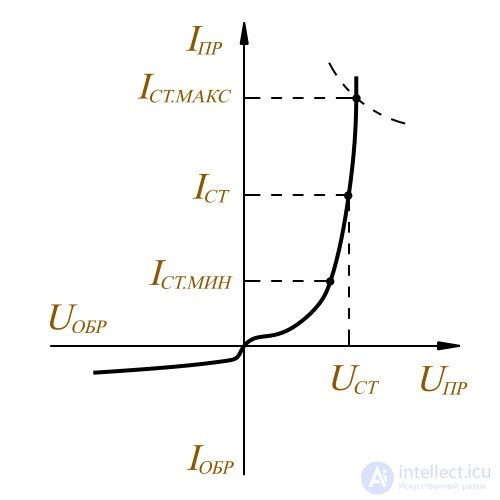
Semiconductor diodes that are used to stabilize the DC voltage across the load are called zener diodes. In the Zener diodes involved a plot of the reverse portion of the current-voltage characteristics in the field of electrical breakdown.
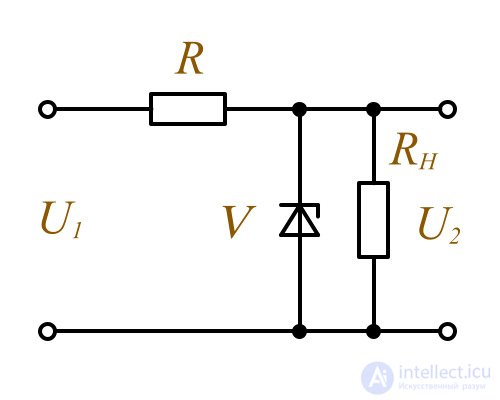
The scheme of the simplest voltage stabilizer
In this case, when the current passing through the Zener diode changes from I ст. мин. I ст. мин. to I ст. макс. I ст. макс. the voltage on it is almost unchanged. If the load R H connected in parallel to the zener diode, the voltage level on it will also remain unchanged within the specified limits of change in the current passing through the zener diode.
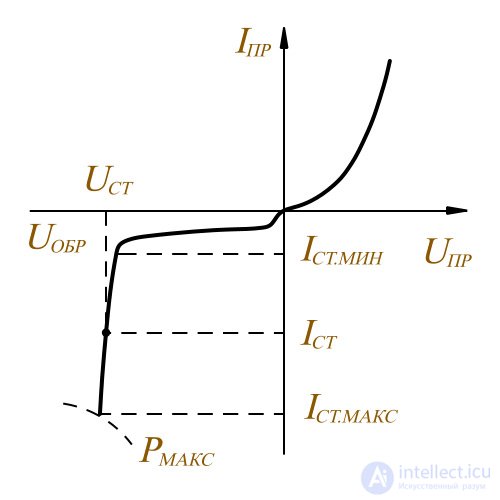
Zener diode graph
Such diodes stabilize the voltage level from about 3,5 В and above. Stabilistors are used to stabilize the DC voltage to 1 volt. For the stabistors, the direct part of the current-voltage characteristic works not the reverse. Therefore, they are not connected in reverse, as they do with zener diodes, but in the forward direction. Electronic components, such as stabilizers and zener diodes, are usually made of silicon.
Voltage-current characteristic of the Stabistor
Planar diodes have high capacitive characteristics. With increasing frequency, the capacitance decreases, which leads to an increase in its reverse current. At high frequencies, due to the fact that there is a capacitance in the diode, the magnitude of its reverse current can reach the value of the forward current, and this diode, thus, will lose its main property of one-sided electrical conductivity. To maintain their functional qualities, it is necessary to reduce the capacitance of the diode. This is achieved with the help of various technological and constructive methods aimed at reducing the area of the p - n junction.
In the diodes used in circuits operating with high-frequency current, products with point and micro-alloy p - n junctions are used. The desired point p n junction is obtained at the point of contact of the pointed end of a special metal needle with a semiconductor. In this case, the method of electroforming is used, which consists in the fact that through the junction of the wire and the crystal semiconductors flow pulses of electric current, forming in the place of their contact p - n junction. Micro-alloys are called such diodes, in which a p - n junction is created by electroforming a contact between a semiconductor plate and a metal object with a flat end.
A semiconductor diode is a semiconductor device with one electrical junction and two leads (electrodes). Unlike other types of diodes, the principle of operation of a semiconductor diode is based on the phenomenon of pn junction.
Planar pn junctions for semiconductor diodes are obtained by the method of fusion, diffusion, and epitaxy. [one]
DG-TS25 diode. 1959
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base