Lecture
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a universal digital IC (a type of LSI) capable of performing the full range of functions of a central computer processor.
With the advent of MP, there is no need to design a new IC for new use.
The main manufacturers of modern microprocessors: Manufacturing companies: IBM, Intel-Pentium, Motorola, AMD, “National Semiconductor”, Apple (USA) Macintоsh
Block diagram and composition of microprocessor system 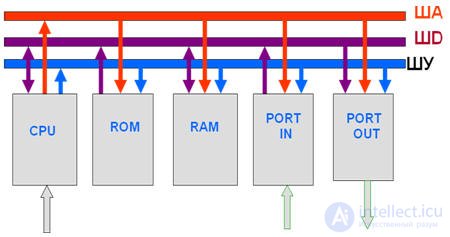
Types of MT tires
Address bus - SHA (16);
Data bus - SM (8);
The control bus - SHU (10-12) are made in the form of a set of conductors connecting the main elements of the MP with each other;
CPU - central processor
ROM (ROM) is a permanent storage device for storing control programs and a set of source data for organizing information processing
RAM (RAM) - random access memory, for storing the changing part of the processed information
UVV-input devices output ports for communication between the MP and the keyboard, monitor, printer, etc.
The internal architecture of the MP 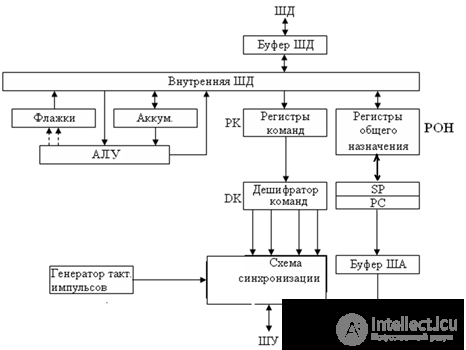
ALU - arithmetic logic unit that implements the set of arithmetic and logical functions of MP.
Synchronization and control node - takes and generates external control. signals.
A set of registers - for the temporary storage of command codes, data, addresses and information about the internal state of the MP.
The contents of some of the internal registers of the MP can be changed, the other part of them is not available to the programmer.
The PK-register of commands accepts the code of the current command from the SM and stores it during the entire time of its execution. Command register is not available to the programmer.
RON or general registers for data storage and intermediate results.
Battery - if the MP has only one special register for storing data and intermediate results.
Register - stack pointer SP - to store the address of the last unused cell of the stack (the memory area, the size of which varies during processing). The work of the stack is organized according to the principle “last arrived, first gone”.
CP is a command counter.
Register of flags - the status or status code register is programmatically available.
All operations in the MP are initiated by synchronization pulses from an external GTI clock pulse generator, stabilized by a quartz resonator.
The frequency of synchronization can be judged on the speed of the MP. The first MP had a speed of 2-4 MHz, modern - 3 GHz
Additional tools - coprocessors
• Arithmetic coprocessor;
• Cache memory;
• Microcontroller;
• Graphic microprocessor.
Basic team MP
• data transfer commands (from memory to the register and vice versa, transfer from register to register);
• arithmetic and logical commands (addition, subtraction, etc., and logical operations AND, OR, NOT, etc.);
• transition commands from one program point to another (conditional transitions);
• team work management MP; input - output, work with the stack, etc.
Writing, reading and debugging programs is simplified by using the writing commands in a machine-oriented language - assembly language or basic.
8-bit MPs are designed to create microcontrollers on their base - simple MS for work in industry, everyday life, as control systems
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base