Lecture
Digital storage devices
Trigger memory registers
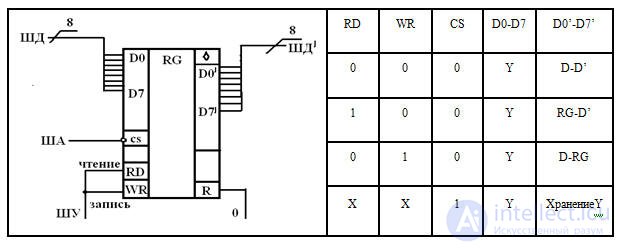
CS is always the active inverse circuit selection input.
The RG register stores 8 bits of information.
If we put 8 registers, we get 8 byte memory
On ШУ: "0" - reading RD, "1" - record WR
Parallel register
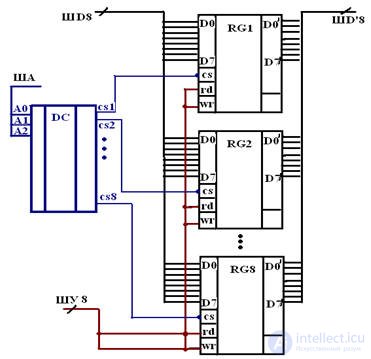
If you put a lot of registers RG1-RG8, then you need a positional decoder DC to select a register for reading or writing information.
For example: we want to read data from RG1 for this, we input “1” to the RDRG1 input; "0" at the output of the decoder CS1 on all other "1".
By combining the decoder and registers in one MS, a memory chip is obtained.
Such MSs have one SD, which is separated by RD / WR signals, i.e. BD bidirectional.
In processors, there is always a bit on 8 wires, in a computer on 16, 32, 64, modern co-processors 96
In SME addresses 4096, with a configuration of 4096 × 8, SHU usually has 10-50 wires
Example1: ША on 64 registers, configuration 64 × 8

Example 2
Determine the information capacity of n SMEs, if the number of address inputs is m = 10
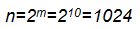
The main characteristics of the memory
• information capacity;
• speed;
• information storage time.
1. Information capacity N is the number of memory bits in the storage device;
2. The number of words of the charger n is the number of addresses of the words in the charger;
3. The bit size m is the number of bits in the storage unit;
4. The number of reprogramming cycles NcY is the number of write-erase cycles at which the memory is operational;
5. Power consumption *** power in steady state Pcc;
6. Power consumption *** storage power in Pccs mode;
7. Storage time tsG.
Static memory parameters
• Ucc power supply
• Icc current consumption
• Current consumption in Iccs storage mode
• Uccs storage power supply voltage
• Voltage of the logical unit Un
• UL logical zero voltage
Dynamic memory parameters:
• chip select time;
• time to select an address;
• signal sampling time.
Memory Classifications:
by function
• RAM (RAM)
• ROM (ROM)
• PROM (PROM)
• RPZU (EPROM)
• RPZU (EEPROM)
• FLASH
by way of storing information
Static
Bistable cells (transistors) reading information without destroying the RAM of 10,000 cells
Dynamic
The inertial properties of reactive elements of capacitors are used to store information (periodic recharging is required regeneration)
on manufacturing technology
• p / p memory on the basis of BPT (TTL, ECL);
• Semiconductor memory based on a PT with an insulated gate CMOS;
• charge-coupled charger;
• with the structure MNOP (metal - silicon nitride - oxide Si - p / p).
by way of accessing an array of memory elements
• with arbitrary treatment that allow for any order of addresses;
• with sequential reversal in which the selection of memory elements is possible only in ascending or descending order of addresses (shift registers)
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base