Lecture
The intelligent network is based on three fundamental components - independence from the type of service, network structure and equipment manufacturer. Intellectual networks are based on the resources of public telephone networks and provide the user with access and performance of a certain set of intellectual services [18], [38].
An example of the most frequently used intellectual services is "service 800" - a service developed in many countries and allowing, for example, the use of telephone cards with paid long-distance services. At the same time, it allows several companies to offer long-distance communication. A subscriber can dial 800 (sometimes a prefix is required before the number, for example, 1) and the company number on the card can be connected to a long-distance connection, sometimes even to a certain national operator. This service has created competition in this market and dramatically lowered the cost per minute of a telephone conversation. Often this service is used to create services paid by the incoming subscriber. For example, companies promoting products or services may receive a number (after dialing 800) where they can answer any questions in detail. The connection will go regardless of the geographical location of the outgoing subscriber. For the convenience of the customer, instead of numbers, a set of letters can be used to indicate the name of the company (for example, FORD). In general terms, we can say that the intelligent network is a superstructure or a further expansion of the public network.
The architecture of the intelligent network platform is shown in Fig. 9.1.
It contains the usual telephone node that performs the initial reception of the number and connects the connection to the service control node (as one type of connection). The platform is provided with additional software that allows you to interact with other elements of the Intelligent network. This system as a node of a similar network is called a Service Switching Point (SSP).
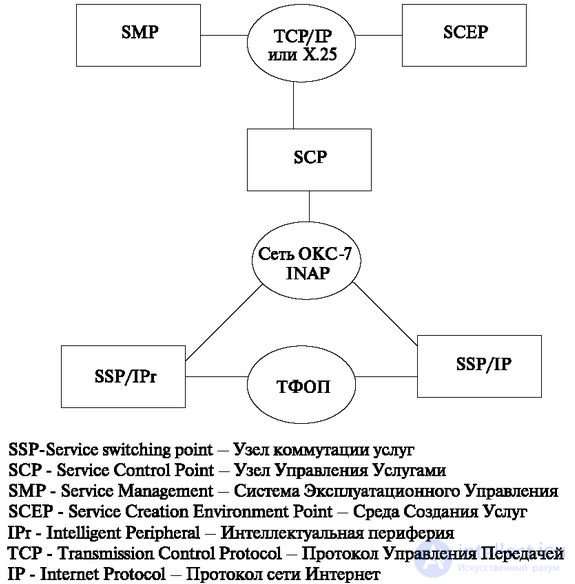
The stations connecting subscribers to the intelligent network are included in the ordinary telephone network. However, the directions to the service control nodes require an ACS with the INAP subsystem, that is, a system designed to transmit signals of the type of network in question. In the ACS section, this level was mentioned. More information can be found on the books [16], [17].
Instruments can be included in a normal station for the realization of additional functions of the Intellectual Peripherals (IPr - IntelligentPeripheral), for example, supporting dialogs with subscribers. This is an invitation to a set of numbers, information about the cost of the service or the value of the loan, etc. All information that comes from the subscriber is presented in a multi-frequency code. In this regard, subscriber devices must be equipped with frequency dialers. To connect IPr to the switching node (SCP), trunks with signaling are used that implement the DSS1 protocols of the primary ISDN access.
The SCP (Service Control Point) service control node contains programs that centrally implement the service logic. Depending on the received information, it remotely controls the switching node (SSP) using a signaling channel. For example, it performs call forwarding to another switching node and other additional switching actions. The switching node, after performing switching actions, suspends its work until new instructions are received from the service control node, until disconnection.
The operational management system and service creation environment (SMP / SCEP - Service management point / Service Creation Environment Point) provide the operator with the ability to manage, control, create, activate, cancel services.
Consider an example of the operation of an intelligent network in the implementation of the service "long-distance connection on a prepaid card." The algorithm of this process is shown in fig. 9.2 (2 sheets).
The service is that the subscriber buys a card in advance, while he pays a certain number of minutes. Using the intelligent network management system, you must check the correctness of the special card identifier number, make sure that the subscriber has not reached the limit, and indicate the connection route, since the connection can be made through a separate network that distributes this card.
Consider briefly this process.
After the subscriber removes the handset, the process follows the usual path, which we have already mentioned in the previous sections.
After receiving the number (or part thereof), it is determined that the connection requires an output to the service control node (SCP). An appropriate connection is established, and a signal containing the dialed number is sent to the SCP. At the station (SSP switching node) the process is suspended.
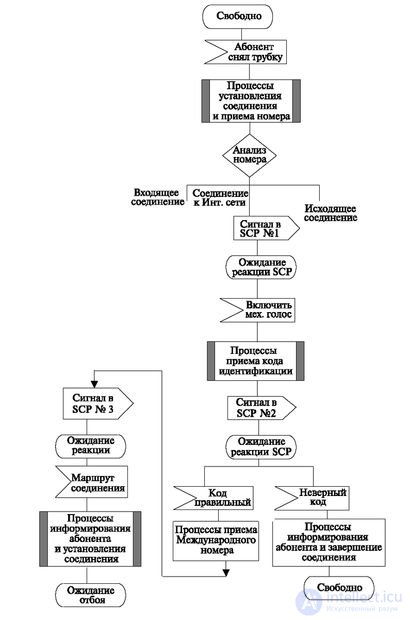
The SCP, after analyzing the number, gives a command to the SSP to connect the intelligent peripherals. Next, the SSP switching node includes a mechanical voice: "Dial the card code."
The card code is received or transmitted through the switching node, and after the reception is finished, a signal is sent to the SCP and the switching node again pauses while waiting for the code analysis.
One of two signals may come from the Service Control Node (SCP) (Code is correct or incorrect). By the wrong code, the switching node informs the subscriber using intelligent peripherals (mechanical voice "Dialed code is incorrect") and terminates the connection (possibly giving the subscriber the right to repeat the number of attempts).
If the code is correct, the service control node requests information about the connection route (the channels may belong to several companies, and therefore the exact route must be indicated, which guarantees the cost of the connection indicated on the card).
The disengagement process is not considered. Although it may be another intellectual action - providing information to the subscriber about the remaining amount of money.
The example makes it possible to give some definitions used in the general predictive call service model.
The model uses the following concepts:
Point of Call Points (PIC).
Points of detection of calls to the services IN (Trigger Detection Points - TDP), in Russian the term "trigger points" is used. They, as can be seen from the example, suspend the call service process to access the logic of the IN services. This happens according to a certain criterion (for example, according to the prefix typed by the subscriber or the code).
It is important to note that the operational staff of the SSP can independently determine the trigger points and assign criteria.
Event Detection Points (EDP). Such events can be: subscriber busy, answer, hang up. Information about these events is used by the SCP service logic.
To study the architecture, protocols and interfaces of intelligent communication networks, you can refer to [18].
Comments
To leave a comment
Telecommunication Services and Devices
Terms: Telecommunication Services and Devices