Lecture
Representation of periodic non-sinusoidal signals
In addition to sinusoidal currents and voltages, non-sinusoidal periodic currents and voltages are widely used in electronics.
For example, rectifiers have single and full-wave instantaneous values of currents and voltages. 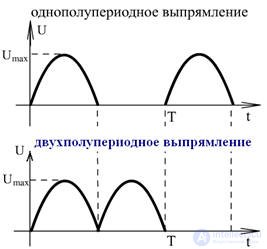
Or GLIN (generators of linearly varying voltages) and the multivibrator at the output have a sawtooth voltage or U - a rectangular shape. 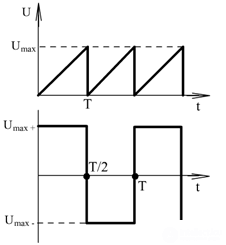
Periodic non-sinusoidal functions of time f (t) for any t must satisfy the condition: 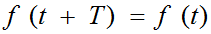 where T is the period of oscillation.
where T is the period of oscillation.
A vivid way to represent non-sinusoidal values are curves and their instantaneous values, which can be seen on an oscilloscope.
The second way is to represent these functions in the Fourier trigonometric series. 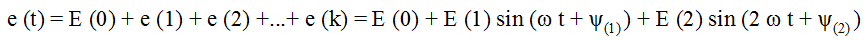
The Fourier trigonometric series converges quickly, so for engineering calculations the number of harmonics is limited to 3-5 members of the series.
For example, the voltage across a half-wave rectifier load resistor. 
Sawtooth voltage: 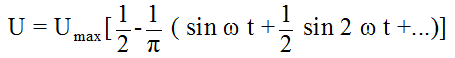
Rectangular voltage: 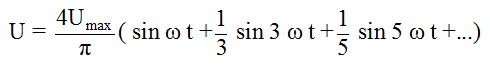
Harmonic is when a non-sinusoidal function can be decomposed into the simplest sinusoidal functions that differ in amplitude, frequency and phase
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design