Lecture
Any active two-terminal network can be replaced by an equivalent two-terminal network with parameters Eeq and Req or Jeq and Geq, the mode of the circuit will not change.
Task 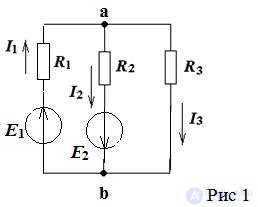
Determine the currents in the branches by the method of equivalent generator in the circuit of Fig. 1
Given:
R1 ÷ R3 = 10 Ohm, Е1 = 100 V, Е2 = 10 V
Let us set the directions of the currents arbitrarily.
Define the first current
Open the branch with R1 to determine the current in the first branch. 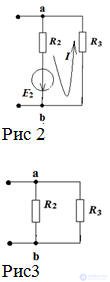
Determine the equivalent EMF with respect to open clips Fig 2 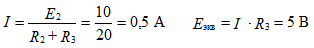
equivalent resistance to rice 3 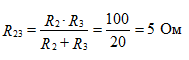
The desired current I1 is determined by the formula 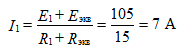
Define the second current
Open the branch with R2 to determine the current in the second branch. 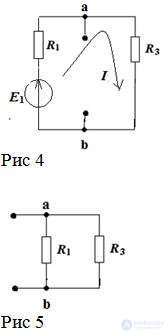
Determine the equivalent EMF with respect to open clamps Figure 4 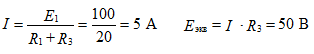
equivalent resistance to figure 5 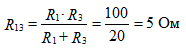
The desired current I2 is determined by the formula 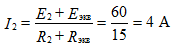
Determine the third current
Open the branch with R3 to determine the current in the third branch. 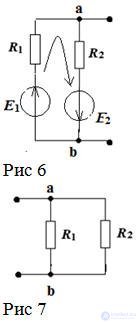
Determine the equivalent EMF with respect to open clamps Figure 6 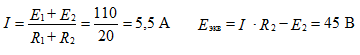
equivalent resistance to figure 7 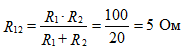
The desired current I3 determined by the formula 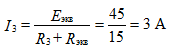
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design