Lecture
Detection and selection of contours (borders) in the image points with sharp differences in brightness, usually carried out by differentiating the function 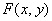 by spatial coordinates and comparison of the result of differentiation with a threshold. First derivatives with respect to spatial coordinates
by spatial coordinates and comparison of the result of differentiation with a threshold. First derivatives with respect to spatial coordinates 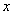 and
and 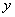 defined as
defined as
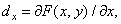 (1.5.1a)
(1.5.1a)
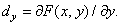 (1.5.1b)
(1.5.1b)
Derivative in direction 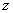 constituting an angle
constituting an angle  with the horizontal axis, by definition [3, p. 10] is equal to
with the horizontal axis, by definition [3, p. 10] is equal to
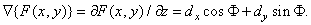 (1.5.2)
(1.5.2)
The gradient module is
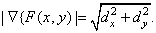 (1.5.3)
(1.5.3)
Second derivatives by spatial coordinates 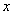 and
and 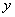 by definition equal
by definition equal
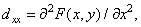 (1.5.4a)
(1.5.4a)
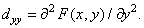 (1.5.4b)
(1.5.4b)
The sum of derivatives (1.5.4) gives the Laplacian
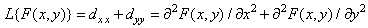 . (1.5.5)
. (1.5.5)
It should be noted that the Laplacian is a scalar quantity that does not depend on the direction on the plane 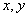 while the gradient is a vector dependent vector.
while the gradient is a vector dependent vector.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital image processing
Terms: Digital image processing