Lecture
Before continuing to study the process of color equalization, it is useful to check whether the results of the experiments and the color adjustment axioms are consistent with the color vision model discussed in section. 2.5. In this model, the response of the three types of receptors with spectral sensitivities 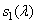 ,
, 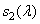 ,
, 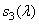 represented by the following values:
represented by the following values:
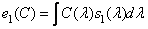 , (3.4.6a)
, (3.4.6a)
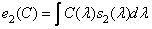 , (3.4.6b)
, (3.4.6b)
 . (3.4.6b)
. (3.4.6b)
If the observer sees an equivalent mixture of primary colors, not the original color 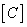 , then replacing the spectral density
, then replacing the spectral density  equivalent spectral density, defined by the relation (3.4.4), should not lead to changes in cone signals
equivalent spectral density, defined by the relation (3.4.4), should not lead to changes in cone signals  . Consequently,
. Consequently,
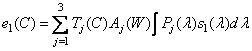 , (3.4.7a)
, (3.4.7a)
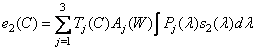 , (3.4.7b)
, (3.4.7b)
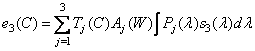 . (3.4.7b)
. (3.4.7b)
Determining the coefficients
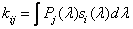 , (3.4.8)
, (3.4.8)
You can rewrite relations (3.4.7) more compactly in matrix form.
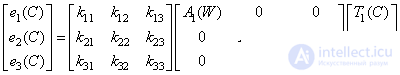 (3.4.9)
(3.4.9)
or even shorter as
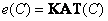 . (3.4.10)
. (3.4.10)
The vectors and matrices included in this relation are defined by expressions (3.4.7) - (3.4.9). It should be noted that for a given set of primary colors and reference white color matrix elements 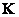 and
and 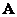 turn out to be constant values. Therefore, if the signals are known cones
turn out to be constant values. Therefore, if the signals are known cones  for a given color
for a given color 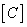 then assuming that there is a matrix
then assuming that there is a matrix 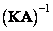 color coordinates
color coordinates 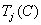 can be calculated by the formula
can be calculated by the formula
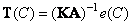 . (3.4.11)
. (3.4.11)
Thus, with a suitable choice of values 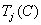 any colour
any colour 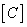 may be replaced with an equivalent mixture of primary colors; at the same time signals of cones will remain unchanged. Unfortunately, these signals are difficult to measure, so the relation (3.4.11) cannot be used to directly calculate the color coordinates. But this was not the goal of the above conclusion. On the contrary, the relation (3.4.11) is derived in order to show the consistency of the results of experiments on the equalization of colors with the color vision model.
may be replaced with an equivalent mixture of primary colors; at the same time signals of cones will remain unchanged. Unfortunately, these signals are difficult to measure, so the relation (3.4.11) cannot be used to directly calculate the color coordinates. But this was not the goal of the above conclusion. On the contrary, the relation (3.4.11) is derived in order to show the consistency of the results of experiments on the equalization of colors with the color vision model.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital image processing
Terms: Digital image processing