Lecture
In addition to the usual two-way radio telephone communication (voice transmissions) with mobile subscribers of the cellular network and fixed subscribers of the fixed telephone network, including long-distance and international telephone communication, GSM mobile systems can offer subscribers a number of other services, including:
- transmission of facsimile messages and computer data;
- call forwarding and auto redial;
- automatic recording of the duration of telephone conversations;
- voice mail and more.
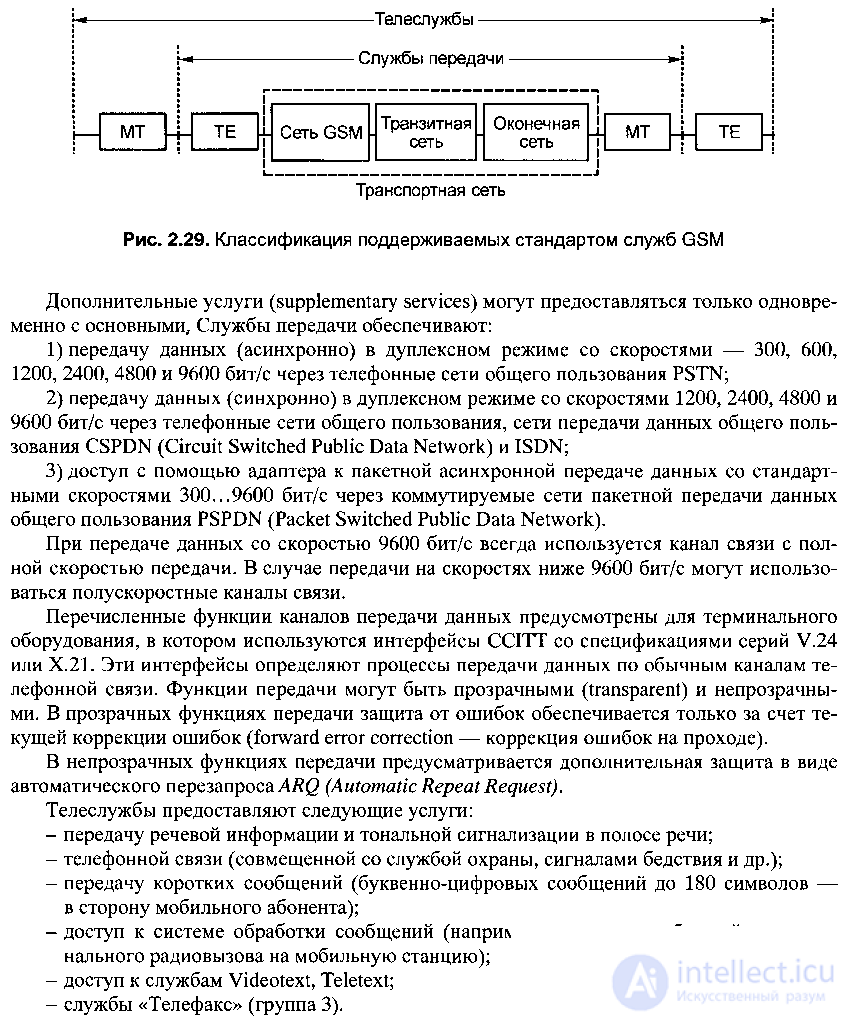
The GSM standard gives a clear classification of the services it supports (servises). GSM network services consist of basic and additional. The first of them can exist by themselves. The main services are divided into two large classes (Fig. 2.29):
- transmission services (bearer servises);
- teleservices (teleservises).
A wide range of additional services has also been standardized:
1) identification and display of the calling or connected number and restriction of identification and display of the calling or connected number (the calling party is given the right to limit the possibility of identifying its number);
2) call forwarding to another number (unconditional call forwarding and forwarding in cases when the subscriber is busy or not answering) and transferring the call (switching the established communication line to another subscriber);
3) call waiting (when the terminal is busy, the subscriber receives a notification of the incoming call and can answer it, refuse to accept the call or ignore its receipt) and save the call (the subscriber can interrupt the ongoing communication session by answering another call and making another call, and then return to the continuation of the interrupted conversation);
4) conference call - simultaneous conversation of three or more subscribers;
5) closed group of users - this function allows a group of users to communicate only between themselves, if necessary, one or more members of the group can have access to the exit / entrance to subscribers who are not members of the group;
6) operational information about the cost of services provided (or services rendered);
7) prohibition of certain functions, for example, on incoming calls, international calls or outgoing calls for roamers;
8) provision of an open network / user communication line for the implementation of functions defined by the operator.
Concluding consideration of the service modes of transmission and teleservice modes, the following should be noted: both terms —bearer services and teleservices are borrowed from ISDN technology, and they refer to different access points, as shown in Fig. 2.29 [(bearer servises - focused only on transporting information between the corresponding user / network interfaces and, unlike teleservices, concern about the compatibility of communication protocols of terminal devices (terminal equipment - TE) remains for the users of these devices, teleservices - focused on direct user communication / user and enable terminal communication function].
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics