Lecture
Dynamics of service introduction
Today, mobile communications is one of the fastest growing telecommunications industries. According to the forecast of the UMTS Forum, the number of mobile subscribers in the world by 2010 will be 1,730 million (Table 10.5).
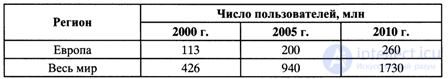
Table 10.5. Prediction of growth in the number of subscribers in land mobile networks.
Of the 200 million European subscribers of the services of the systems of the 3rd generation (3G) in 2005 will benefit from 16%, that is 32 million, and the volume of multimedia traffic will exceed 60%. These conclusions are valid under the condition that the increase in tariffs will be much slower than the growth of traffic. In subsequent years, analysts predict even more rapid growth in mobile service users. In 2005, mobile communications are expected to exceed traditional wired telephone networks (Fig. 10.4) by the number of users, and by 2015, 3 billion people may become mobile subscribers.
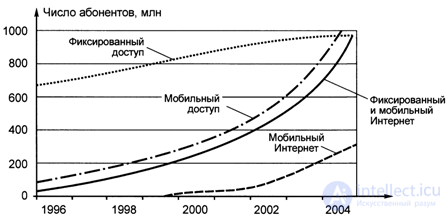
Fig. 10.4. Prediction of growth in the number of subscribers in landline networks.
3rd generation mobile networks will also provide a natural expansion of the range of non-multimedia services currently provided using GSM, TDMA, cdmaOne and PDC networks.
The prospects for creating 3G are more favorable than it was a decade ago before the advent of 2G systems. The introduction of 2G systems took place on the world market in a short time and developed exclusively by “crowding out” old technologies with which interconnection and continuity were not supposed. With the advent of 3G systems, the long-term coexistence of IMT-2000 and 2G systems will begin.
Due to differences in the set and cost of services provided, new technologies will not compete, but harmoniously complement each other. In the future, as the 3rd generation services are developed, a gradual migration of 2G subscriber networks to 3G is predicted.
Speaking about the interconnection of different generations, it is impossible not to mention the promising technologies of the 21st century, which are now commonly referred to as future 4GW (4th General Wireless Infrastructures) network infrastructures or 4G generation.
Although the concept of creating systems of the future has not yet been formed, however, the problems and possible scenarios for the development of such technologies are widely discussed at the international level. The transition to 4G will require the development of global high-speed backbone core networks (3G only assumes their modernization), the creation of new radio interfaces in the frequency range from 5 to 60 GHz, the equipment of almost all professional and home appliances with built-in radio access tools, provision of mobile access to databases ( reference information, geographical, medical), as well as the implementation of broadcasting services in the interests of mobile users.
Multimedia and non-multimedia services.
Unlike previous generation technologies, where speech was the dominant type of service, IMT-2000 is supposed to provide a full range of modern services, including voice transmission, channel and packet switching, interaction with Internet applications, symmetrical and asymmetric transmission with high quality, and at the same time guarantee compatibility with existing systems.
The third generation of mobile communication already at the first stage of deployment provides high bandwidth, which can flexibly change depending on the degree of mobility of the subscriber, that is, different speeds of its movement in the service areas:
- up to 2.048 Mbit / s - for servicing stationary and mobile subscribers inside buildings (speed less than 3 km / h),
- up to 384 kbps - with low mobility (speed from 3 to 12 km / h) and local coverage area;
- up to 144 kbps - with high mobility (speed from 12 to 120 km / h) and wide coverage area;
- up to 64 (144) kbps - with global coverage (satellite).
As for the set of services, it actually comes close to that which is provided in fixed-line networks. Obviously, the achievement of such high speeds with a limited frequency resource and work in fading channels will require the development of fundamentally new approaches to the design of the radio interface. Speaking about the 3rd generation systems, services are usually divided into two groups: non-multimedia (narrowband speech, low-speed data transmission, circuit-switched network traffic) and multimedia (asymmetric and interactive). New information technology "multimedia" was born relatively recently, but it immediately became the basis for the creation of the third generation services - computer video graphics (including three-dimensional), video, text and graphic information. By synthesizing parts of audiovisual information and their transmission over radio channels, the user can be provided with all types of modern services. Multimedia services are usually divided by the type of traffic (asymmetrical / symmetrical) and the way the user interacts with the system (interactive / broadcast messaging, etc.). Traffic in the transmission of multimedia information and data on the Internet has an asymmetric structure (traffic asymmetry refers to the difference in the allowable transmission speeds in the forward and reverse directions, that is, in the lines "down" and "up"). It is interesting to note that as the transmission rate increases, the difference in the amount of information transmitted in the up and down lines tends to increase.
In the future, it is predicted that traffic asymmetries will increase from 1: 4 to 1:40 when transmitting medium-rate information (384 kbit / s) and up to 1: 200 - for high-speed data streams (2.048 Mbit / s).
Interactive multimedia services will be widely used in 3rd generation systems. Such services provide remote subscribers with the possibility of natural communication in real time, that is, they can not only hear, but also see each other. Until recently, video conferencing (basic multimedia service with high interactivity) was used mainly in ISDN networks, where video data was transmitted at 144 kbit / s (1 BRI channel) or 384 kbit / s (3 BRI channels). The highest requirements for the quality of multimedia are made in telemedicine, where it is necessary to obtain high-quality images (at the level of a television picture) in real time. Recent advances in video compression suggest that this service will also be widely used in IMT-2000.
The rapid growth of the popularity of the Internet and the rapid development of mobile communications makes it possible to talk about the merger of these two technologies. Today, the demand for Internet access services is beginning to dominate all others. Internet traffic doubles every 100 days.
The number of Internet users worldwide has increased from 62 million in 1996 to 170 million in 1999, with the growth rates continuing to increase and by 2005 the number of users could exceed 1 billion subscribers.
Despite a number of difficulties associated with the implementation of high-speed Internet access from a portable terminal, it can be predicted that over time this service will become one of the main ones in mobile communications.
The concept of a virtual home environment.
Services of the 3rd generation include the service provided by the Virtual Home Environment Virtual Technology. The concept of VHE is based on the following fundamental differences [10.7]:
- personalization of services, that is, the provision of a subscriber of such types of services, whose profile is adapted to its specific requirements and does not depend on the service environment;
- transparent subscriber access to communication services regardless of the radio access technologies used and network standards;
- service portability without loss of communication quality across the borders of various mobile and fixed networks (PSTN, Internet);
- the possibility of using different types of subscriber equipment in the network or, in other words, the portability of services from one type of terminal to another.
More recently, these services could only provide fixed-line networks. Today, a mobile user can receive the same features, interface, and services no matter what network they currently use. Thanks to IMT-2000, in the near future, it will be possible to transmit video images and multimedia data in real time, which will create a “presence” effect for a subscriber far from the scene, actually creating a sense of a unified (home) environment.
The overall architecture of the VHE environment includes three functional layers: a mobile network, a PSTN, and the Internet. Mobile network-specific VHE functions are implemented using CAMEL, INAP, WAP and other technologies. The standardization of the VHE environment at the regional level (VHE ETSI, 1999) has now been completed and all prerequisites have been created for carrying out similar work within IMT-2000 . Wireless terminals that implement VHE modes have a similar set of personalized services, interface capabilities, and service characteristics that are independent of the specific network, terminal type, and location. However, mobile subscribers should not be under a delusion - being associated with significant technological difficulties, such a service at the initial stage of implementation will be expensive.
Determination of location.
Integration of cellular / satellite communications with autonomous (the method of determining the coordinates based on the use of own means of a mobile communications network) or a global satellite navigation system, such as GPS, is one of the most promising areas for the development of mobile communications. The attractiveness of global positioning technology for users is the ability to determine their coordinates and movement parameters anywhere in the Earth at any time. And, most importantly, do not need to pay for such services. The only costs are the cost of purchasing a navigation receiver and antenna. If the navigation board is embedded in a cell phone or satellite terminal, the costs are even lower, and the cost of such a service is incommensurably lower than, for example, Internet access. The operator, knowing the coordinates of the subscriber, can enter the tariffing of calls with the differentiation of their payment depending on the distance, and also provide the subscriber with information and reference services specifically in the area where he is currently located. This may be information about the nearest pharmacies, traffic jams, train timetables, etc. The integrated technology of mobile communication and navigation has become widespread when creating anti-theft systems for cars. Released mobile phones, combined with a GPS receiver, allowing you to automatically transfer data about the location of its owner. Already today, a victim from a cell phone can automatically notify the police about his location - just press a special button. Cell phones with an "electronic compass" are becoming indispensable assistants to motorists and other categories of people who require this kind of service. In the future, the subscriber terminal will be combined with an electronic map, which will allow you to navigate in the city or in unfamiliar areas.
In many regions of the world, control centers have already begun to operate, providing automatic monitoring of moving objects with their movement displayed on an electronic map in real time. There are tools for automatic logging of the routes of movement of vehicles, including buses (black box mode).
Speech recognition and voice control.
It is well known that one of the barriers that stand in the way of mass implementation of data services in mobile systems is the complexity of the human-machine interface.
Speakerphone adapters provide the ability to conduct telephone communications while driving. However, in the case of data transmission, loud-speaking communication does not solve all problems and new revolutionary technologies based on speech recognition are needed. There are already definite shifts in this direction. For example, Motorola has developed a special language “voice tag” (VoxML) and offers it as a standard way of conducting voice control in motion. The driver can access services through verbal commands. Speech recognition will also allow to identify the caller by voice on the basis of his speech features, that is, to use a kind of voice identifier. Other applications of this new service are possible.
The merging of mobile communications with other technologies will be one of the key trends in the development of 3rd generation services. The greatest success should be expected in the field of e-commerce. The volume of banking services received directly using a mobile phone will be significantly expanded. These will include paid information and reference services, various types of electronic payments (payment for air, rail, bus tickets, parking lots) and, in the future, all types of banking operations from portable or mobile cell phones, which will turn them into "Pocket ATMs".
The new quality of these systems is also the fact that they will allow operators to independently develop applications, functions and services, focusing on market requirements in a particular region and trends in the growth of demand for specific services. Most of the listed services are fundamentally new compared to traditional telephony or even 2nd generation mobile communications.
The revolutionary changes in the field of communications and information access technologies will occur in 2005-2010, when these new services will become widespread and widely used in business, everyday life, studies and medicine. The mass consumer market is known to be very sensitive to the cost of services. If tariffs for new services are disproportionately higher than for traditional ones provided by 2G systems, then they can be claimed only by a limited contingent of consumers. Thus, the success of the 3rd generation systems will largely depend on technological solutions. The market situation may radically change if relatively cheap, low-power portable two-triple-mode cell phones are built.
Ways of transition to the 3rd generation systems are considered in [10.2, 10.6, 10.7, 10.14].
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics