Lecture
The algorithms of functioning of cellular mobile communication systems of various standards are basically similar and are characterized by the following.
1. When MS mobile station is in standby mode, its receiving device constantly scans either all channels of the system or only control channels.
2. To call a subscriber, all BTS base stations of the cellular network use call control signals through the control channels.
3. The MS mobile station of the called subscriber responds to one of the free control channels when receiving a call signal.
4. The BTSs that have received the response signal transmit information about its parameters to the MSC switching center, which switches the call to that BTS base station where the maximum signal level of the called station MS is recorded.
5. During dialing, the MS mobile station of the called subscriber occupies one of the free BTS channels, the signal level of which is currently maximal.
6. As the called party is removed from the BTS or due to the deterioration of radio wave propagation conditions, the signal level decreases, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of communication.
7. Improving the quality of conversation is achieved by automatically switching the called party to another radio channel. Special procedure - handover - transfer of call control or handover allows you to switch the conversation to a free channel of another BTS base station, in which the called subscriber was in range.
Similar actions are taken to reduce the quality of communication due to the influence of interference or in the event of malfunctioning of switching equipment. To control such situations, the BTSs are equipped with special devices that periodically measure the levels of signals from mobile stations that transmit speech signals and compare these levels with permissible limits.
If the signal level from the MS is less than the selected acceptable level, then this information is automatically transmitted to the MSC switching center via the service communication channel. The MSC issues a command to change the signal level of the mobile station to the nearest BTS base stations.
After receiving information from the BTS about the level of this signal, the MSC switching center switches the mobile station MS to the one of the BTS base stations where the signal level turned out to be the highest. In case a situation arises when the flow of requests for service coming from subscribers of the cellular network exceeds the number of channels available on all closely located BTSs, as a temporary measure (until the release of one of the channels), the principle of handover inside the cell is used. At the same time, the channels are connected in turns within the same BTS base station to provide all subscribers with communication.
Initiation and communication
The MSC switching center and BTS base stations operate around the clock and continuously, without shutdowns. In the event of malfunctions in them, operability is maintained by redundancy, with repair (replacement) of failed units in the situation when they are transferred to the reserve position.
In the work of mobile stations, breaks and outages are almost inevitable, including for changing power sources. Consider the operation of the MS mobile station within one cell without a handover. In this case, four modes of MS can be distinguished: on and on; Standby mode; communication establishment mode; communication mode.
1. Turn on and initiate
After turning on the MS (that is, after turning on the power supply), initiation is performed — initial start-up. During the execution of this mode, the MS is tuned to work as part of the cellular network by signals that are transmitted regularly from the BTS via the appropriate control channels, after which the MS goes into standby mode.
In the GSM standard, a mobile station scans all available frequency channels, tunes to the channel with the highest signal level, and determines whether Broadcast Control Channels (Broadcast Control Channels) are transmitted on this frequency channel by the presence of a frequency correction packet. If there is no information in the BCCH channel, then the MS is rebuilt to the next on the high signal level of the BCCH channel.
The MS then finds the synchronization burst, synchronizes with the selected frequency channel, decrypts additional information about the BTS base station (in particular, the 6-bit BTS identification code) and makes the final decision whether to continue the search or to work in this cell. This completes the initiation process.
2. Standby
In idle mode, the MS tracks:
- changes in the information system, which can be associated with a change in the mode of operation of the cellular system, and with the movement of the mobile station MS itself;
- system commands, for example, a command to confirm its performance;
- receiving a call from the cellular network;
- receiving a call from the subscriber.
In the GSM standard, the MS mobile station measures and periodically transmits the following parameters to the BTS:
- the level of the BTS signal of its “own” cell and up to 16 adjacent cells, measured by the signal of the HSN channel;
- quality code of the received signal in the working cell - a function of estimating the frequency of the bit error BER (Bit Error Rate) on the received signal before channel decoding. In addition, the mobile station MS may periodically, for example, once in
10 ... 15 minutes, confirm their performance by transmitting the appropriate signals to the BTS (confirmation of the "registration" or clarification of the location).
In the MSC switching center, for each of the included MSs, the cell in which it is registered is fixed, which facilitates the organization of the procedure for calling the mobile subscriber.
If MS does not confirm its operation within a certain period
time, for example, skips two or three confirmations of “registration” in a row, the MSC switching center considers this MS to be turned off, and incoming calls to its number are not transmitted.
3. Mode of communication
If the MS-number of the called subscriber is called from the cellular network, the MSC switches the call to the base station of the BTS- / cell in which the MS- / called is “registered”, or to several BTS in the vicinity of this cell, taking into account the mutual movements of the called subscriber during the time elapsed since the last “registration”, and the BTS transmits this call through the appropriate channels of the call. The mobile station MS- / answers the call through its BTS- /, simultaneously transmitting the data necessary for the authentication procedure.
If the authentication is positive, a traffic channel is assigned and the number of the corresponding frequency channel is reported to the mobile station MS- /. Mobile station MS- / tunes to a dedicated channel and, together with BTS- /, performs the necessary steps to prepare a communication session. In the mode of establishing an MS- / communication, it is adjusted to the specified slot number in the frame, specifies the time delay, adjusts the output power level of the transmitter, etc. The time delay is selected in order to temporarily reconcile the slots in the frame (for example, in the BTS- /) when organizing communication with MS mobile stations located at different distances from the BTS- /.
In this case, the time delay of the packet of bits transmitted by the mobile station is regulated by commands from the base station. In the GSM standard, when selecting a delay, access packets are used. The delay is adjustable from 0 to 63 bits with 1 bit sampling (3.69 μs). Further, the BTS- / tracks the change in the distance to MS- / and corrects the delay value, issuing the corresponding commands to MS- /.
With small geometric dimensions of the cell, that is, with small values of the delay (within the protective blank or protective interval), the compensation of the time delay may not be made. In the GSM standard, MS- / to BTS- / frequency is also linked using frequency correction bursts and time synchronization MS- / c BTS- / with an accuracy of 1A bits, for which the following are transmitted in the synchronization batch: a) number of quarters of bits (QN - Quarter bit Number), ranging from 0 to 624; b) bit number (BN - Bit Number) ranging from 0 to 156; c) slot number (TN - Time slot Number) ranging from 0 to 7; d) frame number (FN - Frame Number) ranging from 0 to 2715648. At the same time, a 3-bit code (
Then the BTS- / issues a message about the ringing of the call (ring), which is confirmed by the mobile station MS- /, and the calling subscriber is able to hear the ringing tone. When the called subscriber answers the call, that is, “picks up the phone” by pressing the corresponding keyboard on the MS-y control panel, the mobile station MS- / issues a request to end the connection. With the completion of the connection, the communication session begins accordingly - the subscribers have a conversation.
4. Conversation Mode
During the conversation, the MS processes the transmitted and received signals, as well as the control signals transmitted simultaneously with the speech. At the end of the call, service messages are exchanged between the MS and the BTS (request or command), after which the MS transmitter is turned off and the MS station goes into standby mode. In this case, the communication establishment algorithm was considered: stationary TA (telephone set) -> PSTN -> cellular network -> MS- /.
If the call is initiated by the MS-k mobile station located in the cell with the BTS-£, that is, the MS-k subscriber dials the number of the called subscriber, makes sure that the display is correctly set and displays the corresponding call button on the control panel, then the mobile station MS-K transmits through its BTS- & message indicating the called number and data for the authentication of the mobile subscriber.
After authentication, the BTS- & assigns the traffic channel and the subsequent steps to prepare the communication session are performed in the same way as when a call comes in from the cellular network (i.e., cellular network - »MS-k). Then MS-k reports to the MSC switching center that MS-k is ready, then the MSC transmits the call to the network, and the subscriber of the mobile station MS-k is able to monitor its progress (this is reflected in the fact that the MS subscriber hears “ call "or" busy "). The connection is terminated on the GSM network side.
This procedure is schematically illustrated in fig. 6.1.
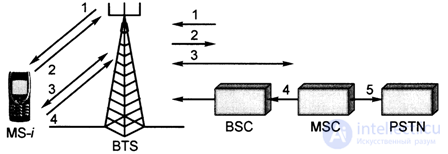
Fig. 6.1. Connection establishment procedure between MS and PSTN
The numbers denote the following process of establishing communication.
Beam 1: MS-i, through the Random Access Channel (RACH) channel, requests a dedicated, fixed SDCCH (Standalone Dedicated Control Channel) control channel to establish communication.
Beam 2: The BSC base station controller assigns the SDCCH channel via the AGCH access grant channel (Access Grant Channel).
Beam 3: (bidirectional) - the MS mobile station, through the SDCCH channel, authenticates and issues a call request (with the called subscriber number).
Beam 4: The MSC switching center issues a command to the base station controller BSC to assign a traffic channel TCH (Traffic CHannel).
Beam 5: The MSC sends the called number to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and ends the call after the called subscriber answers.
The process of conversation and end of communication does not differ from the previous case. The mode of establishing communication between mobile subscribers MS-i and MS-k, as well as the mode of conducting a conversation between them, combines the above algorithms: MS- / and MS-k are in the cellular system of one operator or in the cellular system of several operators, the connection between them is established through MSC switching centers (without access to the fixed telephone network).
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics