Lecture
The roaming function, as one of the important functions of cellular mobile communication systems, allows extending the possibilities of using cellular communication at the interregional and international level, up to the global level.
Roaming is a function or procedure for providing services of cellular mobile communication systems to a subscriber of one operator in the system of another operator.
In order to organize roaming, cellular mobile communication systems must be of the same standard, and MSC mobile switching centers must be connected by special communication channels to exchange location data of the subscriber (roamer).
To ensure roaming, it is necessary to fulfill three conditions:
1) the presence in the required regions of cellular mobile communication systems CMCS (Cellular Mobile Communication System) compatible with the standard of the operating company from which MS was acquired;
2) the presence of appropriate organizational and economic agreements on roaming services for subscribers;
3) availability of communication channels between CMCS / and CMCS; systems that provide the transmission of sound and other types of information for roaming subscribers.
There are three types of roaming:
1) manual, that is, exchanging one MS / for another MS ;, (or changing a SIM card);
2) semi-automatic, when the subscriber MS / informs his operator CMCS;
3) automatic.
A simplified diagram of the organization of automatic roaming can be represented as follows:
- the MS subscriber of the CMCS / cellular communication system /, being in the territory of the “alien” CMCS7 system that allows roaming, initiates a call in the usual way, as if he were in the territory of “his” CMCS system;
- MSC switching center;, making sure that its home register is HLR; this subscriber does not appear, perceives it as a roamer MS / (roamer - subscriber using roaming services) and enters it into the guest register VLR ;. Simultaneously (or with some delay) MSC; queries the home register of the native roamer system, that is, the HLR /, the relevant information necessary for the organization of the service (subscription-based services, passwords, ciphers), and informs which MS / is in the current system. The latest information is recorded in the home register of the HLR / “native” roamer system. After that, MS roamer uses cellular communication as a “home” system:
- Outgoing calls from it are served in the usual way, with the only difference that the information relating to it is recorded not in the home register HLR / (HLR;), but in the guest VLR ,;
- incoming calls to his number are forwarded by the “home” CMCS system / to the CMCS system /, where the MS roamer is staying.
Upon returning MS roamer / home, the address of the CMCSy system where the router was located is deleted in the HLR home register, and in the guest register VLR; that CMCS system; deleted information about MS /.
Payment for roaming services by MS subscriber / is made through the home system CMCS /, and the operator CMCS / reimburses the costs to the operating company CMCS; who provided the roaming services, in accordance with the roaming agreement.
In the GSM standard, the roaming procedure is laid down as a mandatory element. In addition, in the GSM standard, there is the possibility of roaming with SIM-cards with rearrangement of SIM-cards between mobile stations of various variants of the GSM standard (GSM 900/1800/1900), since all three versions of the GSM standard use unified SIM-cards.
The roaming procedure in the GSM standard is most convenient for two- and three-mode subscriber terminals.
GSM Roaming
To implement roaming, the mobile subscriber of the GSM network is assigned the following main numbers and identifiers:
1. International Mobile Subscriber Identity - IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity), which is recorded in the permanent storage of the SIM card. IMSI includes: Mobile Country Code (MCC) —3 characters, Mobile Network Code (MNC) —2 characters, and a subscriber number (Mobile Subscriber Identity Network) —10 characters.
2. Public network number - corresponds to the telephone numbering of each network of the mobile operator.
3. The temporary roaming number —MSRN (Mobile Station Roaming Number). It is allocated when establishing an incoming connection to the subscriber-roamer at the time of establishing a connection, but not more than 30 s. The block of MSRN numbers is distinguished from the general telephone numbering of the network. The location information of the MS subscriber must be updated in the HLR register every few minutes. For this purpose, information is periodically transferred to the HLR database; from the VLR, MSC database of the switching node where MS / is temporarily located. When an incoming call is received by the called MS subscriber, the HLR register determines how to connect to the MS subscriber / depending on its current location. As the MS moves from one cell to another, the content of the HLR is constantly updated. This mechanism provides the mobile subscriber MS / absolutely free movement within the entire cellular network CMCSy without the risk of losing incoming calls.
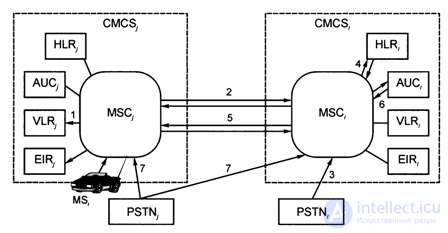
Fig. 6.3. Basic procedures for the interaction of GSM networks when roaming
1. Let the roamer MS subscriber / get into the CMCS visiting network; At the same time, the MS / is fixed by the nearest BTSy, the IMSI identifier is transmitted via the BTS7 via the radio interface to the MSC, and then to the VLR register ;.
2. Next, the MS location * update procedure is performed: the received IMSI / MS roamer / subscriber from the VLR, via the MSC, and via the communication channel (beam 2 from the MSC; -> MSQ) enters the MSQ and then to the HLR / ( ray 4).
3. HLR / checks the subscriber’s right to MS / roaming and sends confirmation of the data update (HLR / -> beam 4 -> MSC / -> beam 2 -> MSC, -> beam 1 - VLR;).
4. The following is the procedure for requesting / transmitting MS / subscriber data (service data, MS / authentication parameters): MSC; beam 2 -> MSC / -> beam 4 -> HLR / or MSC; beam 2 ** MS С / beam 6 - * AUQ.
5. Additionally, procedures for requesting / transmitting an MSRN temporary roaming number are carried out: MSC, -> beam 5 -> MSQ -> beam 4 -> HLR, or MSC, -> beam 5 -> MSQ -> beam 6 -> AUQ to establish a connection .
6. In the case of an incoming call from the PSTN, the call signal passes:
PSTN, ^ beam 3 ^ MSQ -> beam 2 -> MSC, -> BTS, -> MS /, and then the formation of a communication channel of a fixed telephone set in PSTN, and MS, is realized: either through an international network (beam 7), or via national or international roaming network by MSRN.
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics