Lecture
In each radio link, as you know, there are three components:
1) a transmitting device (i-transmitter),
2) receiving device (receiver),
3) the environment in which radio waves propagate, namely the atmosphere surrounding the globe and outer space. 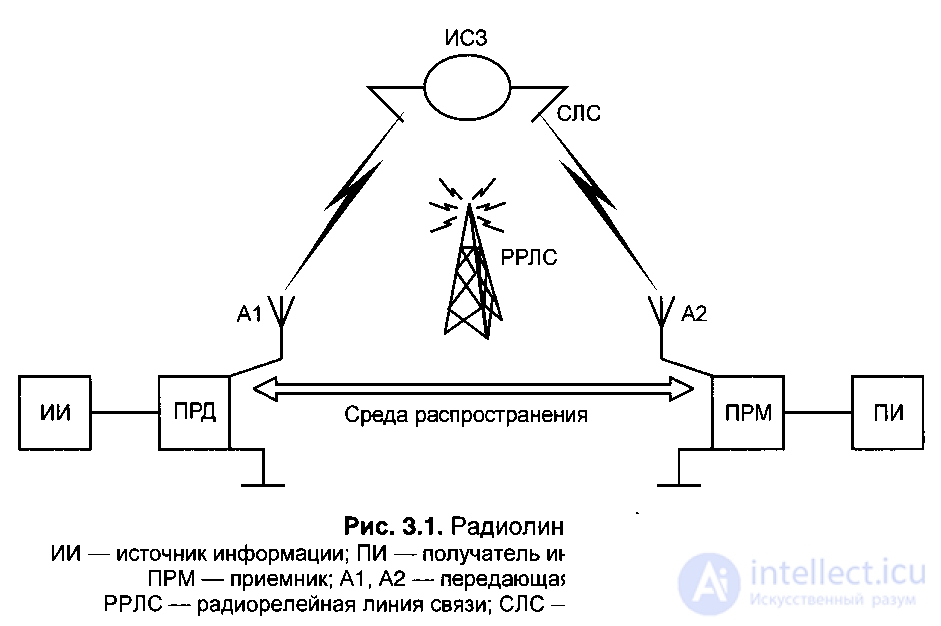
The simplest radio link of the first type is characterized by the fact that the transmitter and receiver are located at its ends. Radio waves in such radio links can propagate either in a straight line, freely propagating, or repeatedly reflecting, or by diffraction bending around the surface of the earth, or repeatedly reflecting from the ionospheric layers and the earth's surface, etc.
Radio lines of the second type are characterized by the fact that radio waves enter receivers by receiving, amplifying and subsequent re-emission (retransmission) by special relay radio stations. For example, in radio relay communication lines (PPLC): ground and space (relay stations are located on the satellite - artificial earth satellites); in the radio links of cellular mobile communication systems (the base transceiver stations BTS perform the functions of relay radio stations).
The third type radio lines are used in communication technology and in scientific research, a feature of which is that the emitted radio waves enter receivers by scattering on atmospheric heterogeneities (troposphere and ionosphere), on ionized traces (meteoric, rocket, etc.) or from space bodies (Moon, Mars, etc.), etc. Examples of such radio lines can serve as a system of radar detection of objects, when the transmitter and receiver are combined in a radar station, and the role of a passive reflector of radio waves is performed by a detectable object.
Therefore, to understand the conditions necessary to create a stable radio communication in cellular mobile communication systems, to enable monitoring of the electromagnetic environment within cells, it is necessary to know both the parameters of receiving and transmitting (BTS) and mobile (MS) radio stations, and radiation conditions and propagation of radio waves in such systems and the basic methods of calculating the electromagnetic field at the receiving points at different distances from the receiving-transmitting radio (BTS), taking into account the influence of the conditions of multipath propagation neniya radio wave propagation loss, the influence of the movement of mobile objects, etc.
This chapter is devoted to the consideration of these problems.
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics