Lecture
Encryptors (encoders) are most often used to convert decimal numbers to binary or binary decimal code, for example, in calculators, in which pressing the decimal key corresponds to the generation of the corresponding binary code. Since it is possible to press several keys at once, the encoder uses the principle of priority of the highest order, i.e. when you press keys 9, 5 and 2, the encoder will generate a code 1001 corresponding to the number 9. It should be noted that the encoders as a separate class of functional devices are presented in the richest TTL series with only two ICs - 74147 and 74148, and the last IC is also available in the library of the EWB program. Its switching circuit is shown in Fig. 9.20.

The purpose of the terminals IC 74148: O ... 7 - inputs; AO, Al, A2 - outputs; El - permission entry; EO, GS - outputs for cascading encoders. When modeling, it is necessary to pay attention to the implementation of the priority principle, while it should be borne in mind that all inputs and outputs are inverse (they are erroneously shown as straight lines in the IMS functional diagram in EWB).
The operating modes used in the circuit in Fig. 9.20 the word generator is shown in fig. 9.21.
A decoder (decoder) is a device with several inputs and outputs, for which the active state of one of the outputs corresponds to certain combinations of input signals, i.e. the decoder is a de-multiplexer facing the inputs, whose address inputs have become information and the former information input has become a permission input. Therefore, decoders are often called demultiplexers, and vice versa.
Decoders and demultiplexers • in the form of serial ICs of medium degree of integration are widely used in information-measuring equipment and microprocessor control systems, in particular, as switchboards-distributors of information signals and clock pulses, for demultiplexing data and address logic in memory devices, as well as for conversion binary decimal code to decimal for the purpose of controlling indicator and printing devices.
Decoders as independent electronic products have 4, 8 or 16 outputs. If a larger number of outputs is required, the decoders are expanded into the system [8].

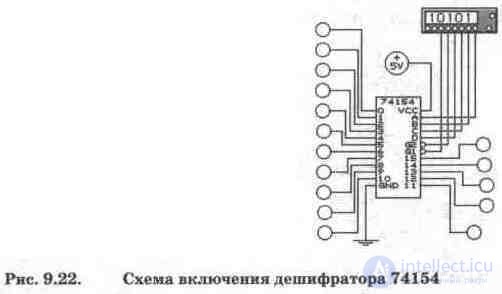
As an example in fig. 9.22 shows the inclusion of the decoder 74154 (domestic analogue K155IDZ). IMS 74154 has four address inputs A, B, C, D, two resolution inputs Gl, G2 and sixteen outputs О ... 15 (the outputs are not direct, as erroneously indicated in EWB, but inverse, i.e. in the initial state on outputs logical unit signal). In the mode of the decoder, from the generator the words 0 are supplied to the inputs Gl, G2, and a code in the range 0000 ... 1111 is sent to the address inputs. In demultiplexer mode, one of the enable inputs, for example, Gl, is used as information. An information signal in the form of a logical 0 from this output is distributed to the outputs O ... 15 in accordance with the state of the address inputs, i.e. the modes of the decoder and demultiplexer are almost indistinguishable.
Test questions and tasks
1. What is an encoder, what tasks is it used to solve?
2. By changing the code combinations in the generator of the circuit word in Fig. 9.20, show what the meaning of the word "priority" in the name of the encoder type 74148 is.
3. When deciding what tasks of digital technology is a decoder used?
4. Prepare the output code combinations of the word generator in the circuit in Fig. 9.22, providing alternate inclusion of LEDs at the output of the decoder, starting from output 0.
5. Translate the decoder in the circuit in fig. 9.22 to demultiplexer mode and perform the task according to p. 4.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital devices. Microprocessors and microcontrollers. computer operating principles
Terms: Digital devices. Microprocessors and microcontrollers. computer operating principles