Lecture

Illustration of signals with different fill factor D
The wellness (in physics, electronics) is one of the classification signs of impulse systems, which determines the ratio of its repetition period (repetition) to the pulse duration. The reciprocal of the duty ratio and often used in English-language literature, is called the fill factor (eng. Duty cycle ).
Thus, for the pulse signal, the following relations are true:
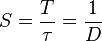 ,
,
where S is the duty cycle, D is the fill factor, T is the pulse period,  - pulse duration.
- pulse duration.
The duty cycle determines the ratio of the peak power of a pulse plant (for example, a radar transmitter) to its average power and is thus an important indicator of the performance of pulse systems. In devices and systems for the discrete transmission and processing of information, an insufficiently high duty cycle can lead to information distortion.
Often used in practice is a signal with a duty cycle equal to two - the meander.
Particular attention should be paid to the relationship between the term “duty cycle” and the duty cycle (English duty cycle ), since this can lead to errors when reading English-language and Russian-language documentation. Duty S S, dimensionless. In English-language documentation, the fill factor D (duty cycle) is usually measured as a percentage. But these are different representations of the same thing. And so that there is no confusion in the question, it is necessary to understand what is meant. Duty ratio, this is the ratio of the pulse repetition period to the pulse duration, and the duty factor D (Duty cycle), this is the ratio of the pulse duration to the repetition period, that is, these are inverse values.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital devices. Microprocessors and microcontrollers. computer operating principles
Terms: Digital devices. Microprocessors and microcontrollers. computer operating principles