Lecture
Strategic planning is the process of forming (adjusting) the organization’s mission, its production profile and goals, choosing strategies * to identify and obtain the necessary resources and their distribution in order to ensure the effective operation of the organization in the future. The strategic planning process * is a decision-making tool. His task is to provide innovations and changes in sufficient volume for an adequate response to changes in the external environment of the organization. In Figure 5.1. A diagram of the strategic planning process is presented. The stages outlined in the figure constitute the process of planning a strategy, and at first glance they look quite simple, but due to the presence of feedback between the stages, they can be repeated many times.
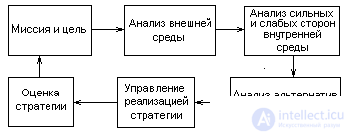
Fig. 5.1. Strategic planning process.
The strategy planning process encounters a number of difficulties in its implementation. The first and main difficulty is that the new strategy always destroys the existing relationships and relationships, and as a result of this the response is to counteract innovations and break the existing relationships. The second problem is connected with the lack of objective information about the external and own environment. The third is the lack of specialists - managers * and the insufficient level of their qualifications.
Consider the content of each stage of the strategy planning process.
Mission * and goals of the organization. The role, significance and content of the mission and objectives of the organization are discussed in the first section. Here we will focus on some aspects of the relationship of mission and goals with the organization's strategy.
The choice of mission and goals (or their adjustment) is the first and most responsible decision in strategic planning * . They serve as a guideline for all subsequent planning stages and at the same time impose certain restrictions on the direction of the organization’s activities. The mission * should be constantly supported by its social significance, profit cannot be proclaimed as the main goal of the organization, it is an internal problem of the organization, although very important. Goals are formed within the mission and in its development. Goals will be significant if they are properly formulated, effectively set, and all members of the organization are informed and stimulated to fulfill them.
Analysis of the external environment. The external environment of the organization greatly influences the effectiveness of its work; therefore, it is necessary in the development of a strategic plan to conduct its analysis and determine the extent of its impact in order to anticipate potential threats or newly opening new opportunities. The scheme of the analysis of the external environment of the organization is presented in Figure 5.2.
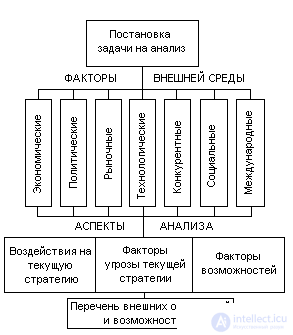
Fig. 5.2. Analysis of the external environment of the organization.
Consider the content of environmental factors.
Economic. It analyzes the rates of inflation (deflation), tax rates, international balance of payments, the level of employment of the population, the solvency of enterprises.
When analyzing political factors in the country and the world, one should follow the agreements between countries on tariffs and trade, customs policies, the level of development of the legal regulation of the economy, and regulatory acts of the government and local authorities.
Market factors to be analyzed include changes in market relations (capacity, stability and security), changes in the democratic situation, income levels of the population and their distribution, product life cycles, market share of the organization.
The organization * is obliged to follow the technological environment in order not to miss the moment of the appearance of changes in it, which will fundamentally transform the production technology. Analysis of the technological environment should take into account changes in production technology (know-how), structural materials, in the application of computer technology, in management, in information technology.
Analysis of competition factors offers control over the actions of competitors. Here you need to answer the questions: who is the competitor? what motivates them? what is he doing? what can do? In the analysis of competitors, the following diagnostic zones are distinguished: assessment of their current strategy * , analysis of the future goals of competitors, analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of competitors and prospects for their development.
Social environmental factors include changing social values, attitudes, expectations, and morals. Currently, in our country, a number of social factors have acquired special significance. This is an aggravation of national feelings, the role of national minorities, relations between regions of the country, relations of the center with the regions, attitude to the economic policy of the state, change of social values.
The analysis of international factors is important, since the possibilities of organizations in economic relations with foreign partners have significantly expanded (the abolition of the state monopoly on foreign trade).
Taking into account the environmental factors, the organization’s strategy may be aimed at seeking protection from the government from foreign competitors, strengthening the domestic market or expanding international activity. Here it is necessary to answer the questions: what changes in the external environment affect the current strategy of the organization? What factors pose a threat and improve the organization’s ability to achieve business-wide goals?
Analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the internal environment. After analyzing the external environment and obtaining data on factors that pose a danger or open up new opportunities, a firm must assess whether it has internal strengths to take advantage of opportunities, and which internal weaknesses may complicate problems. The method for diagnosing internal problems is called a management survey. For strategic planning purposes, it is recommended to include in the survey five functional areas - marketing, finance (accounting), production, personnel * , organizational structure and image of the organization.
When analyzing the marketing functions, the following elements are explored:
Finance (accounting). The financial condition of an organization largely determines which strategy will be chosen for the future, which accounting policy the firm will determine for itself.
Production. Constant analysis of the state of production and the system of its organization is very important for the timely adaptation of the internal structure of the organization to changes in the external environment and its survival in a particular environment.
Staff (human resources). The solution of many problems of modern organization depends on the provision of both production and personnel of the enterprise. When analyzing human resources, the following questions should be answered: how is the type of employees currently employed in the organization characterized and what will they need in the future? What is the competence and training of top management? Do we have an effective motivation system? Do we effectively use the training and development of workers?
Organizational culture and image of the organization. Organizational culture consists of the behavior of people in an organizational environment. Therefore, the organizational culture is understood as an integral system of behavior models, customs, customs, expectations developed in the organization and its members.
The image of the organization, both inside and outside it, is determined by the impression that is created with the help of employees and public opinion in general. This impression helps the organization to keep customers for a long time. The culture and image of the organization is reinforced or weakened by reputation.
By identifying strengths and weaknesses and weighing factors in order of importance, management can identify functional areas that require intervention or can wait, as well as begin to develop and implement an organization's strategy.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management