Lecture
To substantiate management decisions on the choice of advertising media, it is necessary to disclose their features and characteristics.
The choice of means of disseminating advertising information is one of the stages of the planning process of the advertising activity of an enterprise, the implementation of which is complex and multifaceted.
Methods of information transfer (channels, media, carriers) are extremely diverse. There are hundreds of them in advertising - from classic advertisements and posters to key chains, labels and adhesive tapes.
The variety of existing means of disseminating advertising necessitated their classification.
Taking into account Russian specifics, all advertising media can be divided into the following classification groups:
Each of the advertising media, quickly transmitting information to the masses of consumers, has its own specifics and performs the final task of advertising in its own way. Evaluation of advertising media by various criteria is given in Table. 9.1.
T a b and c a 9. one .
Evaluation of advertising media.
Facilities | Criteria | |||||||||||
Cost of | Audience reach | Quality of presentation | Exposure time | Audience selectivity | Personality | Propagation speed | Interactivity | The ability to quickly update information | The amount of information transmitted | The possibility of receiving feedback | Consumer Accessibility | |
Newspapers | Low | Wide for the local market | Low | Small | Low | Not wearing | High | Not | Not | Big | Difficult | Yes |
Magazines | High | Wide | High | Long lasting | High | Not wearing | Low | Not | Not | Big | Difficult | Yes |
A television | Very high | Very wide | Very high | Small | Low | Not wearing | High | Yes | Not | Little | Not | Yes |
Radio | Relatively low | Wide enough | Relatively low | Small | Low | Not wearing | High | Yes | Not | Little | Difficult | Yes |
Outdoor advertising | High, includes printing, delivery, accommodation | Wide enough | High enough | Long lasting | Low | Not wearing | Low enough | Not | Not | Little | Not | Yes |
Direct mail | High cost of mailing and receiving addresses | Low coverage | Relatively low | Long lasting | High | Wears | High | Not | Not | Big | Is real | Yes |
Advertising on transport | Relatively low | Wide enough | Relatively low | Long lasting | Low | Not wearing | Low | Not | Not | Little | Not | Yes |
Internet | Low | For Russian information and low | High | Long lasting | High | Wears | High | Yes | Yes | Big | Is real | Not |
According to the degree of interaction with consumers, the means of distribution are divided into channels of personal and non-personal communication.
Personal communication channels include personal meetings, personal correspondence, telephone conversations, communication with the audience on television and radio. They allow for feedback and provide an opportunity for personal contact, for example, a manager. This channel has especially great weight when applied to categories of high-value goods, liability measures (for example, an airplane for a president), and where there is an increased risk
Personal communication channels are often more effective mass.
The channels of non-personal communication include the means of disseminating information without the presence of personal contact and feedback. These include the media and means of selective influence. The first are designed for large indiscriminate audiences, the second, respectively, for specialized audiences. Mass communication affects personal relationships and behaviors, stimulates personal communication. This is achieved due to the fact that initially the appeal is carried by opinion leaders belonging to the primary audience, with whose opinion they are accustomed to be considered.
For an advertiser, the task of choosing a means of distributing his advertising appeal is very important. To do this, it needs to decide how wide the coverage should be of its advertising * , how often it should appear, choose the main means of its distribution, depending on their cost, etc.
To optimize the process of choosing the means of distribution of advertising at the planning stage of an advertising campaign, some indicators are used.
Reach , implies how many people in one contact will be able to get acquainted with the advertising appeal. For television and radio, for example, this is the total number of viewers (listeners) who are faced with an advertising appeal. For printed products, the coverage includes two components - the circulation and the degree of transmission (how many times each copy gets to a new reader).
The frequency of appearance determines how many times the average representative of the target audience should face the appearance of advertising. It is the largest for newspapers, radio and television, where advertisements appear daily.
The impact of advertising contact depends on the selected distribution channel. For example, an announcement on the radio is less impressive than a TV commercial, as different magazines, for example, can have different degrees of exposure.
The sustainability of the message shows how often the advertisement is seen and remembered. A large number of people see outdoor advertising, ads on the roads and telephone directories; magazines are permanently kept by the consumer, meanwhile, announcements on radio and television last on average about 30 seconds.
Completion refers to the number of advertisements contained in one program, one page, one edition, etc.
The deadline for submission is the period for which the information source can place an advertisement. It is the smallest for newspapers and the largest for magazines and telephone directories.
Frequency refers to the number of cases in which a promotional call is perceived by one person or a family as a whole. For the entire audience, frequency is calculated as the number of times a person or family hears an advertisement. The resulting figure is used to measure the saturation of the schedule for filing an ad.
The impact is called the total number of cases of perception by the audience of this ad.
The general perception of the audience or the density of the presentation of advertising by any media can be expressed by calculating the absolute magnitude of the impact. However, a more common method of expressing such information is the cumulative rating . It is calculated by multiplying the cases of perception of the advertising text, expressed as a percentage of the total audience, by the average frequency. The following formula is used to determine the cumulative rating of an advertising print graphic:


The final step in determining one or another medium of advertising is the analysis of the profitability of each of the media available. The most widely used term in this respect is the term “ cost per thousand (W / T)”.
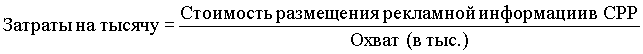
However, when choosing means of disseminating advertising, as a rule, it is more interesting to profitability in achieving the intended audience , rather than the cost of achieving a general audience in the framework of this media.

The process of choosing the means of disseminating information should consist of the following steps:
Making the right choice from a variety of media is quite difficult, so the method of choosing the means of distributing advertising for each particular product must be individual (or appropriate for a specific product group).
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management