Lecture
The effective work of the personnel * of the company involves primarily the rational use of working time. In this section, we tried to present the results of numerous studies aimed at the reasonable use of working time.
Time is the most important, scarce and irreplaceable resource. Time is irreversible, it cannot be accumulated, transferred, it passes irrevocably. Therefore, any employee who wants to improve his work should periodically analyze the level of use and loss of time.
Only if specifically, according to the results of the "inventory" of time in a few working days, to determine how much time is spent on what and with whom, can one see important reserves of personal time.
The effectiveness of working time is influenced by numerous factors:
One of the most important sources of time saving is planning. In the practice of management, it is generally accepted that a ten-minute preparation of the working day provides up to two hours of saving working time. At the same time, the manager must take into account rule 60: 40 - the plan should cover no more than 60% of your time, since 40% should be reserved for unexpected cases, visitors, telephone conversations, etc.
As a rule, as much time is spent on work as it is at your disposal. This pattern should be taken into account when planning time, for example, when setting dates for the beginning and end of meetings, business meetings, project discussions, etc.
When planning time, it is necessary to compile a list of works per day (week, month), to establish the priority (sequence) and the approximate period of work.
One of the main problems of working time planning is setting priorities in solving daily tasks. The Pareto principle, the ABC analysis and the Eisenhower principle discussed below contribute to the successful solution of this problem.
The Pareto principle, in general, states that within a given group or set, individual small pieces show a much greater significance than this corresponds to their relative specific weight in this group. So, American engineers found that 20% of stocks typically make up 80% of the cost of the surveyed inventory. It turned out that the Pareto principle works in various fields. With regard to management activities, it is formulated as follows: in the course of work, 80% of the results are achieved in the first 20% of the time. The remaining 80% of the time spent brings only 20% of the total.
If we talk about the daily cycle, then, since for most people, morning time is the most productive, you should not take up the easiest, most interesting or least costly tasks. First - for a few vital problems, and only then - for numerous minor problems. The Pareto principle finds its indirect expression in ABC analysis.
The essence of ABC analysis is to divide all cases into three categories, based on the fact that the relative importance of tasks (in the sense of contributing to the final result) does not coincide with their relative number.
The most important tasks (category A) make up approximately 15% of the total number of tasks and tasks. However, the significance of these tasks (in terms of contribution to achieving the goal) is approximately 65%. Important tasks (category B) account for an average of 20% of the total number of tasks and 20% of significance; for less important and irrelevant tasks - 65% and 15% respectively (see Fig. 6.9).
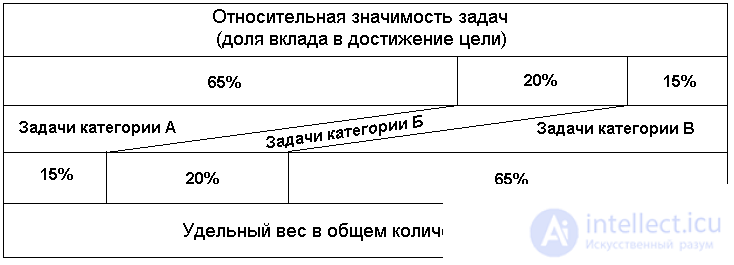
Fig. 6.9. The relative shares of the number and significance of tasks of different categories
Both from the Pareto principle and from the ABC analysis it follows that the establishment of priorities is an important element of the creative work of a manager. Below are questions that can facilitate the identification of tasks in category A.
A convenient aid to decision-making on various tasks is the so-called Eisenhower principle . In accordance with this principle, the task should be considered in the coordinates “importance” - “urgency”, it should be assigned to any category and an appropriate decision should be made on it (see. Fig. 6.10).

Fig. 6.10. Illustration of the principle D. Eisenhower
The efficiency of working time is greatly influenced by the well-being and performance of the company's employees.
On the basis of many years of research into biorhythms, a candidate of medical sciences L. Ya. Glybina came to the conclusion that within a day, a rise in efficiency is observed at 5-6, 11-12, 16-17, 20-21, 24-1 hours, and a decline occurs in 2-3, 9-10, 14-15, 18-19, 22-23 hours. Hence the conclusion: the hours of increase in working capacity should be used for creative, complex work, and the hours of decline - for routine, daily work, such as monitoring the progress of work of subordinates, etc.
A characteristic change in performance is observed during the week. So, on Monday, a person goes through the stage of work, on Tuesday, Wednesday and Thursday, the most stable performance is manifested, on Friday and Saturday it decreases and fatigue can develop. When planning work, these data should be taken into account, for example, on Monday and Friday, if possible, not to schedule meetings, business meetings (or the number of them should be drastically reduced).
A number of authors believe that according to the distribution of the intensity of working capacity during the day, all individuals can be divided into 3 groups:
To determine the optimal mode of operation during the day, everyone can try to use the simple test proposed by the West German scientist G. Holdebrand. The test is based on determining the ratio of heart rate and number of breaths. There are three possible pulse-to-breath ratios: for "arrhythmic", the ratio of the pulse to the breath is 4: 1 (or about this value); for “larks” - 5: 1, 6: 1. An increase in the frequency of breathing and a decrease in this ratio is characteristic of “owls”.
A short nap during the day may halt a decrease in performance. According to a specialist from Germany, some enterprises with a predominantly female contingent of workers entered into a half-day midday sleep. The experience of these enterprises showed that, despite the 30 minutes of working time “falling out”, labor productivity as a whole increased, in the second half of the day there was no fatigue among the working women, or the extent of it was sharply reduced.
Research has established that night performance is not inferior to daytime. However, taking into account the existing periods of decline in working capacity at night, it is necessary for professional groups to develop fitness for an altered rhythm of life, recommend rational modes of work and rest, and organization of proper nutrition. One of the leading factors for the preservation of health and high performance during night physical work is the organization of a balanced diet. A prerequisite, for example, is providing workers a night shift with hot food.
The color climate affects the health and performance of people. So, according to the observations of psychologists, the most tiring color - purple, blue - soothing, green increases efficiency. Colors can be cold and warm, which is important to consider when designing hot and cold workshops, as well as when building enterprises in different climatic and geographical zones. When selecting colors, it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the lighting. Under luminescent lighting, blue-green and yellow-green colors become too sharp. When illuminated with incandescent bulbs, gray, blue and green dim, and orange, yellow and red are perceived as brighter. Due to the correct color of the walls, floor, equipment, rational use of light and easy-to-use machine tools and tools, labor productivity rises on average by 15-20%, and injuries are reduced by 45-50%.
Psychologists say that performance in a good mood is 0.8-4.2% higher, and in a bad mood - 2.5-4.8% lower than the average. In this regard, during the construction and reconstruction of enterprises, the task of specialists is to find such a harmonious set of colors, which, without tiring the eye, would create a good mood and thus make everyday work more attractive and successful. Czechoslovak scientists calculated that the correct color design for industrial plants is 20 times cheaper than the losses caused by color anarchy.
In recent decades, the production of functional music has become increasingly active in production, which has a positive psycho-physiological effect on a person in the labor process. In the morning, before starting work, vigorous marching music is recommended, and after 10-15 minutes - “working music”, which helps a person to completely brake after a recent sleep and to gain maximum performance. Physiological studies show that, as a rule, functional music improves attention, has a beneficial effect on muscle strength, pulse rate, blood pressure. In a sociological survey, many workers stated that they had previously returned home tired, and with the introduction of music, their well-being had improved. In selecting functional music, it is necessary, depending on the technological process and working conditions, the age composition of workers, to take into account the level of intensity, rhythm, duration and nature of the musical material. The most rational intermittent schedule of music programs with a total duration of 1.5-2 hours per shift.
When organizing a workplace, it is necessary to take into account that the height of men and women differs on average by 11.1 cm, the length of the arm extended to the side is 6.2 cm, the length of the arm extended forward is 5.7 cm, the leg length is 6, 6 cm, height of eyes above the floor level - by 10.1 cm.
When constructing a workplace in a sitting position and its hygienic assessment, it is taken into account that, on average, the body of a man in this position is 9.8 cm longer than that of a woman, and the height of eyes above the seat differs by 4.4 cm, respectively.
Creating an operator’s workplace is determined by a number of functional requirements: the distance at which readings are read; the angle of view; illumination; location and method of actuating interconnected controls. The optimal posture of the worker is also provided by the design of the seat, which should support the body and prevent its wrong position. The working seat should be comfortable to perform the planned work, have the required dimensions, be equipped with armrests that do not interfere with movements, allow adjustment in height. In some cases it is advisable to use special steps.
The implementation of the recommendations discussed above in the practical work of managers and specialists ensures an increase in the effectiveness of the firm’s management system.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management