The purpose and content of CAT. Design preparation of production is a set of interrelated works aimed at creating new or improving existing designs of products of a given technical level with fixed deadlines, production volumes and costs.
Criteria for achieving the main goal of the PPC are the minimum duration, complexity and cost of work.
The content and scope of work on the checkpoint conducted by an enterprise depend on the following factors:
- the degree of participation of the enterprise in the design of a new product;
- type of product being developed;
- the degree of novelty and complexity of the product;
- type of production.
There are four types of products in the field of design and production.
- A part is a product made of the same material material without the use of assembly operations with the possible use of local joining operations (welding, brazing, etc.), for example, a roller, a welded sleeve.
- An assembly unit is a product whose components are to be interconnected (assembled) at the manufacturing plant, for example, a ball bearing.
- A complex is a product consisting of several products of interrelated purpose that are not joined at the factory by assembly operations, for example, a garden sprayer.
- The kit - several products of general functional purpose that are not connected at the factory by assembly operations, for example, a set of fuses.
Functions, elemental composition and organizational structure * of the PPC subsystem. The PPC process consists of six main functional blocks of tasks:
- Engineering Forecasting . Includes:
- feasibility study (FS) of the choice of analogue;
- a comparative assessment of tactical, technical, operational and other indicators of the design under development and its analogue.
Parametric optimization is the use of a parametric series (values of the main characteristics of this type of product) to select the desired type of size of the product being developed.
Experimental design. It is carried out in stages and includes the following:
a) Development of technical specifications (TZ). This is a document prepared by the customer and containing:
- name and scope of the product;
- the basis for the development, its purpose;
- tactical and technical, operational and other characteristics;
- quality indicators, feasibility and other requirements;
- the sequence of the development of documentation, the order of control and reception.
b) Development of a technical proposal. This is a document prepared by the developer and containing:
- proposals on the feasibility and possibility of meeting the requirements of the TK;
- options for possible solutions and a proposal for choosing the best option;
- enlarged economic calculations of the cost of production and the effect of the use of the product.
c) The stage of the draft design . Includes:
- the overall layout of the product, as well as kinematic, hydraulic, mounting and other schemes;
- sketch drawings of general views;
- laboratory prototyping;
- analysis of patent purity of the structure, etc.
d) Stage of the technical project. Include execution:
- drawings of assembly units and critical parts;
- calculations for durability, reliability, accuracy, etc.
- specifications and specifications (TU);
- economic justification of the project.
e) The stage of creating working documentation. Include execution:
- drawings of all parts (except guest rooms);
- documents regulating the conditions of operation and repair.
Design testing for manufacturability. It represents the final assessment and optimization of the developed design, providing an increase in quality characteristics that contribute to the simplification and improvement of the production process, maintenance and repair, reducing the complexity of manufacturing.
Pilot production of the product and the development of mass production. In the process of pilot production, the design, technological processes, processing modes are tested, the conformity of the process equipment and equipment is checked.
Metrological examination of the product. It consists in checking the conformity of the product parameters obtained as a result of the design. Examination is based on the requirements of the State Standard.
The elemental composition of CAT includes:
- Human resources (managers, specialists, technical performers).
- Material resources (basic and auxiliary materials for the manufacture of models and prototypes, stationery, etc.).
- Technical means (equipment, control rooms, computers, copying equipment, etc.).
- Information support (standards, regulations, classifiers, etc.).
- Economic and mathematical software (mathematical models, modeling methods, etc.)
Organizational structure * PPC subsystems. A typical scheme of the structure of the PPC subsystem of an enterprise with a serial type of production can be represented as follows (Fig. 7.3).
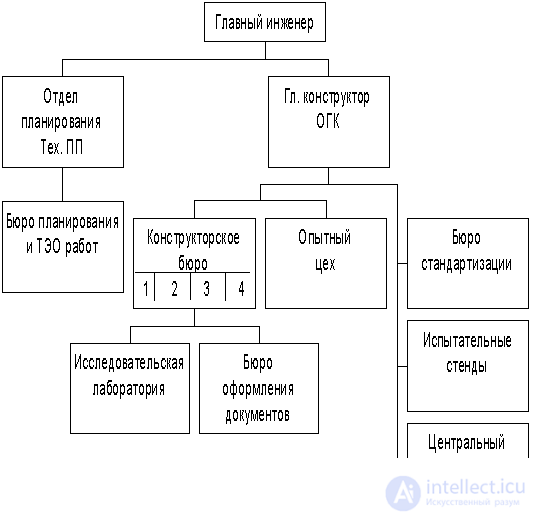
Fig. 7.3. Typical scheme of the structure of the subsystem CAT.
The main requirements for product design. Existing standards establish the following groups of indicators characterizing products:
- technical purpose of the product;
- reliability;
- manufacturability;
- unification and standardization;
- ergonomic;
- patent law;
- economic.
- Indicator of the technical purpose of the product - a set of indicators that determine the technical compliance of this type of product.
- Reliability indicator - i.e. the property of the product to preserve the values of operational parameters for a given time (reliability, accuracy, etc.).
- The indicator of manufacturability - characterizes the level of achieved optimal design of the product at the lowest possible cost of its manufacture. It comes from:
- simplify the geometric shapes of parts;
- rational assessment of the required accuracy and purity of processing;
- increase the availability of elements of control and the level of interchangeability, other factors.
- Unification * and standardization * .
Design unification is a set of measures to bring products or their elements into a single form, size, structure, composition, etc.
Standardization is the establishment of standards and requirements for the physical and dimensional values of manufactured products.
The objects of standardization * are: specific products, norms, terms, designations, etc. - everything that has the prospect of multiple use.
The ordering of these objects is made out of special documents - standards.
Design unification * and standardization in instrument making are implemented in the process:
- use of design normals;
- parameterization;
- aggregation and modular design;
- typification and simplification (reduction of the variety of objects), etc.
- Ergonomic indicators are taken into account the psycho-physiological qualities of a person as a link in the "man-machine" system.
- Patent-legal indicators are characterized by security of patent product purity (absolute copyright in the Russian Federation and abroad) and patent protection (unhindered manufacturing and sale of products).
- Economic indicators - characterize the degree of profitability of the product as an object of production (labor intensity, material consumption), and the object of operation (maintenance, repair, etc.).

Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management