Lecture
Basic concepts of the theory of labor valuation. In accordance with the functions of labor standards in society, the establishment of the principles of labor valuation should take into account the requirements of the basic economic laws - time savings, planned, proportional development, distribution according to work, reimbursement of labor costs.
When considering the requirements of economic laws, the following system of principles of rationing follows.
Under the method of regulation is understood a set of methods for establishing labor standards, including: analysis of the labor process; designing rational technology and work organization; calculation of norms The choice of the method of valuation of labor is determined by the nature of the rated work and the conditions for their performance. According to the rate setting scheme, all methods are divided into analytical and total.
Due to the fact that production processes differ significantly in the nature of product manufacturing, materials used, equipment, technology, production volume and other parameters, the application of various types (systems) of standards is objectively necessary for calculating standards. Standards for determining the required labor costs can be established on almost all structural elements of production processes and products. Thus, standards were developed for the execution time of labor movements, actions, methods, complexes, surface treatment of parts, assembly of components and machines, standards of labor intensity for types of work and the product as a whole.
A set of standards is a multi-level system, i.e. standards of each level can be obtained by enlarging the standards of lower levels (from movements to labor methods, etc.).
Depending on the scale of enterprises, the organizational forms of building associations and other features, the system of standards can be modified; economic-mathematical methods and computers are widely used.
The main methodological provisions for the justification of labor standards. The object of technical regulation in engineering is an operation. It is divided into its constituent labor elements - movements, actions, techniques, and complex techniques.
The structure of a technically sound standard of time includes only those categories of working time that are necessary for a given job in normal conditions. Thus, the structure of the norm of the piece and piece-calculation time is expressed by the formulas:
T pcs = t о + t в + t to + t oo + t from
Where t o - the main (technological) time * ;
t in - auxiliary time * ;
t then - the time of maintenance;
t oo - time organizational service;
t from - rest time;
t pcs = t pcs + t nz / n
where t nz - preparatory-final time * ;
n is the size of the wage lot.
The structure of the norm of time varies depending on the organizational conditions of the operations.
The sum t о and t в constitutes the operative time (t op ), it, as a rule, must be established analytically-by calculation based on the optimization of the operating modes of the equipment and the methods of labor. At the same time, standards of varying degrees of integration are used. When mass production of products used microelement standards for labor movements. In large-scale production, the standards for labor actions and receptions are used, in serial, in small-scale and individual - the most comprehensive standards, as well as typical standards.
Given that t on = t o + t in , it is necessary to strive to increase the overlapped t in , i.e. parallel to perform auxiliary work.
The service time (t ob = t so to + t oo ) should be established on the basis of designing the optimal division and cooperation of labor between the main and auxiliary workers in securing the workplace with workpieces, tools, auxiliary materials, chip cleaning, etc.
At most enterprises, service time is set according to standards as a percentage of t on and t o .
These values are calculated by the formulas:
t then = (t o · a then ) / 100
t о.о = (t on · a oo ) / 100
where a then a oo is the standard percentage of service time.
In the conditions of a single production for the valuation of handicrafts
t obs = (t on · a ob ) / 100
where a obs - the standard percentage of time for maintenance.
Existing standards t obs are established, as a rule, on the basis of photographs of working time for a group of homogeneous workshops and therefore do not take into account the characteristics of each. Therefore, for some industries, it is recommended to install the obs in minutes per shift, taking into account the rules for servicing the RM. t pz is set to study the technical and planning records, lining equipment, obtaining materials, blanks, tools for a batch of parts, for the delivery of finished products.
In mass production, tpz is not counted. With serial, small-scale and individual types of production, tpz are set for each operation on the basis of general engineering standards.
t from and personal needs are set according to general engineering standards, in general t from should be 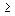 10 min. in shift +
10 min. in shift + 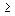 10 min. for personal needs, i.e. t from
10 min. for personal needs, i.e. t from 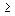 20 minutes. per shift, t from is calculated as a percentage of t op .
20 minutes. per shift, t from is calculated as a percentage of t op .
Norms of duration and laboriousness of operations, norms of development and standardized tasks should be established after calculating the operating modes of the equipment, design of labor practices, optimal division of labor, regulations for servicing the Republic of Moldova and labor and rest schedules.
The following formula is usually applied:
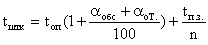
This formula is used in practical calculations, however, in modern conditions it does not always provide justification for the norms of time, primarily due to the fact that the duration and laboriousness of operations are strictly different, which is essential for the collective maintenance of equipment and multi-station work. Therefore, it is advisable to rate the duration of the operation in the form of N d = t p 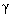 + t ps where t p - the direct costs of operational time, which, depending on the production process, include either all t op . Or just t ma (machine-automatic time),
+ t ps where t p - the direct costs of operational time, which, depending on the production process, include either all t op . Or just t ma (machine-automatic time), 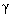 - coefficient taking into account indirect costs.
- coefficient taking into account indirect costs.
For example, to work on automated equipment that does not stop during the rest of the workers, N d = t ma 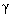
After establishing N d, the rate of labor input for the operation is N t = Ng · Nd, where H r is the number of workers for performing operations, if H r = 1, N t = N d Then the output rate is determined by the dependence
H = T pl / H d
where T PL - the period of time (hour, shift), for which the output is determined. If the operation is performed by several workers, then
H in = (T pz · H g ) / H T
In conditions of multi-maintenance, the value of N d is the norm of the duration in relation to the machine N do ., And the norm of the duration in relation to the working
N d.r. = H others / H o
where N about the rate of maintenance of machines workers. Then
H in = (T pz · H o ) / N d.o
Usually, H in is set based on the normalized duration of the operation, but there may be a reverse order.
In case a worker or a brigade produces heterogeneous products, the result of labor is established by a standardized task. The normalized task sets the volume of production in the nomenclature, norm-h, or norm-rub., Which must be produced within a given period of time.
The peculiarities of labor valuation in automated production are the determination of optimal variants of the number and impact of employees (operators, service engineers, programmers, etc.).
Optimizing the impact of workers should consist in the division of work performed into two types: production and support. The first are the work, the duration of which is included in the duration of the production cycle of products.
To ensure include work that can be performed simultaneously (in parallel) with the main process. The execution time of the maintenance work is not included in the duration of the product production cycle. The number of workers required to perform support work is established on the basis of the usual volumetric calculation, i.e. by comparing the labor intensity of work in the planning period with the time fund of one performer.
Otherwise, the number of employees required to perform production work is calculated. In this case, the group of machines (line) should be considered as a multi-phase queuing system, in which the process equipment is the source of the requirements, and the workers - the service channels.
The main method of optimizing such systems is statistical modeling of a computer process. Based on this model, the number of service personnel is determined.
The methodology of rationing the work of specialists is determined by the content of the labor of this category of workers. By the nature of the performance of functions, the content of labor of specialists and employees is divided into three categories - the existence of leadership, the development of solutions and the preparation of information. In accordance with this official composition is divided into - managers, experts, technical performers.
When rationing the work of specialists and employees, basically two tasks are solved: the labor intensity of certain types of work is determined and the required number of employees is identified. When rationing labor professionals and employees use the following types of standards: time, production, maintenance, manageability, the ratio and number. Standards of time - the required time to complete a unit of work, are used to rationing repetitive work. This is the work of engineers, designers, technologists, accountants, etc.
Production rate - the number of units of work performed per unit of time, is used in the rationing of labor performers performing operations with technologically regulated content - accounting and other operations.
Norm of service - determines the number of RM workers serviced by one or a group of performers. It is used for rationing works that are stable in volume, but with the presence of repetitive elements. With their help, the work of dispatchers, timekeepers, cashiers, etc. is normalized.
Under the norm of manageability refers to the number of employees or departments, which should lead the head under appropriate conditions. The difference of the norm of controllability from the norm of service is that the worker, whose work is rationed, directs others under his direct subordination.
The ratio ratio is the number of employees of a position or qualification per one employee of another position, qualification.
The number rate is the number of employees of a certain professional composition required to perform work on the relevant management function or work assigned to a structural unit.
When rationing the work of specialists and employees, various methods are applied - analytically-calculating and analytically-research.
An important factor in improving the productivity of normalizers and improving the quality of standards is the automation of calculations, the use of economic-mathematical methods and computer equipment designed to solve special problems of rationing and has a certain scope of application ..
Nomographic tools allow you to graphically depict complex multifactor dependencies characteristic of calculations of cutting conditions and time norms.
Normalization calculation rulers are used for operational rationing and checking the effectiveness of modes in the workplace. Special computers are based on analog modeling of processing modes. The basis of calculations on a computer is based on the main calculated dependences of the general engineering standards, while applying both specialized and universal PCs.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management