Lecture
The main content of TEP is the formation of an integrated system of indicators of the company. In this regard, various implementation plans are developed, based on the study and analysis of previous periods of production and business activities of the enterprise, assessment and analysis of the internal environment of the organization, factors of external influence, the situation on the product market.
Calculations of the required indicators and the development of relevant plans are carried out by the employees of the functional services and departments of the company. The main functions of TEC are:
Planning of TEP is preceded by forecasting, which is the most important information basis for planning.
Forecasting is a scientifically based assumption about the development of the system, which is the basis for developing future plans. Forecasts are probabilistic in nature and, unlike plans, do not determine the ways and means of implementing the intended goals. They help to increase the level of continuity, validity, rationality and reality of the plans. When developing forecasts, methods of mathematical modeling, extrapolation, etc. are used. The purpose of forecasting is to assess the internal weaknesses and strengths of a company, its future capabilities, adaptation to a changing external environment, as well as an assessment of the organization’s perspective development in various areas and levels: the country's economy in general, the region, industry; markets whose activities are in the interests of this company. This information is necessary for the formation of common goals for the development of the company and its individual divisions.
Forecasting is closely related to marketing and is the basis for the firm’s market strategy. It is in marketing that the forecasts of two categories are combined: long-term and short-term. The long-term forecast mainly concerns strategic decisions, such as the development of new products, access to new markets, investment decisions, cash flow plans, etc. The short-term forecast refers to such items as budget, finance, raw materials and materials, and labor. production plans, etc.
Forward planning has two forms: long-term and strategic, and involves a planning period of 5 to 15 years.
Long-term planning is based on the fact that the technical and economic indicators of production and business activities of the company for the future can be established using the extrapolation method, i.e., the continuation of a number of previously achieved indicators for the future according to the revealed pattern.
The company's management believes that in the future, the company's performance will improve (worsen) compared to the past in accordance with the rates that have been recorded over a number of past years. On this basis, management establishes expected quantitative indicators for the future. There is a setting of optimistic goals, which are often practically not implemented.
In fig. 9.2 shows the results of planning by extrapolation of previous indicators. A successfully operating enterprise (result A) shows a steady increase in the sales rate, despite a periodic decrease in the baseline data of each stage compared to the results achieved earlier (the form “saw teeth”). At the lagging behind enterprise, the achieved indicators (result B) are below the level of extrapolation and are characterized by periods of both a fall and an increase in volumes with a general tendency of decline in results (the form of a “trail of a hockey stick”).

Fig. 9.2. The results of enterprises in the planning method of extrapolation.
The long-term planning procedure involves the implementation of a number of stages, which are presented in Fig. 9.3.
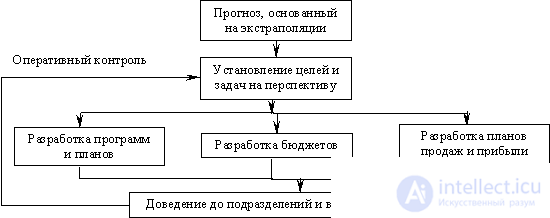
Fig. 9.3. The scheme of long-term planning of the company.
Strategic planning is a set of actions and decisions taken by the management of the company aimed at achieving the goals set by the firm. Making strategic decisions is felt in the following order:
If the current programs and budgets orient the production units of the company in their daily work to ensure the current profitability of production, the strategic programs and budgets lay the foundation for future profitability.
In strategic planning, the method “Analysis of gaps between goals and achieved results” is used. It includes an analysis of prospects, competitive positions, ranking of activities, the need for diversification and other programmatic issues. The stages of the analysis and the influence of various factors on improving the performance of the company are presented in Fig. 9.4.
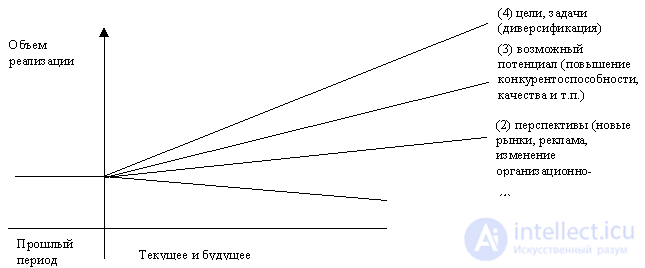
Fig. 9.4. Factors of strategic development of the company.
The process of strategic planning involves the implementation of both short-term and strategic goals and objectives. (fig. 9.5.)
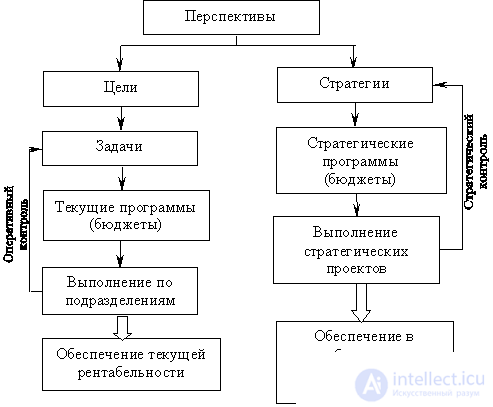
Fig. 9.5. The scheme of strategic planning of the company.
Describing the effectiveness of long-term and strategic planning, it should be borne in mind:
Long-term planning for the implementation mechanism does not require the involvement of highly qualified specialists and uses the information base of the results of the company for a number of years. Its use is advisable when the company operates in a traditional, technologically stable industry.
Strategic planning requires, firstly, a thorough analysis of the most significant internal strengths and weaknesses of the firm’s work and, secondly, sufficiently accurate predictions of environmental changes and the information base of the company's previous performance results. It is advisable to use it when planning in complex, developing industries.
Annual feasibility planning. The main content of the annual TEP is the development of a set of interrelated plans for the most important activities of the company. These plans determine the detailed program of the entire production, economic and social activity of the company for the planned period. In the process of developing plans, calculations of various indicators of the company's production activity are carried out, deadlines and responsible performers are established, if necessary, the values of previously established norms and standards are adjusted. In addition to functional plans, the annual TEP includes promising research and development work, preparation for the development of new types of products, etc. In developing the plan for the annual TEP, planned organizational and technical innovations are taken into account, such as: the introduction of new technology and technology, cost reduction, changes in product range and other reasoned changes in the activities of the company during the entire period.
Development of plans of TEP is carried out by employees of the relevant functional services and departments of the company (for example, development of a plan for cost, profit and profitability - planning and economic department).
In the current market economy conditions, when planning an enterprise, there is no regulation regarding the composition and focus of annual TEP plans. The criterion for the effectiveness of an enterprise planning system is, in this case, the level of justification for the implementation of various multifaceted final goals facing the firm.
The main objects of the annual TEP are the plans that determine the activities of the company. (fig. 9.6.)
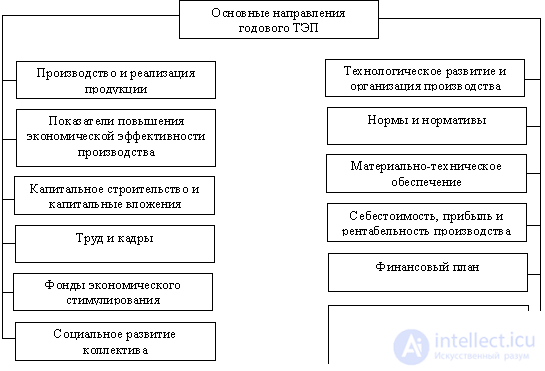
Fig. 9.6. The main directions of the annual TEP activities of the company.
Consider the content presented in Fig. 9.6. The main directions of the annual TEC of the company.
The defining, basic for the formation of other plans is the plan "Production and sales of products." In this plan, based on the calculation of production capacity, a program of production and sales of products is developed, the volume of commodity and gross output is determined, the equipment load is calculated, the balance of production of semi-finished products of own production is drawn up.
Plan "Technical development and organization of production." It is a complex of technical and organizational measures aimed at creating new and improving the quality of products, introducing advanced technologies, saving raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, improving management, planning and organizing production.
Plan "Indicators of increasing the economic efficiency of production." This section, which consists of calculations, the resulting economic effect from the implementation of the plan "Plan" Technical development and organization of production. "
The “Norms and Standards” Plan clarifies and develops regulatory materials in the following parts:
Plan "Capital construction and capital investments". Determines the volume of the planned construction and installation works, the cost of purchasing equipment with an indication of the time of their commissioning, the order and amount of funding, their sources, the need for adequate personnel and material and technical supply, calculations of the payback of capital investments.
Plan "Logistics". It consists of calculations of the need for material resources for the main production, the introduction of new technology, repair and operational needs and the creation of the necessary reserves.
Plan "Labor and Personnel". It contains calculations related to the balance of working time, determining the number of employees by categories, planning the s / n fund, justifying the need for training and retraining of personnel.
Plan "Cost, profit and profitability . " The plan includes the following calculated data: estimated production costs; cost estimate for the maintenance and operation of equipment; general business expenses estimate; estimate of general works costs; planning costing per unit of production; calculations of balance sheet profit and profitability of production.
Plan "Economic Incentive Funds". Calculated and determined by the size of the economic incentive funds in the directions.
Plan "Financial Plan". Includes balance of incomes and expenses, their sources, other necessary sections. Given the calculation of the need for working capital in all areas of costs.
Plan "Social development of the collective". The plan includes measures to improve working conditions and safety, improve social, living and cultural conditions of employees.
Plan "Conservation of nature and rational use of natural resources." Environmental protection measures are developed taking into account the specifics of the company.
These plans are the basic working documents of the relevant services, departments and production units of the company. All of them are interrelated, actual results are periodically checked against planned ones, analyzed, if necessary, there is a redistribution of material resources and other actions aimed at fulfilling the goals set.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management