Lecture
The main tool that ensures the implementation of the advertising campaign is the advertising budget.
The advertising budget assumes: 1) determining the total number of funds allocated for advertising; and 2) the distribution of funds allocated to advertising. As with most other decisions, in advertising the determination of the total cost is mainly a matter of good judgment. When there is no method for precise determination of the contribution of advertising in increasing sales and profits, distributors cannot rely upon developing a budget for some simple formulas. On the contrary, they should take into account many factors and go to the figure, which, in their opinion, most fully meets the requirements of a specific combination of circumstances.
Here are some of the most significant factors that need to be considered: 1) market volume and dimensions, 2) advertising role in the marketing complex, 3) product life cycle stage, 4) product differentiation, 5) profit size and sales volume, 6) competitors costs and 7) financial resources. All these factors are interdependent, interrelated, constantly changing, and when developing a budget, they need to be considered as a whole.
1. Market size and dimensions.
The amount of the budget is determined depending on how many people need to be covered. Coverage of large, widely distributed nationwide markets is more expensive than coverage of highly concentrated small local markets.
On mixed markets, you need to use expensive TV, general trade magazines and newspapers. On smaller, well-defined segments, cheaper specialized magazines and local radios can be dispensed with with less useless coverage. However, the use of local advertising media with high selectivity makes it possible to reach specific market segments with minimal useless coverage.
2. The role of advertising in the marketing complex.
The greater the role of advertising in the development of sales, the more likely it will be the size of the advertising budget.
An important factor of the marketing complex, directly affecting the size of the planned advertising costs, is the amount of funds that need to be allocated for sales promotion activities aimed at both the consumer and the retail trade. Due to the sending of samples, the distribution of coupons, the provision of discounts to retail merchants, etc., quite often in the year of launching new items on the market, sales promotion is much more expensive than on advertising.
A new product, as a rule, requires more intensive advertising. Expenses on the withdrawal of the product of the brand on the market with a high degree of competition can completely absorb all the gross profit of the first year. Building awareness about the brand, including the period of trial sales and establishing a retail network, requires a large initial investment in advertising and sales promotion.
After a successful launch of a new brand on the market, i.e., after reaching or increasing the control indicators in the field of sales, capturing market share, reimbursing costs, etc., the company can use one of the following three strategies: 1) strategy of further growth, 2) the strategy of keeping the achieved position or 3) the strategy of reaping the fruits of the achieved. The strategy of further growth requires a significant expansion of advertising, which is accompanied by a drop in income for the nearest time segment, but opens up the possibility of winning a higher market share before the brand. For labeled brands on a fully market-based market, which is typical of most brand products, the strategy of keeping the achieved position requires to keep approximately the same relative level of advertising from year to year. The strategy of reaping the fruits of what has been achieved is calculated on the growth of revenues during the nearest time slice and replenishment of funds due to a reduction in allocations for advertising and a fall in the market share.
3. Differentiation of goods.
When a product has a unique advantage that customers instantly recognize in the process of use, the amount of advertising required is usually less than in cases where such a clear difference does not exist. In the absence of a competing brand of visible differences in the budget, funds must be provided for the creation of promising long-term value of the subject of advertising in the form of a brand.
4. The size of the profit and sales.
The indicators of the size of the commodity unit and sales volume indices are inseparable from each other. With a substantial amount of profit - even if the sales volume is small - the advertiser has quite a lot of freedom in determining the size of the advertising budget.
The small size of the profit in the calculation of the commodity unit can be more than offset by a large volume of sales.
Advertising * increases the value of marketers in the eyes of consumers, allowing the seller to charge a higher price, which in turn contributes to the growth of the advertising budget. Naturally, this forward movement is constrained by the elasticity of demand, depending on the level of prices and competition.
5. Cost of competitors.
Indicators of the share of brands in total sales and in the total amount of advertising costs, in the framework of the product category are usually closely interrelated. In other words, the share of the brand in the volume of sales, in all likelihood, quite accurately corresponds to its share in the total amount spent on advertising. The share in the sales volume is correlated with the share of attention gained, which in turn is the result of the share of advertising (the share of the audible voice). This ratio can also be a self-fulfilling prediction: the higher the sales, the more we spend on advertising. In any case, the estimated market share of the brand implies a certain level of the advertising budget, taking into account the total costs in the product category.
The costs in themselves do not guarantee advertising success, and the level of competition participants should not be considered as the sole determinant factor. However, since the share of attention behind which the competitive struggle goes is comparable to the share of the market, this factor should not be overlooked.
6. Financial resources.
The most obvious limiting factor in the size of the budget is the availability of funding funds. Advertising costs for entering the national market in many categories according to the strength of a company that is comparable to a few companies with huge financial resources.
Comparatively small companies offering a first-class product or a first-class service, but with limited funds, can start small and increase advertising allocations gradually, as sales grow. The scope of the advertisement, as well as the scope of production, must be commensurate with the size of the funding.
The value of the advertising budget is determined in several ways. In practice, they usually do not rely entirely on any one, but use a combination of several of the following methods.
Consider the methods of calculating the value of the advertising budget:
1. The budget is determined as a percentage of the previous or estimated sales volume, taking into account the volume of costs and the advertising practice of competing firms. The most frequently used indicator of the percentage of advertising costs to the total cost of sales, less often - set the amount (norm) of advertising costs of the product. In this case, the indicator is expressed in rubles / unit of goods. To link competitors in a single measure of costs, advertising costs and total sales value, they use the value of advertising costs per unit of market share.
In the amount of costs per unit of market share, actions of competitors are taken into account, because the market share of an individual firm depends on the market share held by the rest. This indicator is useful when comparing the effectiveness of advertising of individual firms. It is believed that a firm that spends a smaller amount on advertising per unit of market share is seeking greater efficiency.
2. Taking into account the goals and objectives, attention is focused on the goals that need to be achieved, and the role that advertising * should play in this, which is no longer considered as a consequence, but as the reason for sales.
This method provides the following procedure for the preparation of the advertising budget:
The main drawback: the method does not contain indications of the criteria for selecting the goals themselves.
3. Method of residual funds - the company allocates as much money for advertising as is left after distribution to all other purposes. The management of the company does not see the connection between the amount of funds allocated for advertising and the volume of trade.
This method is ineffective and, as a rule, leads to unsuccessful advertising and marketing activities. Usually this method is chosen by a company that has no advertising experience and does not know its exact goals.
4. The budget is determined on the basis of modeling the relationship between the level of communication and consumer behavior. These techniques are especially useful in the process of planning an advertising budget when launching a new product on the market. The rationale for this model is the idea that in order to achieve the planned sales volume it is necessary to have a sufficient number of consumers. The creation of this basic contingent of consumers of a new product during the first year begins with the achievement of a certain level of awareness (the number of people who saw the advertisement of the product), prompting for the first purchase (the number of persons who made the first purchase), ensuring repeated purchases and maintaining the intensity of purchases of a new product. Based on the required levels of awareness, trial use and repeat purchases, they determine the necessary level of coverage and frequency of exposure, develop a plan for using advertising media and give a rough estimate of costs, and derive a numerical budget indicator.
5. The budget is determined on the basis of mathematical models of decision making, for example; models describing changes in turnover depending on the value of advertising costs.
Distribution of allocated funds for advertising is dependent on: 1) functions of advertising activities, 2) sales of advertising, 3) means of advertising and 4) advertised goods.
1 . Distribution of allocations for the functions of advertising activities.
Advertising budget items represent expenditures on the purchase of funds, advertisements, general administrative overhead costs, expenditures on production work and research costs. The advertising budget should indicate the amounts allocated to each of these basic functions of advertising activity. If the budget is intended to serve as a guide to action and as a control tool, it should be reasonably adjusted to the situation.
2. Distribution of allocations for sales requirements.
When distributing the total cost of advertising on sales, the sales department and the department of advertising should work together. The distribution itself depends on many different factors. Among them can be called the number of dealerships on a specific basis, the population, the number of vendors, potential sales opportunities and the nature of advertising media covering a particular area.
The most significant indicator of the distribution is the indicator of potential sales opportunities. The number of dealerships is not in itself of great importance. A great value is acquired by the indicator of the volume of dealerships, since it carries with it an indication of the potential sales of the company. Not important and indicator of the population. It is important to take into account not just the number of people, but their purchasing power, purchasing habits, desires and common features.
3. Distribution of appropriations for advertising media.
The lion's share of the budget are the costs for the purchase of advertising media. Distribution of the planned costs across the different means of advertising, largely determines the scale and nature of the advertising program as a whole.
The size and composition of the audit that needs to be covered, the number of appeals that need to be conveyed to it, and the time of bringing these appeals are the main indicators of any advertising program requiring careful planning.
In case of distribution of costs in the media of advertising, the advertiser must take into account the many existing interrelations and interdependencies. There are no generally accepted solutions that do not exist, although nowadays, when choosing specific characteristics of the media, advertisements use a number of mathematical models. The main thing that should be based on the distribution of funds for advertising means is the achievement of the goals set in the most efficient way.
4. Distribution of appropriations for the advertised goods
It is usually useful to concentrate promotional efforts on goods or price categories readily accepted by the consumer. When the public demonstrates its preference for a particular product, a good sense suggests that it is necessary to go to meet and satisfy everyone’s desire. And this is not necessarily the path of least resistance. Rather, it is a healthy commercial judgment to make, as is usually the case, the main focus on products that provide the bulk of sales.
In the advertising budget should list the goods to be advertised, and specify the amount of costs for each of them. This will give you the opportunity to control the behavior in advance of planned and carefully planned activities.
The advertising budget of the marketing department is the annual amount of investment in support of the company's goods, fixed by a document with a monthly breakdown of budget amounts for specific investment items. It is compiled once a year as part of annual strategic planning and is an integral part of the marketing plan.
The article describes the process of development and formation of the advertising budget of the company in great detail. In the article you will find not only information about what actions you need to start planning for advertising investments, but you will also see examples of the application of the best methods for calculating the size of marketing expenses of an enterprise.
After reading this material, you can definitely calculate the necessary marketing budget for promoting your goods or services from scratch, even if this is your first time doing it. Ready-made examples and a convenient template - a sample will help you with this.
Table of contents:
The calculation and distribution of the advertising budget must be fully justified, otherwise you will simply “waste” money and waste the limited resources of the company aimlessly. There are “3 golden rules of advertising investments” that will help you wisely approach the process of planning the marketing budget for an enterprise.

Before making a forecast of the advertising budget, it is necessary to evaluate the maximum investment opportunities of the company. For this:
Estimate the level of income in each month throughout the year. The assessment is similar to a “rough” sales forecast based on available statistics. In other words, based on the historical data on the company's sales, plan how much sales the company will bring in next year in terms of months, i.e. seasonally adjusted.
Important: do not exaggerate, try to evaluate the most reliable, but rather the minimum level of income. If the sales volume varies from 20,000 to 50,000 rubles, for budget planning it is better to take the minimum value - 20,000 rubles.
The next step is to determine the amount of company expenses in each month of the year. This may be: the cost of buying materials, paying employees, renting space, tax payments, etc.
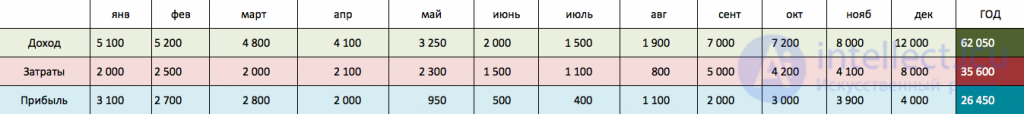
Table 1: Calculation of the possible size of advertising investments
The result of the first two actions is to obtain an indicative amount of the company's future profit, which can be invested in future growth.
Now identify all the priority areas of your business for the next year, in other words, key sources of growth and business opportunities . Marketing is only one of the directions for future investments. It may turn out that it is more important to upgrade the equipment at the moment, or to direct all resources to the development of new technologies, or to staff training.
When the boundaries of the marketing budget are defined, you can proceed to the next stage of planning: identify the products that need to be developed through advertising and marketing activities. Key principles that will help identify priority areas:
An example of an assessment of the directions of investing a marketing and advertising budget:
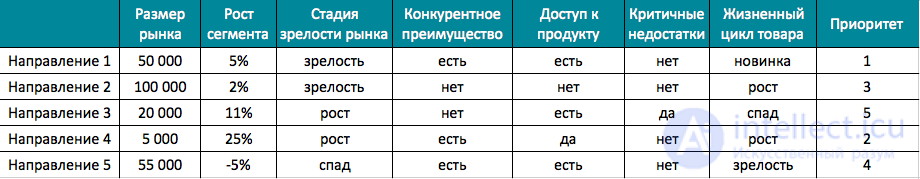
Table 2: Assessment of key areas of marketing support
Under the lines of business in this table are understood the company's products: specific product lines, key launches of new products, support for top-of-the-line locomotive products, strengthening the competitiveness of certain goods or services.
After you identify the key areas for investment, it is important to set the goals for supporting the selected business areas.
An example of setting goals, see the article: How to properly set and manage marketing goals in a company
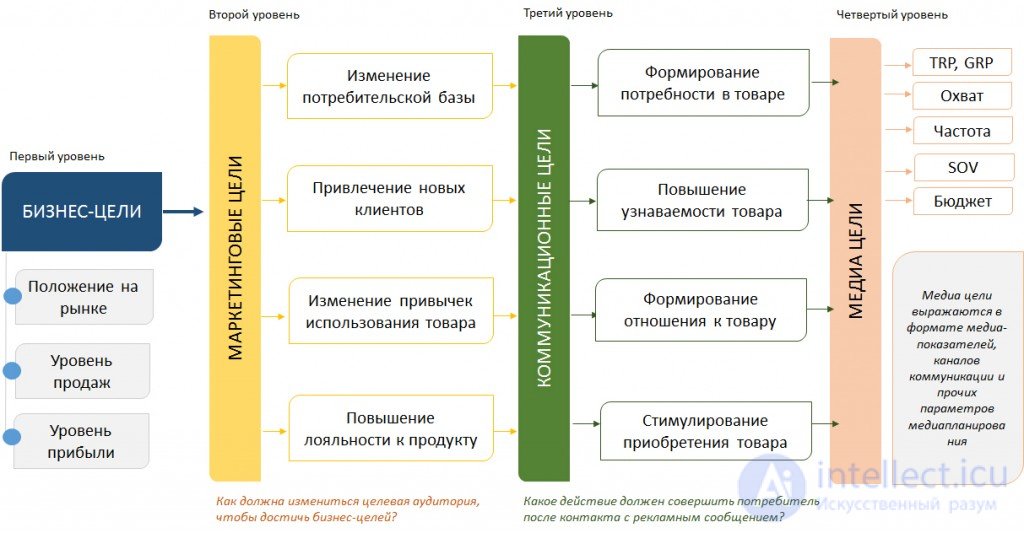
Before proceeding to the calculation of the advertising budget, let's clarify its structure. In practice, there are 5 main articles of marketing costs:
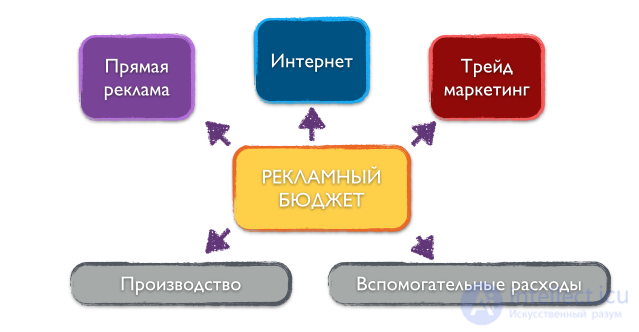
The article “Direct advertising”: this article includes the costs of paying for the actual placement of product advertising on TV, radio, in the press, in print or outdoor advertising.
Article “Production”: this article includes the costs of production and creation of promotional materials. For example, the production of a commercial, printing an advertising poster, designing a layout for advertising in a magazine, paying celebrity fees, etc. World practice: the article “production” should not exceed more than 10% of the total advertising budget.
The article "Supporting materials": this expense item includes the production of small supplies for marketing events: brochures, leaflets, catalogs for customers, catalogs for sales personnel, branded pens, envelopes.
The article "Internet": in connection with the growing importance of the Internet in the effectiveness of marketing communications, this item of expenditure is usually allocated separately. It includes: expenses for the creation and promotion of the site, content creation, promotion in social networks, payment for hosting and maintenance of the site, contextual advertising.
Article “Trade marketing": in this section of the budget marketing expenses for carrying out promotions aimed at the end consumer and on shares for resellers, as well as the production of POS materials and trade equipment, are prescribed.
An example of how an advertising budget in Excel might look like by main article:
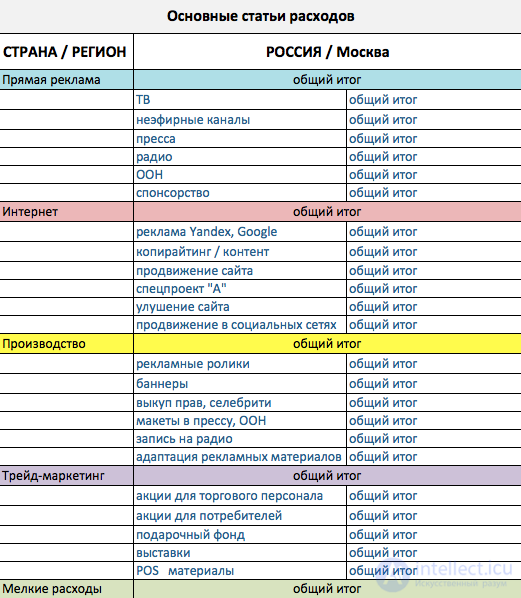
So, now we have all the information for the final preparation of our document. Namely:
Now is the time to calculate the company's total advertising budget for next year. The budget development process is as follows:
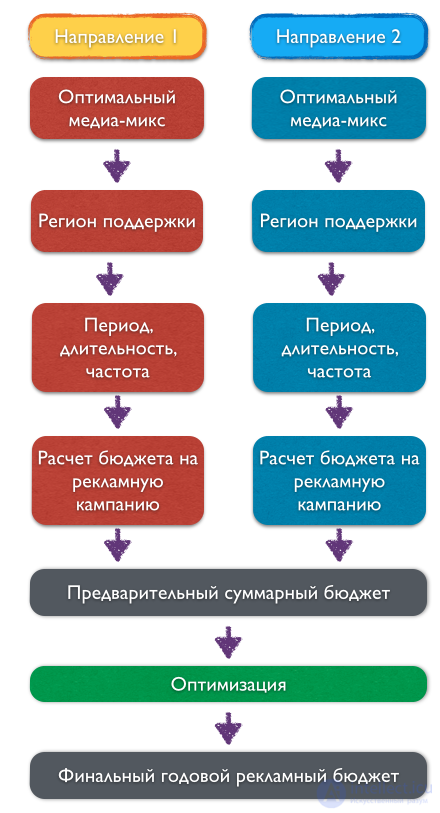
The costs of marketing programs are calculated for each direction separately, then combined into a single advertising budget and optimized taking into account the importance of the project. Knowing the goals that the company plans to achieve for each product, you can choose the most appropriate communication channels, or the so-called media mix.
For information on how to choose the right media mix for an advertising campaign for a product, see the article: Selecting a media mix for an advertising campaign .
After the necessary communication channels are determined, the territory of the advertising campaign is determined: a large-scale national campaign, support for individual regions or individual points of sale.
For information on how to choose the period of the advertising campaign that will bring maximum effect for the minimum investment, read the article: Choosing the location of the advertising campaign
The next step determines the strength of the advertising pressure, which is characterized by indicators: the period and duration of support, frequency of display and target coverage of the advertising message . Depending on the values of these indicators, the budget of each advertising campaign is calculated.
After combining the budgets of all advertising campaigns, we get a preliminary budget figure, which should be adjusted by the following principle:
The method of developing an advertising budget described above is called the "method of forming a marketing budget from the goal", is the most common and is used by all leading companies in the market. In practice, there are 4 more ways to determine the budget of the marketing department:
The essence of the method is as follows: the advertising budget of the company = a certain percentage of the company's turnover for a specified period. The budget can be calculated as% of annual sales, as% of sales for any reporting period (quarter, month), as% of sales of goods only during the period of the company. This percentage is called Advertising to Sales and is determined on the basis of the company's expert assessment.
In world practice, there are guidelines for this indicator in the main sectors:
The method is based on the use of accumulated experience to predict the effectiveness of future advertising campaigns. Knowing what effect a similar promotion had in the past, you can correctly make a sales forecast and calculate the marketing budget. It is one of the most risk-free methods, so based on the experience of the company.
In this approach, the most difficult is to correctly systematize the available information about the campaigns: the campaign period, the competitive environment during the campaign, the brand, the type of advertising message (educational campaign, information about the new product attribute, image formation, etc.), the complexity of the advertising message , novelty of the product, etc. The method is not suitable for completely new products and launches, it is also difficult to use it with a significant change in the competitive environment in the market.
This approach to calculating the advertising budget is based on a proven model of the dependence of the share of voice of the advertising campaign and the market share occupied by the product in the industry. This approach allows you to determine what advertising pressure you need to plan to achieve the target market share of the product.
Read more about the method in the article “Dependence of the voice share and market share” , and about the strategies for using the model in practice in the article “Brand strategies depending on the ratio of SOV and SOM”
The method is based on a competitive analysis of market share and advertising costs of key competitors:
Limitation of the method: lack of open information about the costs of competitors; when using parity with competitors, it is necessary to take successful competitors; It does not take into account the possibility of cost optimization (perhaps, when optimizing the costs, the goals set can be achieved with lower investments, improving the competitiveness of the company in the segment); does not take into account the difference in the quality of advertising messages.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management