Lecture
The conductive pattern is formed by: printed conductors, contact pads, interlayer connections, transition and mounting holes.
The minimum dimensions of the elements of the conductive pattern may be limited by design-technological or electrical factors. Technological variation in the reproduction of linear dimensions, the minimum width of the printed conductors b and the distances between the edges of adjacent elements s for various types of boards and methods for their manufacture are given in the relevant standards, for example, for software in GOST 23751—86.
In the case of large currents through the printed conductor, its cross section limits the condition
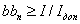 (15.1)
(15.1)
where b, h n is the width and thickness of the conductor, mm; I - current through the conductor, A; I additional - permissible current load, A / mm 2 .
The value of I SS , set by the permissible overheating of the printed conductor, depends on the technology of manufacturing the printed pattern and varies in the range of 50 ... 250 A / mm 2
If we denote the minimum width of the conductor, limited by the load capacity and found from (7.1), and b technology is the manufacturing technology, then the width of the conductor is b> max [b tech . b load ]
The smallest nominal distance l for laying n printed conductors of width b (Fig. 7.1) is calculated by the formula
 (15.2)
(15.2)
where s is the distance between the edges of neighboring elements, mm; D 1 , D 2 —diameters of contact areas, mm; T l is the standardized value of the positional tolerance of the location of the printed conductor relative to the adjacent element, mm.
The minimum dimensions of the elements of the multilayer pattern, in addition to the reproducibility of the linear dimensions of the elements in the layers, limit the possible displacements of the layers relative to each other. In this case, a guaranteed overlap of the layers in areas under the influence of displacements should be ensured.
The design of the contact pads determines the quality of the electrical connection and the mechanical strength of the coupling of the IET leads with the base of the board. Contact pads perform square, round or close to them. To install the IET with the pin terminals, mounting holes are provided in the contact pads (see. Fig. 7.1, a). The diameter of the mounting hole d m 0 choose a larger diameter pins do to get a gap? = 0.1 ... 0.6 mm, which provides capillary penetration of solder during soldering:
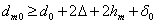 (15.3)
(15.3)
Where 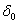 - error of hole diameter, mm; h m — average thickness of the metallization layer, mm.
- error of hole diameter, mm; h m — average thickness of the metallization layer, mm.
The minimum diameter of a round or smaller size of a rectangular contact pad is chosen from the condition of obtaining a guaranteed metal belt B min around the hole, which provides a quality connection with predetermined maximum dimensional deviations and positional tolerances for the pad and the hole.
The minimum dimensions of the contact pads when installing the IET on the surface is determined from the condition of guaranteed quality of connection, taking into account possible displacements. The vias should have a low resistance, and for obtaining a high density of the printed pattern, small sizes. However, with a small diameter of the holes and a large thickness of the boards it is difficult to ensure good quality of metallization, therefore the minimum diameter of the vias is chosen from the condition
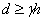 (15.4)
(15.4)
where h is the thickness of the board, mm; ? - the ratio of the nominal value of the diameter of the smallest of the metallized holes to the thickness of the board specified in the standards for the design of boards. Usually? = 0.2 ... 0.4. For multi-layer mounting, vias can connect both external and intermediate layers.
The spatial arrangement of printed conductors, contact pads and holes is tied to the coordinate grid applied to the circuit board drawings. In the overwhelming majority of cases, grids with a rectangular coordinate system are used, the pitch of which depends on the type of boards and the pitch of the pins installed by the IET. The centers of the contact pads and holes should be located in the nodes of the grid. If the lead pitch does not coincide with the grid spacing, then the following rule must be observed: the center of the pad or hole, into which the first lead is soldered, must coincide with the grid node, and the others must be on one of the horizontal or vertical coordinate lines.
Comments
To leave a comment
Design and engineering of electronic equipment
Terms: Design and engineering of electronic equipment