Lecture
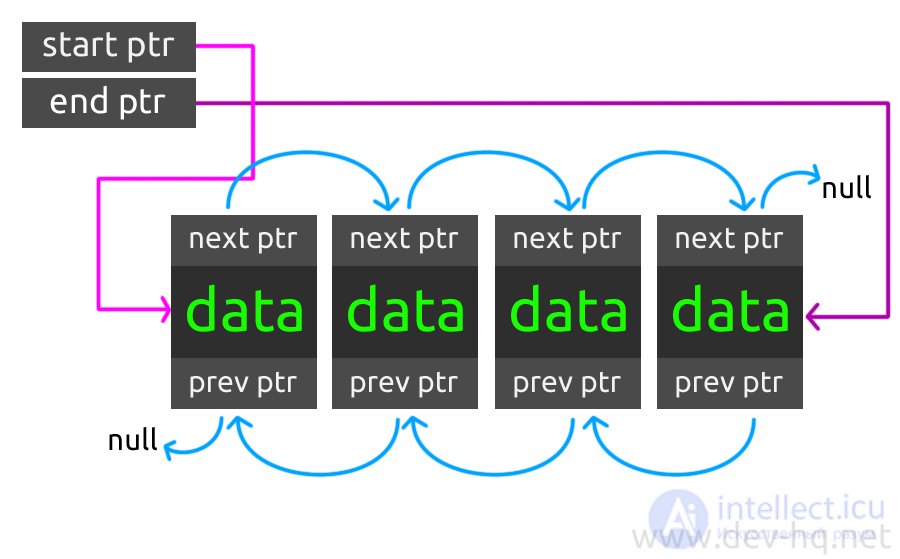
Unlike single-linked linear lists, doubly-connected, in addition to the data and next fields, have a prev field (a pointer to the previous list element):
type
Node <T> = class
data: T;
prev, next: Node <T>;
constructor (d: T; p, n: Node <T>);
begin
data: = d;
prev: = p;
next: = n;
end;
end; In the case of a doubly linked list, it is enough for us to have a link to any node, then all the rest can be found. However, for convenience, we will assume that we have two links:
Delete the first list item
+ ------- + + ------- + + ------- +
\ / \ / \ -> | data | | data | | data |
+ --- + --- + + --- + --- + + --- + --- +
| 0 | | ---> | | | ---> | | 0 |
+ --- + - A- + + - | - + - A- + + - | - + --- +
| ________ | | ________ |
turns into
+ ------- + + ------- + + ------- +
| deleted | \ / \ / \ -> | data | | data |
+ --- + --- + + --- + --- + + --- + --- +
| 0 | 0 | | 0 | | ---> | | 0 |
+ --- + --- + + --- + - A- + + - | - + --- +
| ________ |
Remove item from the middle of the list
+ ------- + + ------- + + ------- +
\ / \ / \ -> | data | | data | | data |
+ --- + --- + + --- + --- + + --- + --- +
| 0 | | ---> | | | ---> | | 0 |
+ --- + - A- + + - | - + - A- + + - | - + --- +
| ________ | | ________ |
turns into
___________________
| |
+ ------- + | + ------- + + --- V --- +
\ / \ / \ -> | data | | | deleted | | data |
+ --- + --- + | + --- + --- + + --- + --- +
| 0 | | - '| 0 | 0 | ---> | | 0 |
+ --- + - A- + + --- + --- + + - | - + --- +
| _____________________ |
Delete the first list item
+ ------- + + ------- + + ------- +
\ / \ / \ -> | data | | data | | data |
+ --- + --- + + --- + --- + + --- + --- +
| 0 | | ---> | | | ---> | | 0 |
+ --- + - A- + + - | - + - A- + + - | - + --- +
| ________ | | ________ |
turns into
+ ------- + + ------- + + ------- +
\ / \ / \ -> | data | | data | | deleted |
+ --- + --- + + --- + --- + + --- + --- +
| 0 | | ---> | | 0 | ---> | 0 | 0 |
+ --- + - A- + + - | - + --- + + --- + --- +
| ________ | |
Fig. 22.7. Removing a doubly linked list item
Comment. When performing any operation you need to monitor possible changes in the head and tail .
head: = nil; tail: = nil;
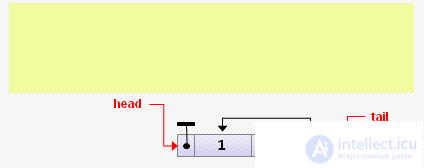
Note. If the list was initially empty, after adding an element, you need to remember to make tail pointing to it.
head: = new Node <T> (0, nil, head); if head.next <> nil then head.next.prev: = head else // if the list was empty tail: = head;
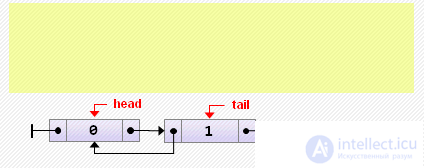
tail: = new Node <T> (2, tail, nil); if tail.prev <> nil then tail.prev.next: = tail else // if the list was empty head: = tail;
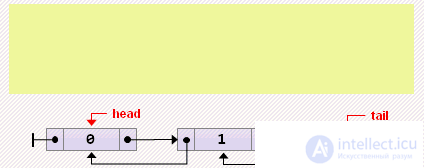
head: = head.next; if head = nil then tail: = nil else head.prev: = nil;
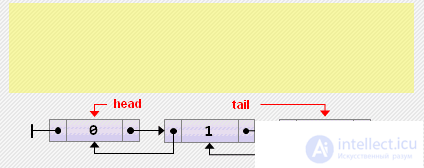
tail: = tail.prev; if tail = nil then head: = nil else tail.next: = nil;
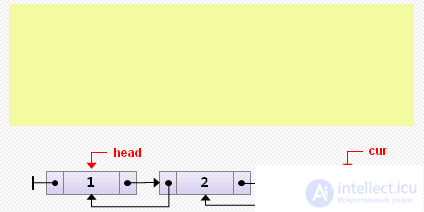
if cur = head then // insert to the beginning else begin cur.prev: = new Node <T> (3, cur.prev, cur); cur.prev.prev.next: = cur.prev; end;
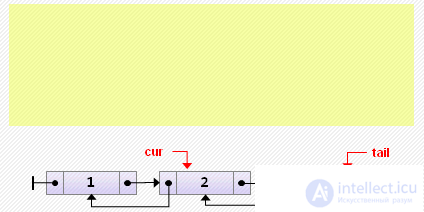
if cur = tail then // insert at the end else begin cur.next: = new Node <T> (3, cur, cur.next); cur.next.next.prev: = cur.next; end;
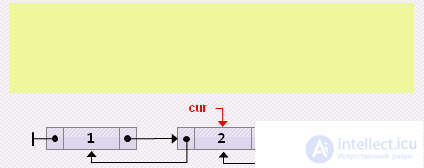
if cur = head then // remove from start else if cur = tail then // delete from end else begin cur.prev.next: = cur.next; cur.next.prev: = cur.prev; cur: = cur.next; end;
An example .
Given a doubly connected linear list with integer values.
Remove all its negative elements.
var list: DoublyLinkedList <integer>;
// create a list
var cur: = list.head;
while cur <> nil do
if cur.data <0 then
cur: = list.RemoveAt (cur)
else
cur: = cur.next;
type
Node <T> = class
data: T;
prev, next: Node <T>;
constructor (d: T; p, n: Node <T>);
begin
data: = d;
prev: = p;
next: = n;
end;
end;
DoubleLinkedList <T> = class
head, tail: Node <T>;
constructor;
begin
head: = nil;
tail: = nil;
end;
procedure AddFirst (d: T);
begin
head: = new Node <T> (d, nil, head);
if head.next <> nil then
head.next.prev: = head
else // if the list was empty
tail: = head;
end;
procedure AddLast (d: T);
begin
tail: = new Node <T> (d, tail, nil);
if tail.prev <> nil then
tail.prev.next: = tail
else // if the list was empty
head: = tail;
end;
procedure DeleteFirst;
begin
head: = head.next;
if head = nil then
tail: = nil
else
head.prev: = nil;
end;
procedure DeleteLast;
begin
tail: = tail.prev;
if tail = nil then
head: = nil
else
tail.next: = nil;
end;
procedure InsertBefore (cur: Node <T>; d: T);
begin
if cur = head then
AddFirst (d)
else
begin
cur.prev: = new Node <T> (d, cur.prev, cur);
cur.prev.prev.next: = cur.prev;
end;
end;
procedure InsertAfter (cur: Node <T>; d: T);
begin
if cur = tail then
AddLast (d)
else
begin
cur.next: = new Node <T> (d, cur, cur.next);
cur.next.next.prev: = cur.next;
end;
end;
function RemoveAt (cur: Node <T>): Node <T>;
begin
if cur = head then
begin
DeleteFirst;
Result: = head;
end
else if cur = tail then
begin
DeleteLast;
Result: = nil;
end
else if cur = tail then
begin
DeleteLast;
result: = nil;
end
else
begin
cur.prev.next: = cur.next;
cur.next.prev: = cur.prev;
result: = cur.next;
end;
end;
procedure Print;
begin
var cur: = head;
while cur <> nil do
begin
writeln (cur.data);
cur: = cur.next;
end;
end;
procedure PrintReverse;
begin
var cur: = tail;
while cur <> nil do
begin
writeln (cur.data);
cur: = cur.prev;
end;
end;
end; the number of operation (n - the number of elements)
| Array | List | |
|---|---|---|
| Insert at end, delete from end | 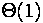 | 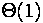 |
| Insert at the beginning, delete from the beginning | 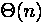 | 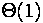 |
| Insert in the middle, removal from the middle | 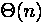 | 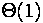 |
| Pass | 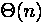 | 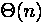 |
| Access by index | 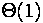 | 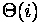 |
| Search | 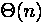 | 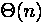 |
Comments
To leave a comment
Structures and data processing algorithms.
Terms: Structures and data processing algorithms.