Lecture
A battery (fr. Batterie ) is a group of electric bipolar networks connected in parallel or in series. Usually, this term refers to the connection of electrochemical sources of electric current (galvanic cells, battery cells, fuel cells).
In electrical engineering, electrical energy sources (galvanic cells, batteries), thermocouples or photo cells are connected to a battery to get the voltage removed from the battery (with series connection), amperage or capacity (with parallel connection) formed by a source greater than one cell can produce.
The battery is constructively performed, as a rule, in a single case in which there are several electrically connected battery cells. Outside the case, usually 2 pins are removed for connection to the charger and / or the consumer circuit. A battery can also have auxiliary devices that ensure the efficiency and safety of its operation: thermal sensors, electronic devices protecting both the battery cells that make up the battery and the battery as a whole (for example, a lithium-ion battery). Battery and battery cells used as a source of direct current.
Most often, the electrochemical cells in the battery are connected in series. The voltage of an individual element is determined by the material of its electrodes and the composition of the electrolyte and cannot be changed. A series connection of several elements increases the output voltage of the battery, and the total battery voltage in a series connection is equal to the sum of the voltages of all the elements. The maximum output current of a sequential battery does not exceed the current of the lowest-current cell. The lack of a serial connection is the unevenness of the discharge and charging with non-uniform elements included in the battery, with an elementary inclusion in the charge / discharge circuit, the more capacious elements are under-discharged, and the less capacious ones are discharged. For some types of battery cells, such as lithium cells, overdischarge leads to their failure. Therefore, lithium cell batteries are usually equipped with built-in or external electronic control circuit optimization of the discharge. Similar problems arise when charging the battery of battery cells. Since, in series connection, the electric charge that has flowed through each element is equal, this leads to recharge of less capacious elements and undercharging of more capacious ones. The capacity of even the same type of elements varies slightly due to the inevitable technological variation and may become significantly different after multiple charge / discharge cycles. Therefore, modern battery batteries are usually equipped with electronic charge optimization schemes.
An example of a rechargeable battery with a battery cell in series is any car battery containing 6 or 12 cells.
The parallel connection of electrochemical cells into a battery increases the total capacity of the battery, increases the limiting output current and reduces its internal resistance. Parallel connection has several disadvantages. With the inequality of the emf parallel to the connected elements between the elements begin to flow equalizing currents, while elements with a higher emf give a current to elements with a lower emf. In batteries, this overflow of currents is not very significant, since cells with a higher EMF, while discharging, recharge cells with a lower EMF. In non-accumulator batteries, the flow of surge currents leads to a decrease in battery capacity. In addition, when the elements are connected in parallel, the charging mode of the battery is complicated, as it usually requires separate charging of each element and switching elements while charging, which complicates the internal or external electronic control circuit of charging. Therefore, the parallel connection of the battery cells is rarely used, preferably used elements of greater capacity.
The progenitor of a battery of series-connected electrochemical cells can be considered a volt pillar, invented by Alessandro Volta in 1800, consisting of series-connected copper-zinc galvanic cells.
A battery in everyday life is often not quite correctly called single galvanic cells, such as AA, which are usually connected to a battery in the power sources of the devices to obtain the required voltage. The use of the term “battery” in the technical literature is not recommended.
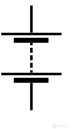
A battery is a circuit that contains only passive electrical elements: resistors (to increase power dissipation or change resistance), capacitors (to increase capacitance or increase operating voltage), to change capacitance. Such devices, equipped with switching elements - switches, sockets, etc., are often called shops (resistance store, capacity store).

Basically, batteries imply a chemical current source, but there are cells and batteries on different physical principles. For example, nuclear batteries on beta decay (the so-called beta-voltaic batteries
International Universal Codes for Recycling Batteries and Batteries
|
|
The most common sizes of batteries [3] :
| Type of | IEC JIS Nomenclature | Soviet | The form | Sizes, mm | Voltage, V | Everyday life. title |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAA | R03 | 286 | Cylinder | 44.5 × 10.5 | 1.2—1.6 | "Mizinchikovaya", "Mikropalchikovaya" |
| AA | R6 | 316 | Cylinder | 50.5 × 14.5 | 1.2—1.6 | "Finger" |
| WITH | R14 | 343 | Cylinder | 50.0 × 26.2 | 1.2—1.6 | "Average" |
| D | R20 | 373 | Cylinder | 61.5 × 34.2 | 1.2—1.6 | "Big" |
| - | 6F22 | Crown | Parallelepiped | 48.5 × 26.5 × 17.5 | 9 | "crown" |
| - | 3R12 | 3336 | Parallelepiped | 67 × 62 × 22 | 4.5 | "Flat" |
| Type of | Merits | disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Dry ("Salt", coal-zinc) |
The cheapest, massively produced. | The smallest capacity; discharge curve; bad in working with powerful loads (high current); bad at low temperatures. |
| Heavy duty ("Powerful" dry cell zinc chloride) |
Less expensive than alkaline. Better at high current and low temperatures. | Low capacity. The falling curve of the discharge. |
| Alkaline ("Alkaline", alkaline-manganese) |
Average cost. Better than previous with high current and low temperatures. When discharged, it maintains a low impedance value. Widely available. | The falling curve of the discharge. |
| Mercury | Constancy of voltage, high energy intensity and energy density. | High price. Due to the harmfulness of mercury, almost no longer produced. |
| Silver | High capacity. Sloping discharge curve. Good at high and low temperatures. Excellent storage time. | Dear. |
| Lithium | The highest capacity per unit mass. Sloping discharge curve. Excellent at low and high temperatures. Extremely long storage time. High voltage per element (3.5-4.2V). Light. | Dear. |
| Type of | Description | Merits | disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Electroplating. Reactions occurring in them are irreversible, so they can not be recharged. Usually they are called the word "battery". Attempting to charge the primary battery can result in damage and leakage of alkali or other substances in it. | Higher capacity and / or cheaper. Less self-discharge. | Single use. |
| Secondary | Batteries. In contrast to the primary, the reactions in them are reversible, so they are able to convert electrical energy into chemical energy, accumulating it ( charge ), and perform the reverse transformation, giving electrical energy to the consumer ( discharge ). For common batteries, the number of charge-discharge cycles is usually around 1000, and depends significantly on the operating conditions. | Reusable, rechargeable. | Lower capacity and / or more expensive. Stronger self-discharge. |
The most common among household batteries are salt, alkaline (alkaline) and lithium. Salt differ low cost, but low capacity and load capacity. Alkaline batteries are more capacious and powerful, but their cost is much higher. Lithium cells also have a high specific capacity and relatively high cost.
Air-zinc elements have a high capacity with low load capacity. They are most often used in devices with low consumption and long working hours, for example, in hearing aids.
Comments
To leave a comment
Power supplies for electronic equipment
Terms: Power supplies for electronic equipment