Lecture
Color models.
For color image processing there are various color models consider them .
To simulate color in image processing, palettes are used. way to describe the color.
For emitted light (monitor screen), an RGB palette is used.
For reflected light (printing on paper), a CMYK palette is used.
The intensity of each ink is set in absolute value (0..255), in% (0..100).
RGB ( red - red, green - green, blue - blue )
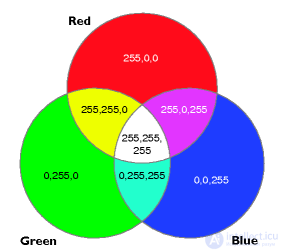
Figure 7 - RGB color model
CMYK ( cyan - cyan, pink or magenta - magenta, yellow - yellow, black - black )
For each base component is given in% integer 0..100
Color = С + M + Y - additional colors complement the primary colors to white: cyan complements red, magenta - green, yellow - blue.
This palette is based on the perception of the reflected color.
Colors in a palette are formed by subtracting certain colors from white:
White = (C = 0, M = 0, Y = 0);
Cyan = WR = G + B;
Yellow = WB = R + G;
Magenta = WG = R + B.
Figure 8 - CMYK color model and RGB
HSB ( hue - hue, saturation - saturation, value - value )
H (hue) - determines the color in the spectrum and is set as an integer from 0 to 360; 0 is red, 360 is purple.
S (saturation) - characterizes the proportion of white added to the selected hue. Set in% (from 0 to 100). With minimal saturation, any color shade becomes gray.
B (brightness) - is determined by the admixture of black color to the selected shade and is set in% (from 0 to 100). At minimum brightness, the image becomes black.
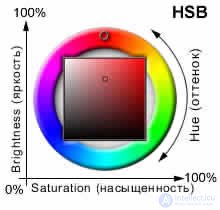
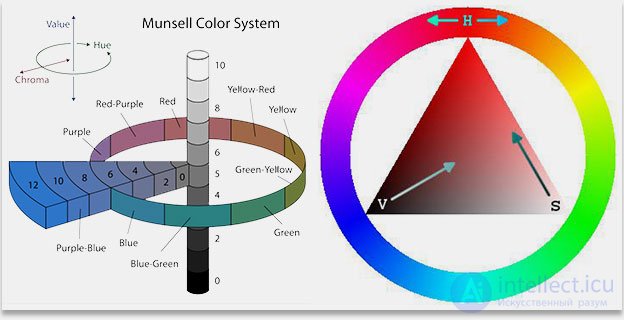
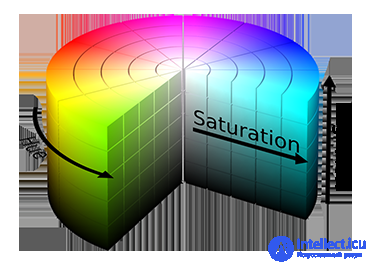
Figure 9 - HSB color model

Alvy Ray Smith (Alvy Ray Smith) - known pioneer in the field of computer graphics. In 1974, at the headquarters of Xerox PARC, he developed SuperPaint, one of the very first computer programs for drawing. Smith's main contribution to this program was the creation of the HSV color space, also known as HSB. He also created his first computer animations in the SuperPaint system.
On February 3, 1986, he founded Pixar with Ed Catmull. At the time of Pixar financing, Steve Jobs, Elvi Smith was executive vice president. In 1991, Smith left Pixar to establish the Altamira Software Corporation together with Eric Lyons and Nicholas Clay. In 1994, the company was acquired by Microsoft, where Elvi became the first schedule. He left Microsoft in 1999 and is currently lecturing and exploring the history of digital technology.
The HSB color model can be visually depicted in a three-dimensional graph in the form of a cake. On the upper edge of Hue, the colors are arranged in a circle, like on a dial. That is, points 0 and 360 denote the same color. Saturation adjusts the color saturation from 0 (black and white gamma) to 100 (maximum saturation). Brightness changes the brightness from 0 (black) to 100 (no black at all).
After reviewing all available in Adobe Photoshop color systems, users usually stop the choice on HSB. This model is most convenient to use when it comes to creative work with color. The human being is intuitively understood with the functions of the Hue scales (tone or wavelength of light), Saturation (saturation or intensity of the wave) and Brightness (brightness or amount of light), which allows to obtain predictable results.


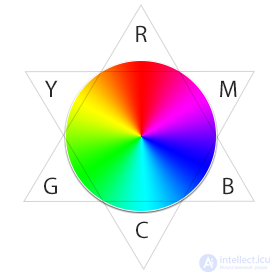
In the figure above, you can see that the HSB color wheel consists of the RGB and CMY sets already known to us, which are arranged in such a way that each color is opposite to the complementary (complementary) color, and is itself between two, from which it was obtained by the additive principle.
The additive principle of color mixing occurs with a combination of color radiation, as previously mentioned in the article about RGB. In this case, the colors change in the direction of clarification, in contrast to the subtractive principle, as on paper. For example, when applying red and green, it turns yellow.
Another feature of HSB is hardware independence. When entering information on the device, the maximum values of red, green and blue are measured, which are then converted to HSB. When displayed, this color model is converted to RGB. It does not have its own color channels, therefore its coordinates are an abstract concept.
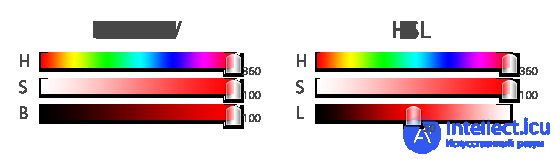
The HSB Brightness Scale changes the brightness from black to brightest. The Lightness scale of the HSL model allows you to change the brightness (or lightness) of the color from black to white, without touching the Saturation scale. The point of greatest color saturation is in the middle of the scale. That's all the difference. A particular type is found in different editors, because the coordinates of the same color may differ slightly.
Developed in the 70s for the pioneers of digital painting, the HSB model caught on well. Unlike RGB and CMYK, in it the color tone is separated from saturation and brightness. Thus, it allows you to select colors intuitively, as when drawing paints in real life.
Basic color image processing.
1. changing the saturation pitch of the individual color channel



2. Conversion of color images to halftone

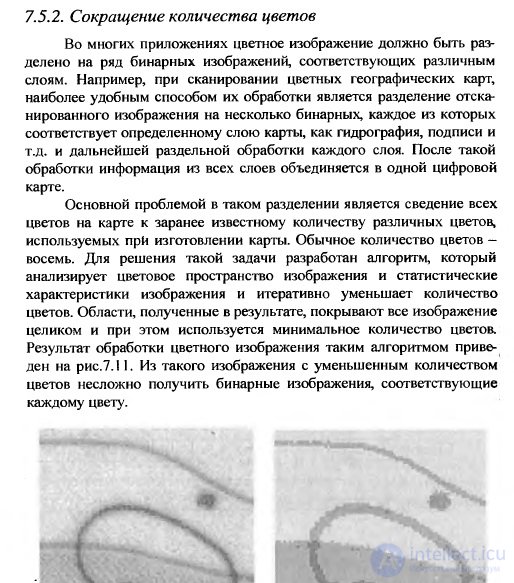
3. Shorter than colors
Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology