Lecture
Another sign of the classification of signals is based on the possibility or impossibility of predicting the exact values of the signal at any time or at any point in the spatial coordinate. Accordingly, the signals for which the specified prediction is possible are called deterministic , and the signals for which it is impossible to accurately predict values are random . Random signals are described by random functions, the values of which for each given argument value are represented by random variables. A random function of time is called a random process . With one observation of a random process, a certain functional dependence is obtained, which is called implementation . An example of the implementation of a random process can serve as a segment of the signal 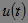 recorded at the microphone output when you make a hissing sound. An example of a deterministic signal is harmonic oscillation.
recorded at the microphone output when you make a hissing sound. An example of a deterministic signal is harmonic oscillation. 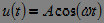 .
.
If a random signal is probabilistic in nature, then its statistical characteristics are known, which are described by the theory of probability.
Probability that the magnitude 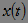 falls into the specified interval, is determined by the expression:
falls into the specified interval, is determined by the expression: 
Where  - boundaries of possible values;
- boundaries of possible values;
 - is a differential law of random variable distribution and is called one-dimensional probability density;
- is a differential law of random variable distribution and is called one-dimensional probability density;
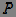 - integral distribution function of a random variable.
- integral distribution function of a random variable.
For practical applications, the following statistical characteristics of a random variable are important:
1) The expectation of a random variable:
, (2)
if events are equally probable, then 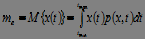
2) Variance of the random variable (deviation from the mean): 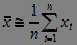
, (3)
if events are equally probable: 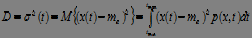
.
3) Standard Deviation (MSD): 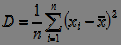
. 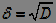 (four)
(four)
A stationary process is a process if its -dimensional distribution law depends on a time interval. 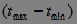 but does not depend on the position on the number axis. For strictly stationary processes, the expectation and variance do not depend on time.
but does not depend on the position on the number axis. For strictly stationary processes, the expectation and variance do not depend on time.
When considering random variables, time and population are taken into account, i.e. sampling. A random process is called ergodic if, in determining any statistical characteristics, averaging over the population and over the sample is equal to time averaging.
A stationary random process with a constant spectral density is called white noise . It is characterized by the fact that its two values are not correlated. White noise with an unlimited frequency spectrum is called mathematical white noise. White noise with a limited frequency spectrum is called physical white noise.
Correlation - the magnitude of the similarity of the two signals. If two different signals are compared, then the cross-correlation function is a measure of their similarity. If the signal is compared to itself, then the degree of similarity is determined by the autocorrelation function.
The main characteristics of deterministic signals are its energy characteristics.
Energy characteristics of signals:
1. Instant (current) power:  . (five)
. (five)
2. Energy: 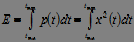 . (6)
. (6)
3. Average power on the interval: 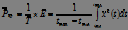
. (7)
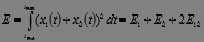
 ,
,
, 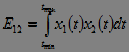
. (eight)
The mutual energy and power of two signals characterize the degree of similarity of two signals .
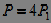 .
.
6. If the signals are opposite, then they are called orthogonal . Energy orthogonality always implies orthogonality in power, but not vice versa:
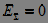 .
.
7. If the signals do not completely coincide, they are called partially coincident signals.
Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology