Lecture
When solving many problems of speech processing, the temporal characteristics of speech signals are of interest. Since speech is a non-stationary process, it is customary to analyze it in short sections ( 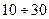 ms), where the spectral-correlation characteristics remain approximately constant.
ms), where the spectral-correlation characteristics remain approximately constant.
One of the important parameters of a speech signal is its energy :
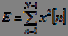 . (one)
. (one)
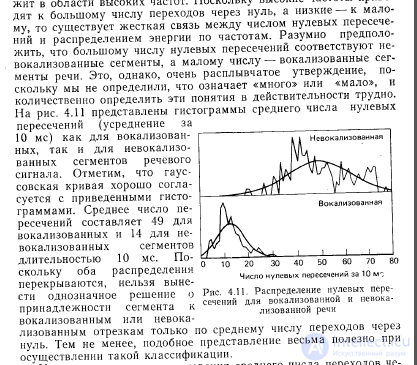
Another way to detect voiced and unvoiced areas of speech is based on measuring the average number of zero crossings of the speech signal. This measurement is a rough estimate of the frequency composition of the speech signal. It is known that the energy of vocalized sounds is concentrated in the range below kHz, while the energy of fricative sounds is concentrated mainly at frequencies above kHz. Therefore, if the average number of zero transitions is large, this indicates an unvoiced character of speech, and vice versa.
An important task of analyzing speech signals in the time domain is estimating the pitch period. The period of the fundamental tone can be defined as the time interval between the corresponding peaks of the voiced portion of the speech signal. However, the main difficulty here is that even at short time intervals the speech signal does not have a strict periodic structure.
Another way to determine the period of the fundamental tone in the time domain is based on the calculation of the short-term autocorrelation function :
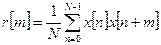 ,
, 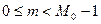 , (2)
, (2)
where is the maximum signal delay.
In identifying the period of the fundamental tone P by the autocorrelation function, it is necessary to take into account 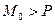 . For voiced speech plots
. For voiced speech plots  traced peaks with an interval equal to the period of the fundamental tone.
traced peaks with an interval equal to the period of the fundamental tone.
In order to sharpen peaks in the graph  signal
signal  clipping. The essence of this non-linear operation is shown in fig. 1, a. In fig. Figure 1b shows the autocorrelation function of the clipped signal.
clipping. The essence of this non-linear operation is shown in fig. 1, a. In fig. Figure 1b shows the autocorrelation function of the clipped signal.
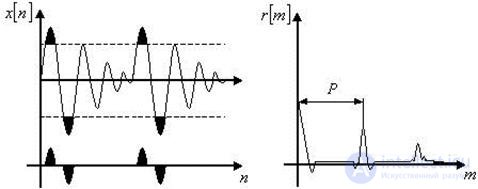
a) b)
Fig. 1. Clipping operation.
The disadvantage of the considered method for determining the period of the fundamental tone is that a large number of arithmetic operations are required to calculate the autocorrelation function.
function of the average number of zero crossings for speech processing
 uh
uh

Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology