Lecture
Content
The project form of business activity is gradually gaining momentum. Firms of a purely project orientation are opening up, the structure of operating companies is becoming more complicated. Business development in our reality is based on modern templates, standards of organization and management. Who is this man who stands at the forefront of events transforming the world? Who leads the temporary teams to overcome the routine and build a new one? This is a project manager with special character traits, possessing special skills and capable of taking on unique tasks.
A project manager (project manager, project manager, PM) is a person with the responsibility and rights to lead work in a project task. The delegation of PM to the appropriate authority is made by the investor or customer on the basis of a contract, the essential terms of which and the KPI are agreed upon at the stage of the development of the project charter. The manager makes efforts to create favorable conditions for the fulfillment of project tasks within the agreed time and without exceeding the budget. To make the project successful, the project manager provides:
In essence, the above list is the main functions of the RM. Formally, the duties of a manager begin with the issuance of an order to open a project. In fact, his work begins long before the release of the document. The actions of the RM are connected, first of all, with the curator, who involves the future project manager in the process of initiating and launching the project. The curator is always interested with the least effort to get the best result. Therefore, he needs a reasonable and productive project manager.
The Republic of Moldova, in turn, is interested in a curator distinct and trusting him. For him, the curator is an understandable, unified channel for the escalation of problems that arise. An experienced manager knows in advance that problems and difficulties in the project cannot be avoided. And in order to promptly eliminate difficulties when they arise, PM wants not to beat the thresholds in “cabinets”, but to address only one manager.
The curator as a representative of the top management should be open to contact with the project manager. He understands why the project manager came to him, finds time to sit with him, discuss, prompt and help somewhere. This is a little, but very important, including psychologically. It is necessary to understand that both links: both the curator (sometimes the director of development) and PM constitute the management of projects in the enterprise. In large and medium-sized companies, it also includes the project office manager.
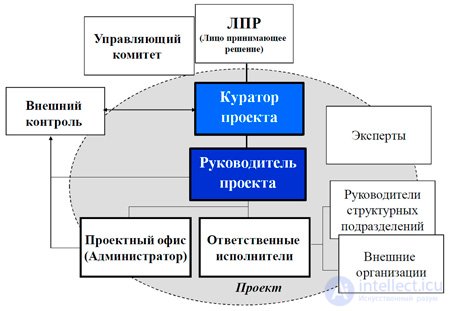
A project manager is not so much a position as a role that an employee or an external person takes on, designed to realize a unique task. It should be borne in mind that the functional worker assigned to a specific department, service, often acts as a project manager and not even one. It is quite natural in modern business. The needs of development management lead to the fact that the project architecture is allocated in the structures of companies into a separate organizational superstructure.
If this happens, then the need for professional PM also increases. Accordingly, there are allocated staff units with all the ensuing consequences: professional profile, job description, wage system, etc. For a specific project, the assigned powers and responsibilities are described in the statute. Expanded requirements for rights, duties, skills and abilities, education and other parameters are recorded in a special document, which is the job description PM, an example of which is presented below.

Job description, the main part of which is located in this article, also prescribes the requirements for the social and professional profile of the project manager. As a rule, this is a specialist with a higher economic or technical (by project profile) education at the age of thirty to forty years. He must have management experience in operational or general management (at least 3 years). The official role of PM sets the conditions for the personal qualities of the leader: stress resistance, dedication, enterprise, sociability and pragmatism. To fully perform the duties, the project manager must be able to do the following.
Official functions and the duties arising from them are the common basis for setting PM on the project result. A much better guideline is to motivate the manager for the goal, product, and project objectives. Based on the criteria for success of a unique (project) task, key performance indicators (KPI or KPI) are formed. Below is the traditional list of KPIs in order of decreasing their applicability:
Examples of the last KPI can be indicators taken directly from the quantitative parameters of not only the top-level tasks, but also of the decomposed subtasks. For example, reducing waiting time, reducing the number of complaints, reducing churn, attracting new customers, etc. Here, almost all BSC (Balanced Scorecard) tools can be applied quite favorably.
In this article, we examined the central figure of the project management - the project manager. The variety of areas of project activity, the type of organization of the company dictate completely different approaches to such management elements as functions, duties, professional profile of PM. First of all, all this is necessary for the project supervisor and staff member. The project manager is also important. And even more important for him is what resources are assigned to him, given powers and indicators. Such is the full range of organizational and motivational means as applied to the key to success in a project.
Comments
To leave a comment
software project management
Terms: software project management