Lecture
Classification of methods for calculating reliability
The main purpose of reliability calculations should be considered
- a comparative analysis of various structural (circuit) variants of the product at the stage of its design for a reasonable choice of components, a general structural diagram, backup methods, control and maintenance methods;
- an approximate, predicted assessment of the reliability of the product at the stage of approval of the technical design to substantiate the conclusion that the designed product can be manufactured to meet the requirements for reliability;
- an approximate, predicted reliability assessment of a complex product at the stage of testing a prototype to justify the distribution of requirements for the reliability of parts of the product and a reasonable, albeit indicative, determination of the composition and quantity of spare parts and the terms of service.
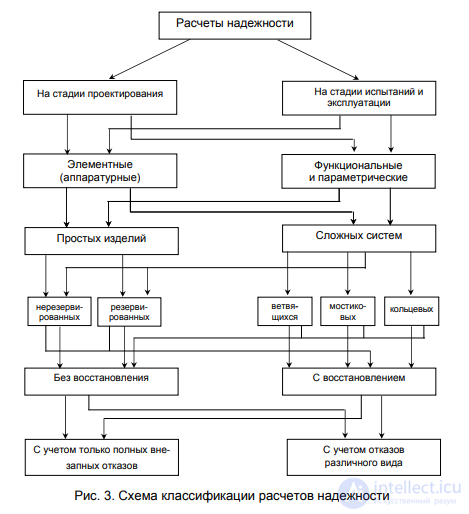
In relation to the stages of the life cycle of systems, there are distinctions between calculations at the design stage (predictive calculations) and at the stage of operation and testing (mainly stating calculations). The first includes calculations based on an analysis of the structure of the system and specified working conditions. They are usually called analytical or reliability calculations. To the second - the calculations associated with the processing of the results of an experiment or operation. They are called - settlement experimental or processing of experimental, statistical data. According to the fundamentals, the calculations are divided into elemental (system) and functional (a particular case of which are parametric calculations).
According to the nature of the failures taken into account, the calculations are distinguished taking into account one type of failure (sudden, complete) and taking into account the characteristics of the failures (sudden, gradual, complete, partial, such as a circuit, open, failures, etc.).
By type of systems - calculations of simple systems and complex systems. The calculations of simple systems, in turn, are divided into the calculations of redundant and non-redundant systems, systems without recovery and with recovery. Calculations of complex systems are divided into calculations of the reliability of control loops and state calculations of systems.
From the above classification (Fig. 3) it can be seen that various methods for calculating reliability have been developed.
Their development follows the path of developing ever new calculation models. Real systems correspond to a calculation model with a certain similarity coefficient.
Of the reliability calculations given in the classification, the simplest and most developed are the elemental, systemic calculations, taking into account one type of failure (sudden, complete). The most time-consuming include functional calculation, taking into account the nature of failures (especially failures), as well as the calculation of the reliability of complex and large control systems.
Calculation Methods
The following basic methods are used to calculate reliability:
- method of structural schemes;
- method of logic circuits;
- circuit-functional method;
- matrix method;
- graph method.
Let's consider some of them.
The method of structural schemes.
This method is used for simple systems under the following conditions:
- elements of systems are considered as single-fault;
- the system is presented in the form of a single structural diagram, consisting of the sum of serial and parallel connections of elements, subsystems;
- in the structural diagram the same event should be presented in the form of one element, subsystem, that is, the ordinary should be observed.
The methodology for constructing a structural diagram includes the following main steps:
- drawing up, based on the study of the design of the functional system, the concept of the system;
- drawing up a text formulation of the system’s dependability conditions;
- drawing up a structural diagram, on which the element failure-free operation event is indicated by a rectangle, and the connecting line denotes the connection — the sequence of implementation of the failure-free operation of the system as a whole (serial or parallel connection);
- an equation is compiled to assess the probability of a fail-safe operation of the system.
The formula for calculating the probability of failure-free operation of the system Pc (t), consisting of n series-connected elements has the form:
where Pi (t) is the probability of uptime of the ith element.
With a parallel connection of two elements, the probability of failure-free operation of the system has the form:
Pc (t) = 1 - Qc (t) = 1 - [1 - P1 (t)] · [1 - P2 (t)] = 1 - [1 - P1 (t) - P2 (t) + P1 (t ) · P2 (t)] = P1 (t) + P2 (t) - P1 (t) · P2 (t).
The method of logic circuits.
This method is applied:
- for systems when it is difficult to ensure conditions for the independence of events and the ordinary types of failures, that is, for complex functional systems;
- systems with redundancy with fractional multiplicity;
- systems with different types of failures for the same elements;
- systems that perform several functions.
Thus, the essence of the method consists in constructing the equations of a complete group of events characterizing the state of system operability.
The procedure for determining the probability of uptime with the logical circuit method is as follows:
- the conditions for the failure-free operation of the system as a whole are formulated, depending on the combination of the possibility of occurrence of failures, its separate
Comments
To leave a comment
Theory of Reliability
Terms: Theory of Reliability