The task is set as follows: from all possible sets 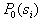 under conditions under conditions 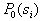 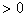 and and 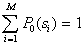 it is necessary to choose such (and further use it with recognition), when the maximum component of the vector it is necessary to choose such (and further use it with recognition), when the maximum component of the vector  is minimal. is minimal. Algorithmically, one of the simplest is the Monte Carlo method. Randomly 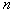 times vectors are selected times vectors are selected 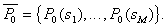 The vector at which the maximum component The vector at which the maximum component 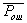 takes the smallest value accepted for use. The more takes the smallest value accepted for use. The more 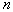 , the higher the probability of "hitting" the nearest neighborhood of the optimal vector , the higher the probability of "hitting" the nearest neighborhood of the optimal vector  . Of course, complete enumeration of options is possible, but it is acceptable only if there is not a very large number of possible . Of course, complete enumeration of options is possible, but it is acceptable only if there is not a very large number of possible  . In some particular tasks, an analytical approach to searching can be implemented. . In some particular tasks, an analytical approach to searching can be implemented.  . Consider the case with two images. . Consider the case with two images.  (Fig. 21). (Fig. 21). 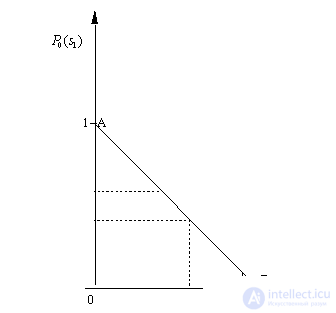
Fig. 21. Scope of the problem of definition 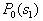
by minimax criterion The solution of the minimax problem lies on the line segment 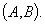 Denote by Denote by 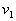 the object area of the first image, and through the object area of the first image, and through 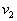 - the second. It's clear that - the second. It's clear that 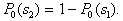 The average probability of recognition errors is determined by The average probability of recognition errors is determined by 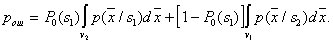 Build a graph Build a graph 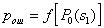 (Fig. 22). (Fig. 22). It's obvious that 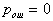 at at 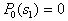 and and 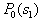 = 1. Between them are values = 1. Between them are values  at which at which 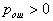 including its maximum value. Let's say we chose including its maximum value. Let's say we chose 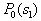 = = 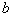 . Then . Then 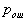 as a function of true (but unknown) value as a function of true (but unknown) value 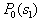 lies on a straight line tangent to lies on a straight line tangent to 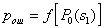 at the point corresponding to at the point corresponding to 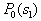 = = 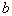 . Moreover, if the true value . Moreover, if the true value 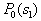 lies to the left of the point lies to the left of the point 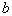 (eg, (eg, 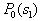 = = 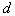 ), then the actual average recognition error ( ), then the actual average recognition error ( 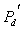 ) will be less than predicted at ) will be less than predicted at 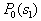 = = 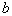 . But if the true value . But if the true value 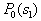 = =  , the actual average error ( , the actual average error ( 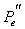 ) will be significantly more predictable. Similar reasoning can be given for the right slope of the curve ) will be significantly more predictable. Similar reasoning can be given for the right slope of the curve 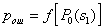 by putting for example by putting for example 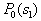 = = 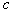 . Only by choosing . Only by choosing 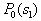 = =  that corresponds to the maximum curve that corresponds to the maximum curve 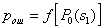 we guarantee that we guarantee that 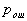 will not exceed will not exceed 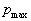 whatever the true meaning whatever the true meaning 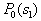 . . 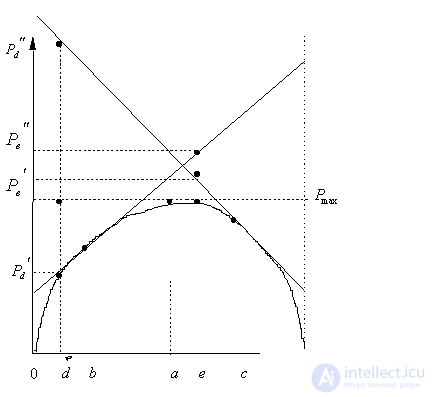
Fig. 22. Dependence of the probability of recognition error
from 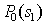 Consider the analytical formulation of the problem of finding a minimax solution (it should be borne in mind that 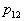 and and  depends on depends on 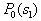 since they are functions from since they are functions from 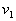 and and 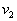 , and the latter depend on the prior probabilities of the images). , and the latter depend on the prior probabilities of the images). Denote 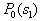 through through 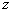 . Need to find such a value . Need to find such a value 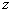 in which in which 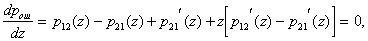
Where 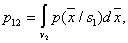 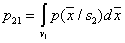 . . From this equation it is clear that to find its analytical solution is very difficult. First, you need to write explicitly the dependency.  and and 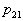 from from 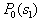 and secondly, the equation and secondly, the equation 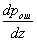 must have an analytical solution. In the simplest cases, this is possible, but the simplest cases, unfortunately, are extremely rare in practice. must have an analytical solution. In the simplest cases, this is possible, but the simplest cases, unfortunately, are extremely rare in practice. |
Comments
To leave a comment
Pattern recognition
Terms: Pattern recognition