Lecture
| Title | Description | Noise level | Resource | Cost of |
| Sleeve bearing | The simplest type of bearing consists of a sleeve coated with antifriction material, inside which the shaft rotates. | In good condition, it is low, but as these bearings wear out, coolers as a whole start to make a lot of noise due to vibration. | Relatively low and highly dependent on operating temperature and vibration loads. In modern versions, a resource of up to 35 thousand hours is claimed; however, it is attainable only under ideal conditions; in practice, such bearings serve two to three times less. | The cheapest type of bearing. |
| Sliding bearing with rifle (rifle bearing, Z-Axis bearing) | Sliding bearing with specific grooves on the sleeve and the axis that recirculates the lubricating fluid. | Low. | Significantly higher than that of the simplest bearings and close to FDB-bearings. | Slightly higher than conventional plain bearings, but lower than FDB bearings. |
| Hydrodynamic Bearing (FDB bearing) | An improved sliding bearing in which the shaft rotates in a layer of fluid that is constantly retained inside the sleeve due to the pressure difference created during operation. | Significantly higher than the bearings, the figures are claimed to 80 thousand hours, but in real operating conditions, these figures should also be reduced at least twice. | Higher than conventional plain bearings, but lower than rolling bearings. | |
| Rolling bearing (ball bearing) | Of all types of rolling bearings in coolers, only radial ball bearings are used, consisting of two rings, rolling elements (the ball itself) and a separator. | Formally, it is higher than that of sliding bearings; however, due to a longer life under equal conditions of long-term operation, coolers on such bearings do not turn out to be more noisy than analogs on sliding bearings, which are more susceptible to wear. | The claimed resource can be from 59 to 90 thousand hours, in actual use such bearings are much more durable than plain bearings. | Higher than the bearings. |
| Ceramic rolling bearing (ceramic bearing) | Rolling bearing using ceramic materials. | Low. | The claimed resource can be up to 160 thousand hours at sufficiently high operating temperatures; in fact, at present these are the most durable bearings used in coolers . | The tallest. |
| Oil Pressure Bearing (SSO) | Advanced hydrodynamic bearing.It features an increased layer of fluid (lubricant). To reduce wear, the shaft is centered with a permanent magnet mounted in the base. | The lowest. | The claimed resource can be up to 160 thousand hours at sufficiently high operating temperatures; in fact, at present these are the most durable bearings used in coolers. | Higher than rolling bearings, but lower than ceramic rolling bearings |
| Self-lubricating plain bearing (LDP) | Advanced sliding bearing. It has IP6X-compliant dust protection and a special slot for reconstituted oil that increases fan life. | In good condition - low. | The claimed resource can be up to 160 thousand hours at sufficiently high operating temperatures; in fact, at present these are the most durable bearings used in coolers. | Higher than sleeve bearings (lower bearings), lower than hydrodynamic |
| Bearing with polyoxymethylene (POM Bearing) | Advanced sliding bearing. To increase the service life, the shaft is coated with polyoxymethyl, which has a reduced coefficient of sliding friction. | In good condition - low. | The claimed resource can be up to 160 thousand hours | Higher than sleeve bearings (lower bearings), lower than hydrodynamic |
| Thermoelectric cooler | Thermoelectric cooler works on the basis of the Peltier effect. In the thermoelectric module, the semiconductor component functions as a small heat pump. A typical single-stage cooler consists of two ceramic plates with p- and n-type elements made from bismuth telluride alloys (see Fig. 4). When a constant voltage is applied, electrons are transferred from the p-type element to the n-type element, and the temperature of the cold side decreases as the electron current passes through until it reaches equilibrium. Cooling is proportional to the current and the number of thermoelectric pairs. Heat is transferred to the hot side of the cooler. |
none |
| Title | Scheme |
Sliding bearing(Sleeve Bearing) |
 |
Sliding bearing with screw thread(Rifle Bearing, Z-Axis Bearing) |
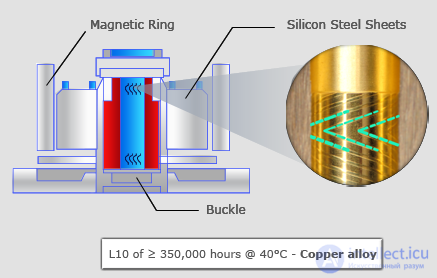 |
Hydrodynamic bearing(FDB Bearing) |
 |
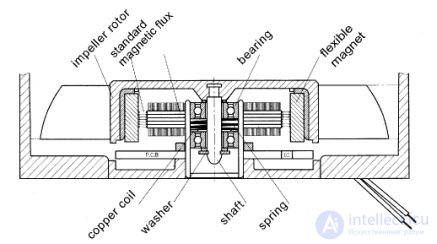
Friction bearing(Ball Bearing) |
 |
Ceramic rolling bearing(Ceramic Bearing) |
 |
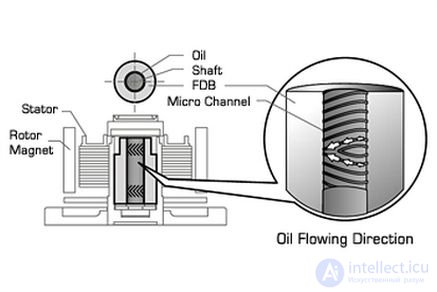
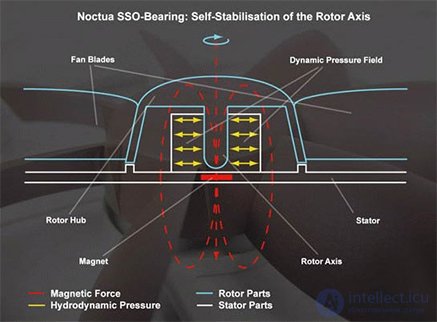
Oil pressure bearing(SSO) |
 |
Self lubricating slide bearing(LDP) |
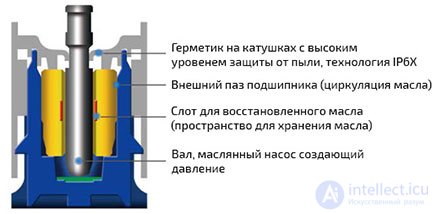 |
Polyoxymethylene Bearing(POM Bearing) |
 |
| Thermoelectric cooler | 
1 volt - 0.3 amps - temperator difference - 3 volts - 1 amp 5 in - 1.5 A 12 volts - 4 Amps - working voltage temperature difference of 70 degrees surface 40x40 mm |
Comments
To leave a comment
Electromechanical devices of electronic devices
Terms: Electromechanical devices of electronic devices