Lecture
History of the evolution of printers
The era of printing devices began in the middle of the 20th century, when the USSR invented ADCU - an alphanumeric printing device, and in the USA its analogues, which were called Printer. But in fact, the prototype of the printer appeared much earlier: in 1822, Charles Babbage invented a miracle machine that prints tables, but it was too heavy and bulky, so it was built only after 150 years.
Further developments were carried out around the matrix, inkjet, then laser, sublimation and thermal printing, and each direction developed independently of each other.
History of the evolution of printers
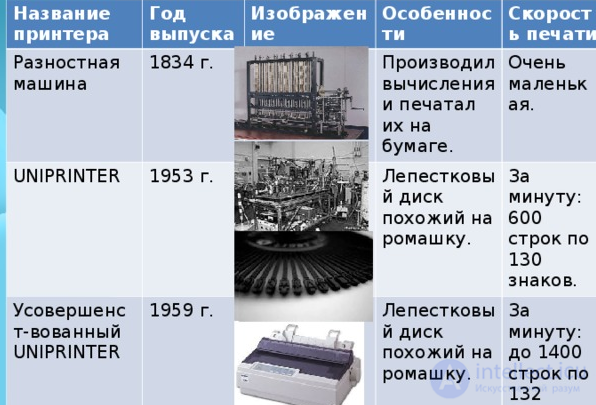

Uniprinter is considered the very first real printer, was released by Remington Rand (USA) in 1953. Its main structural element was a single-sheet-wide drum with embossed letters and numbers placed on it. For one revolution of the drum, one line was printed. The desired symbol was knocked out on it thanks to the work of the hammer, which pressed the paper to the drum through the coloring pigment.
Instead of a drum, they used a plastic disk with flexible petals, during rotation, the desired petal with the symbol was pressed to the paper through the ink ribbon due to the operation of the electromagnetic element. In this case, the technology of impact printing was used.
Matrix printers with a similar printing mechanism came to replace the petal devices, but instead of the petals with the symbols, the print head left the print on the paper through the ink ribbon. The image or the desired character in them is formed from dots that are obtained due to the work of the print head with numerous small thin needles. The first such printer was introduced by Seiko Epson in 1964.
Matrix printers, sometimes called needle-like printers, are seriously inferior to inkjet printers and laser ones in terms of print quality. They are much noisier, since the printing mechanism is based on the percussion method (in different models, 9 or 24 percussion needles). Today, almost all such printers are monochrome, i.e. they allow printing in one color. But not everyone and not everywhere require photographic print quality. There are many practical applications where speed, simplicity and low cost of the printing process are much more important. And the durability and reliability of the printer are often more weighty than the possibility of printing in colored letters of printing quality. A well-known matrix printers possess a set of such qualities.
Another advantage of matrix printers is the ability to print on layered forms (printing at the same time up to 6 copies on sheets laid through copy paper). Expensive materials (paint, tape) are extremely cheap.
Epson has left the most visible mark on the global market for dot-matrix printers. Epson, which produces both inkjet and laser printers, reports that, oddly enough, but the demand for dot-matrix printers does not fall further.

It is expected that it will exist in the future as well, because there are places where you want to print documents and you need to immediately receive several copies - payment orders, tickets, invoices, invoices, stickers with addresses or bar codes and other financial, trade and warehouse documents
They have a similar to a matrix printing device, where the image is also formed from dots. However, instead of needles, the print head consists of numerous nozzles through which liquid dyes are sprayed by various mechanisms. Compared to dot matrix printers, inkjet printers are quieter, cheaper, and provide better print quality.
The principle of inkjet printing was invented back in the 19th century, and the first prototype of such a printer belonged to Siemens in 1948, and in 1951 it produced a printer with a continuous ink supply system, although most models still use ink supply on demand (it was developed thermal and piezoelectric).
In terms of price, inkjet printers occupy an intermediate position between matrix and laser printers, they outperform matrix printers in print quality, but (for now!) Are a little inferior to laser printers.
Modern inkjet printers display text and graphics of high quality and are more than twice cheaper than laser (often around $ 100). In addition, they are smaller, not so noisy and consume less electricity than their laser counterparts. Studies by International Data Corporation show that this is one of the reasons why inkjet printer sales are growing faster than printing devices of all other types.
However, choosing an inkjet printer instead of a laser entails the need to make certain compromises: you will most likely have to sacrifice speed, and if you print more than a few dozen sheets per week, it is expensive because of the high cost of consumables (ink-cartridge).
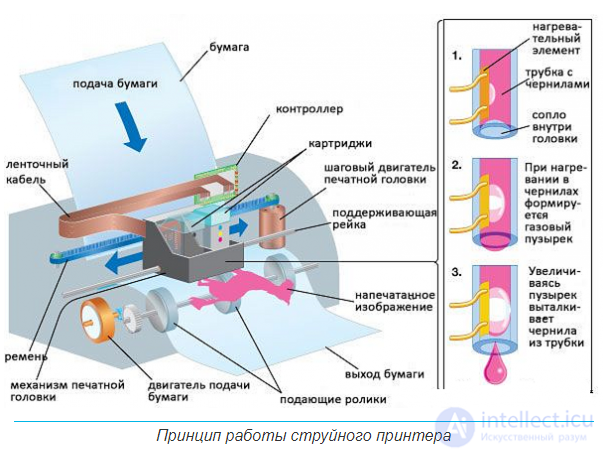
Like laser printing, the inkjet method is “shock-free”. The physical principle of the technology that provides inkjet printing is similar to the principle of operation of a jet engine and is based on the shooting of a drop of liquid from a special nozzle. A printhead containing ink has a group of tiny nozzles, each diameter thinner than a human hair. Behind each nozzle on the miniature resistor is a micro-reservoir with ink. When a resistor is heated by an electric current passing through it, the ink surrounding it boils, forming a small vapor bubble. This expanding bubble pushes the smallest ink droplets out of the nozzle onto paper, flying at a speed of about 700 km / h. After the drop is pushed onto the paper, the vapor bubble is compressed, and the resistor at this time waits for the next heating under the action of another current pulse. Such a cycle takes a fraction of a second, allowing the printer to print quickly and silently (since there are no mechanical impacts on the paper), pushing out droplets of 4 picoliter (in the most “advanced” models).
Significant progress in the inkjet printer market has recently occurred largely due to the efforts of the former undisputed leader in the dot-matrix printer sector, Epson. High quality at a low price has become a reality.

With an increase in the resolution and speed of printing, it turned out that the pursuit of improving these characteristics would not in itself provide a significant gain if it did not improve the image carrier, that is, paper. Any “tricky” technology will be powerless if you put simple office paper in the printer tray.
The surface of ordinary paper has a fibrous structure, due to the technology of its production. As a result, tiny, strictly calculated by the size of the drop begins to spread on the surface in an unpredictable way. One solution to this problem is the use of pigment inks, which are a suspension of dispersed particles in a colorless liquid carrier, since solid particles cannot penetrate into the inner layers and spread over the fibers of the paper.
Pigment-based inks produce bright and saturated colors, but they also have certain disadvantages, in particular, low resistance to external influences.
The technology of inkjet printing is such that the best result can be achieved only when using special paper. Photos on plain paper look faded and less clear. Unlike conventional paper with a special coating and the so-called photo paper have several special layers. Prints on it are almost indistinguishable from photographs obtained when printing with the use of chemical photoprocess.
Simple budget inkjet paper typically has a density of 90–105 g / m2, a relatively small thickness and excellent whiteness. Due to the special treatment of the front or both sides of this paper is more resistant to the vagaries of ink and prevents them from spreading and penetrating deep into the sheet.
Attention is paid to such important aspects as the rate of drying of ink and their resistance to sunlight and gases contained in the air (in particular, ozone).
refill cartridges - is the game worth the candle?
The main disadvantage of inkjet printers is the large overhead, the lion's share of which is the cost of new cartridges. And the most annoying thing is that every time you have to throw out almost a new device, which most often retains its full functionality, but has lost ink (moreover, it is not always completely spent).
Is it possible to save?
After all, for this "only" you need to learn how to refill cartridges. The answer of most manufacturers to such a proposal is "NO!" (this can be seen by opening the instructions). The main argument - the use of refilled cartridge increases the risk of the printer or its individual parts failing. If the service team finds out that the refilled cartridges are used, the owner will lose the warranty and hope for free repair. Many still decide on self-fueling, but the result of such an attempt to save may be different and quite ambiguous, depending on the brand of printer, the specific type of cartridges and ink used.
For example, in most Hewlett – Packard printers, the cartridge is combined with the print head in one case and they are replaced at the same time. This design increases the likelihood of refueling success and reduces the risk of printer failure - pouring a new batch of ink does not have to worry about the print head (following the instructions, you still have to throw it out with the cartridge!). With a known skill, you can successfully refill HP cartridges 5-10 times with a fairly stable result. The situation is completely different with Seiko Epson printers. The print head in them is made non-removable (at least, maintenance does not require it), only the cartridges are replaced, which are actually ink tanks. Firm CATEGORICALLY does not recommend refilling cartridges and in this matter it is impossible to disagree. The cost of such savings is often very high - poor quality inks clog the nozzles of a precision printhead and it is not always possible to “reanimate” it even at a service center. There is a great risk that the printhead will dry out during the time it is without a cartridge. If necessity forces to save, it is less risky to use cheaper third-party cartridges (for example, the same Print – Rite). At the same time, despite a number of successful experiments, we recommend that owners of Epson printers refrain from refilling and replacing the recommended cartridges with alternative ones.
The optimal (and most importantly - standard), dose adjustment scheme from our point of view is provided by many Canon printers (in particular, BJC – 50, BJC – 2000, BJC – 6000), which provide for the replacement of not only the cartridge combined with the print head, but also individual ink tanks inserted into the cartridge. With such a replacement, the most complete development of the resource is provided not only for the print head, but also for each reservoir (especially important for a color cartridge). The savings are also significant - for example, the ink tank for a BJC-50 monochrome cartridge costs 5-6 times less than the cartridge itself.
These examples are quite enough to understand the following - refilling cartridges is justified if the risk is minimized (refueling is provided by the manufacturer) or small (due to the design features). In this case, skillful refueling actions can really save a significant amount to the owner without any complication.
If refueling can most likely lead to the failure of an expensive printer unit (printhead, for example), such a risk is unjustified and other ways out of the situation should be sought.
The progenitor of laser printing is Chester Carlson, who called the invented printing method xerography. This principle formed the basis of laser printing when the first laser printer was invented in 1971 by Xerox Corporation.
Laser printers are characterized by high speed and print quality, a more stable print and its lowest price, low media requirements (can be printed on any paper), environmental friendliness, noiselessness, simplicity and cost-effectiveness of maintenance.
The mechanical components of laser printers become easier over time: the number of moving parts decreases, reliability increases and ease of maintenance increases.
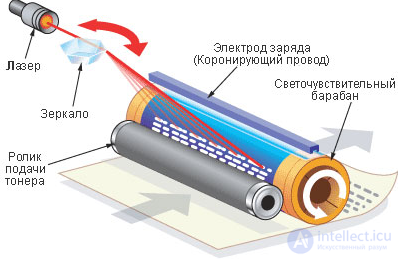
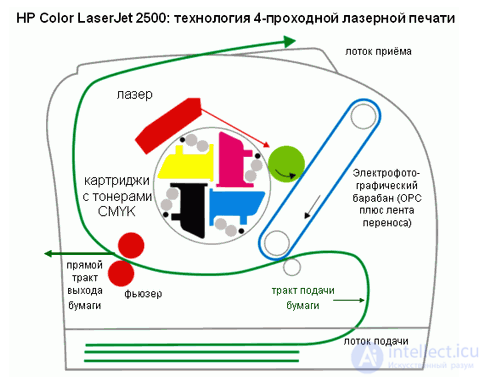
The laser printing process is based on technology developed by Xerox. On a special photosensitive drum with a beam of light, areas charged with static electricity are created (a picture is drawn with a beam across the drum). The drum rotates in front of the cartridge, and the charged areas attract the toner, which consists of plastic-coated iron particles. Then the drum moves over a sheet of paper that is charged even more strongly than the drum. In this case, the toner particles are transferred from the drum to the paper and then sintered under heating, turning into a waterproof imprint.
The technological difference between the different models may lie in the way the "image" is created by the light beam on the drum. In real laser printers, a laser gun directed at a rotating mirror is used, the angle of its rotation determines the charged points of the drum, from which the image is formed.
Another way is to use a constant light source and a system of liquid crystal "windows" (diaphragms). As the drum rotates, they switch from a transparent state to an opaque state and vice versa, creating charged regions corresponding to the image. The further development of this technology was the use of a "strip" of LEDs (as in OKI printers).
The situation with photographic images containing shades of gray is somewhat more complicated. The area covered by several points is transformed (combined) into one large virtual point. It may look lighter or darker depending on the number of real points forming it. This creates the effect of gray gradations. Naturally, the higher the resolution of the printer, the more real points can be in one virtual, which means higher quality of the final image. An even more perfect way is to vary the size of each point.
In laser printers, in contrast to the matrix, can only be used sheet paper, but can not roll. The printing speed of laser printers varies considerably. It is for different models from 4 to 40 pages or more per minute.
The faster the printer prints, the more important the capacity of the paper feed tray.
Printers have different capacities of random access memory (RAM) used to store the fonts loaded into them (for example, Russian) and printed pages. A small capacity of RAM (512 KB) does not allow to print large (full page) images and at the same time store a sufficient number of fonts. If a printer is bought for making original layouts of books with a large number of drawings, then it is better to choose a printer with a large amount of RAM or additionally purchase several megabytes of memory.
Prices for personal and group laser printers have fallen, making them affordable for those people who would have previously chosen for themselves inkjet or matrix models.
The cost of a laser printer is influenced by two factors: resolution and speed. In the lower price range are devices capable of printing four pages per minute with a resolution of 600 dpi. More expensive models have a resolution of 1200 dpi or higher and print at eight or more pages per minute.
The most expensive consumable part of laser printers is toner. In some printers, the drum and toner are a single unit, and they have to be replaced at the same time, which incurs additional costs. An alternative are models with separate toner and drum. If you intend to print a lot, then this solution can save you money. However, the drum is also not forever: you have to replace it every 8,000–20,000 pages (depending on how much you usually print at a time). Costs of operation can be reduced by buying a printer with a cartridge that can be "recharged". Currently, there are many companies offering the exchange of empty cartridges to refilled for about half the cost of a new one. Although the powder in the cartridge is not poisonous, we do not recommend trying to recharge yourself: this is a very “dirty” procedure.
Another item of expenditure - additional features. For example, some models include the installation of additional trays for feeding paper, printer memory expansion modules, network tools, etc. One of the most “desirable” possibilities is the simultaneous printing on both sides of the paper. This feature is still a privilege of expensive models, however, if you plan to further upgrade your printer in this way, you need to make sure that it supports duplex printing before purchasing.
Color Laser Printers
Of course, it is unlikely that in the near future color laser printers will compare in popularity with color inkjet printers and will be used as desktop printing devices for personal use. However, the noticeable progress of technology in this area has recently made the price-quality ratio of print much more attractive.
According to various estimates, the market for color laser printers is still quite narrow - after all, their price, as they say, bites. Nevertheless, we must admit that the print quality of these devices is improving, and they themselves are becoming more and more attractive. If this goes on, then over time, color laser printing will compete with inkjet. For the time being, it is only “about” the implementation of numerous marketing forecasts, the authors of which predict a “simple” growth in the popularity of color laser printers, independent of the success of other types of printers.
A printing method is used in which a solid dye is immediately converted to a gaseous state without a liquid phase. Most often they are used in photo printing. Sublimation printers have good quality, print speed and color reproduction, they are quiet, environmentally friendly, simple and reliable in maintenance.
They are used in cash registers, faxes, ATMs, when printing on receipts, do not require ink, the image is formed due to the thermal print head on heat-sensitive paper, they are simple, high speed printing, environmental friendliness and low cost, but low print quality.
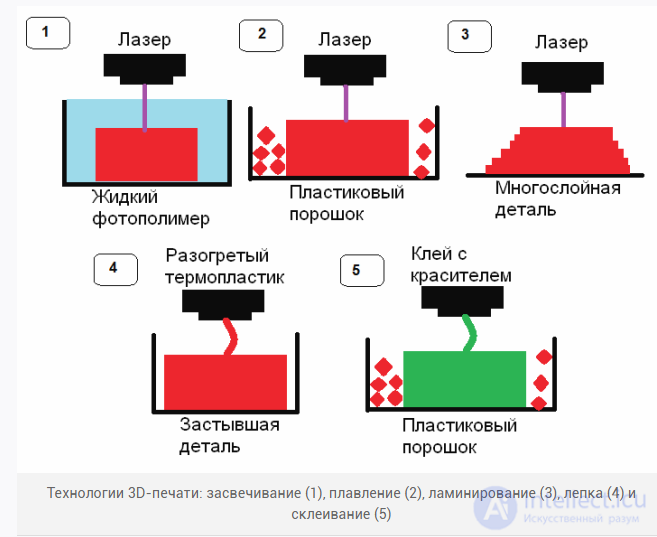
This is a device that reproduces a 3D model layer by layer through the creation and integration of individual sections. They can be used to create images not only on flat media (paper, foil), but also on voluminous objects (mugs, phones, souvenirs).
Plotters, are intended for displaying graphical information, creating schemes, complex architectural drawings, artistic and illustrative graphics, maps, three-dimensional images. Plotters are used to produce high-quality, color documentation and are indispensable for artists, designers, designers, engineers, and
The maximum length of the printed material is limited, as a rule, by the length of the paper roll, and not by the plotter design. The image on paper is obtained using the print head. Point by point, the image is put on paper (tracing paper, film), hence the plotter's name - plotter (to plot - “draw drawing”).
The main characteristics of plotters include:
Plotters are connected to the computer via a parallel or serial interface, or a board is built into the expansion slot.
By design, plotters are divided into tablet and drum. In flatbed plotters, the paper is stationary and the print head moves in two directions. In the drum one head moves along one coordinate, and paper moves along another axis using the clamping system.
By the principle of operation, plotters are divided into pen, inkjet, electrostatic, thermal transfer, pencil.
Pen plotters use ordinary feathers to produce images. To obtain a color image, several feathers of different colors are used.
Inkjet plotters form an image like inkjet printers, spraying ink droplets onto paper. Print quality beyond the capabilities of pen-based plotters determines the wide distribution of ink-jet plotters in various fields of human activity, including automated design, engineering design.
Electrostatic plotters create an image using electric charge. Electrostatic plotters are very expensive and are used when high quality output documents are required.
Thermal transfer plotters create a two-color image using heat-sensitive paper and electrically heated needles.
Pencil plotters use an ordinary stylus to obtain an image. They are the cheapest and require cheap consumables

Pictures on demand multifunction device history
A multifunction device (MFP) is a very useful thing, both for office work and for home use. The MFP consists of two devices - a printer and a scanner. Another device - a copy machine, obtained from a bunch of the first two.
Interestingly, the idea of creating an MFP did not arise in the mind of any engineer from a well-known or little-known computer company. The idea of combining several office devices into one belongs to the Garther Group company, which was engaged in the analysis of information technologies and consulting (advising manufacturers of various products) at the end of the 90s of the last century. Representatives of the company calculated the costs of office equipment maintenance and came to the conclusion that they could be significantly reduced if the office had less electronics, and at the same time it would be more functional.
This idea did not pass by manufacturers of office equipment and in the late 90s the first multifunctional devices saw the light. First, standard fax machines (faxes) were taken as their basis. Manufacturers only added the ability to connect them to a computer to exchange data and print documents. The device so far could only scan and print documents. However, a little time passed and the manufacturers realized that it would be better to add the ability to copy (multiply) documents - so the MFP also acquired the functions of a copy machine. The new models were based on photocopiers. Although the first MFPs were rather damp (malfunctioning) and bulky, the idea itself no longer left the minds of engineers at leading electronic companies.
The first truly full-fledged MFP came out of the assembly line of the Japanese company Okidata. It was already a truly multifunctional device, combining a scanner, printer and copier. Other companies from Xerox, Canon, Epson and HP (Hewlett-Packard) were not long in coming and released their versions of the MFP. The further development of such devices went by leaps and bounds together with the development and improvement of printer printing technologies.
Now MFPs are already truly multifunctional office devices, which users, however, are happy to use for home use. Take, for example, a household printer-copier, which in its functionality and print quality can compete even with a professional machine.
Comments
To leave a comment
History of computer technology and IT technology
Terms: History of computer technology and IT technology