Causes and the beginning of the war. The war of independence in North America was a direct consequence of the growing contradictions between the metropolises and the colonies, especially the resettlement ones, like the American colonies in England. The colonies quickly gained strength, striving for economic and political independence, while the metropolis continued to see in them only sources of raw materials and huge incomes. In 1763, England banned, for example, independent relocations to land seized from France in the West of the country. Colonists could receive industrial goods only from England, at prices set by England, and sell raw materials only to England.
In the middle of the XVIII century. in North America there were 13 independent states (provinces), subdivided into smaller administrative units. The population of the colonies exceeded 1.5 million people. All the most important cases in individual colonies and small districts were decided in the meetings of all adult citizens, and in the main cities of the states - in the meetings of elected representatives from the districts assigned to these states.
The colonies were ruled by governors appointed by the English king. The British government cared little about the need of the colonists in faraway America and did not grant them any rights.
The self-serving policy of the British government, attempts to impose large-scale land tenure, limit free enterprise, the arbitrariness of governors and royal officials, forcibly accommodate increasing contingents of British troops in American colonies, the introduction of a “stamp duty” - which was levied on trade deals, documents, and newspapers and announcements. All this caused a sharp discontent of the English settlers. Tensions between the British authorities and the colonists resulted in an armed clash in Boston between the local population and the British forces in March 1770, during which soldiers killed several people. The following year, in 1771, in North Carolina, British troops again opened fire on civilians.
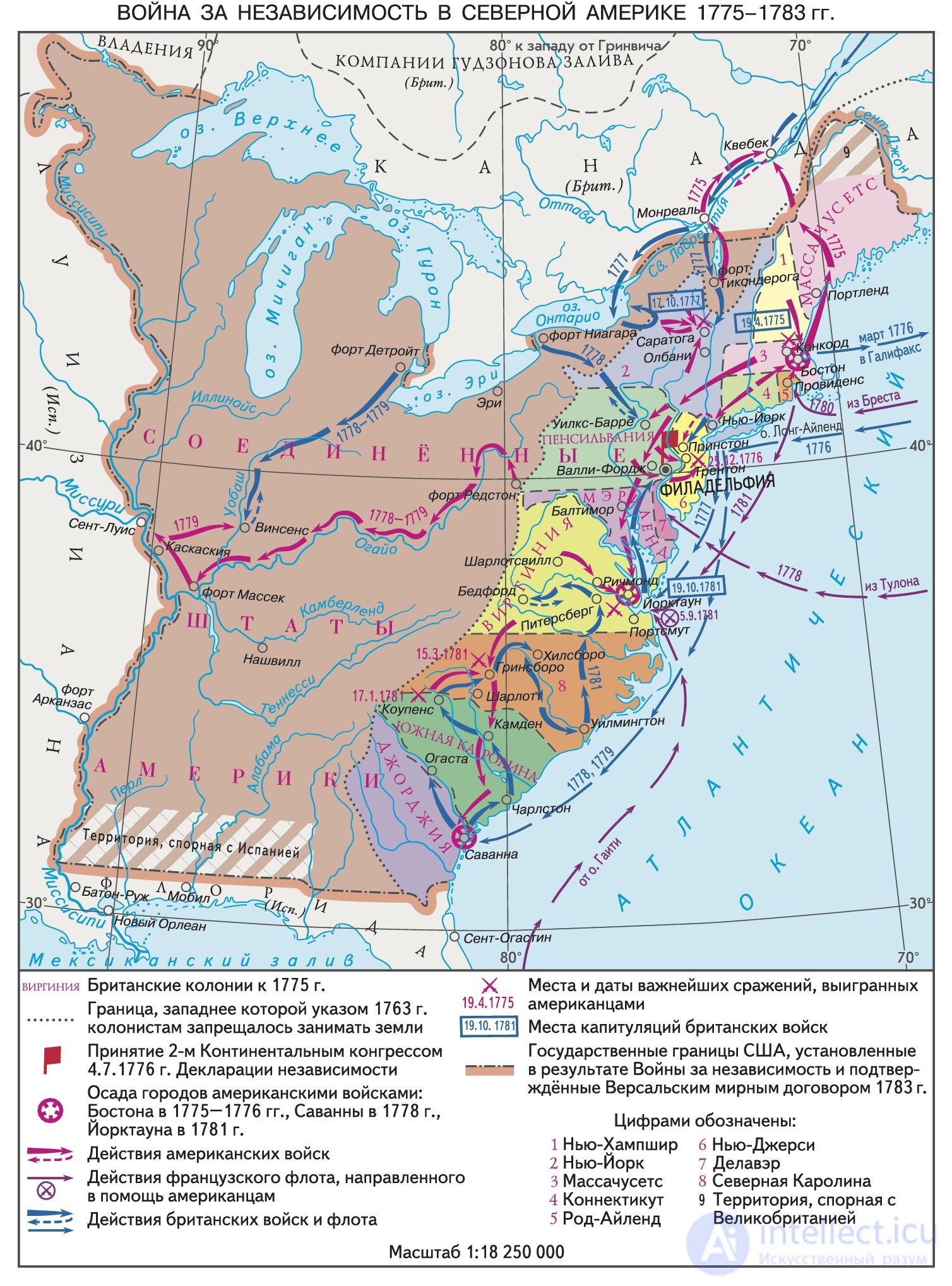
The British government expected cruelty to suppress public discontent in the colonies. But this led to exactly the opposite results. In 1774 the first partisan detachments of fighters for the independence of the colonies appeared. On April 19, 1775, the first battle took place between government forces and partisans. The partisans contrasted regular and sedentary royal troops with the speed and initiative of the shooters who were dispersed into small units. The royal troops suffered heavy losses and were forced to retreat in disarray.
So began the war of the North American colonies for independence. It is called the First Bourgeois American Revolution. It freed the Americans from the power of the king and the English aristocracy, established the republican system, which opened the way for bourgeois progress and private initiative. But, on the other hand, it was significantly different from the preceding and subsequent revolutions, when progressive forces destroyed reactionary regimes, but a single territory and a single unitary state remained. As a result of the war of independence from Great Britain, a significant part of the population of 2.5 million people (the population of Great Britain numbered 10 million people) broke away.
Decloration of independence. The Second Continental Congress in Philadelphia, held in May 1775, representing all the colonies that had risen against England, decided to break off relations with it and create an American army. It also included previously created partisan detachments. George Washington (1732-1799) was appointed commander-in-chief. In his difficult and responsible post, Washington showed himself to be a skilled commander, determined to fight until the complete liberation of the rebel colonies from English oppression.
July 4, 1776 Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. By this document, the insurgent colonies proclaimed themselves free and independent states united in the United States of America. July 4 is celebrated annually in the United States as Independence Day, although after signing the Declaration five long children passed before the final victory of the Americans in the war and seven years before the signing of the Paris Peace Treaty.
The author of the Declaration of Independence was the youngest 33-year-old congressman Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) - an outstanding democratic leader of the American revolution, a student and follower of the French educators, whose progressive democratic ideas were the basis of the Declaration of Independence. In accordance with these ideas, Jefferson introduced a clause in the draft declaration that provided for the abolition of slavery, but rich planters and tenants, represented by a majority in Congress, succeeded in excluding him from the final text of the Declaration.
Thus, slavery was preserved in a young, free state that had just defended its independence. But on the whole, for the time when the feudal system dominated almost all over the world, with its class estate inequality, political lawlessness and medieval inertia, the Declaration of Independence, which proudly proclaimed the rights of people to freedom, was a very progressive document. The ideas of the talented leaders of the American Revolution were reflected in this most important document of the era; D. Washington (1732-1799), D. Adams (1735-1826), S. Adams (1722-1803), B. Franklin (1706-1790), T. Payne (1737-1809).
The most famous American leader of the war of independence was the commander in chief of American troops, the first president of the United States, one of the most revered heroes of the United States, George Washington. His name is the capital of the state and one of its states.
The declaration was the first document that justified the rights and principles of democratic government. Chief among them was declared political power, coming from the people and designed to protect the interests of all citizens.
Proclaiming the independence of the United States did not mean to ensure it in practice. For this it was necessary to go through a difficult, long war with England, with varying success. Many progressive people from different countries, including the future famous utopian socialist Saint-Simon (1760-1825), the leader of the Polish liberation movement Tadeusz Kosciuszko and others, have already fought with the “freedom guys”, as the American warriors were called.
The outcome of the war. Among the most important events of the war are: the battle of Saratoga in October 1777, when the American troops surrounded and forced the six thousandth expeditionary force of the British to leave the south, leaving the city of Montreal. This victory not only gave confidence to the young American army, but also became a pretext for concluding an allied treaty between the United States and France, which decided the outcome of the war. This treaty of friendship, commerce, defensive alliance, signed on the American side by Franklin, became the first official recognition of the new state. In addition, he contributed to the active involvement of European countries in the war against Britain. In 1779, Spain followed the example of France, and in 1780 - Holland.
The French fleet unblocked the eastern ports of the United States, and regular units and volunteers from almost all European countries appeared in the American troops.
By joint efforts of the American, French, Prussian warriors, British troops were surrounded and capitulated on October 19, 1781 at Yorktown. This predetermined the outcome of the war.
On September 3, 1783, peace treaties were signed between the warring states at Versailles, under which the United States was recognized as an independent sovereign state.
US Constitution . Having conquered England, the young country was in an extremely difficult position. With the disappearance of the war danger, the bonds that held together 13 US states broke. Because of the eight-year war, the financial and economic situation of the country deteriorated. To save the young state, it was necessary to establish law and order in the country.
In 1789, the first Congress and the first President were elected. The foundations of social and state structure in the United States were laid during the war of independence and were subsequently enshrined in the Constitution adopted in 1787. The Constitution proclaimed the United States as a federal state, a republic in which the highest legislative power belongs to Congress and the highest executive power to the president. Each state was recognized as a completely independent state, possessing within its territory full legislative, judicial and executive powers and managing its elected representatives. Both in private and in the allied structure of the states, the principle of separation of powers was strictly implemented. The full independence of judges was expressed in their irremovability and in the right not to apply laws contrary to the Constitution. With all kinds of religions existing in the country, divided into many sects, the dominant religion was not established in the USA and full tolerance was allowed. As can be seen, much of the Constitution of the United States was borrowed from the ideas of the French Enlightenment. In 1791, Congress passed ten amendments to the Constitution, which went down in history as the Bill of Rights. These amendments proclaim freedom of speech, assembly, press, personal integrity, etc. The Bill of Rights did not abolish the slaveholding system in the USA, but introduced the foundations of bourgeois democracy in the young republic.
International relationship. According to a number of the newest American researchers, the colonists could hardly have won without the help of European states. The total amount of subsidies that the Americans received from their allies in terms of the value of money today was about $ 2.5 billion, while they themselves spent $ 1 billion to fight.
England lost the war, she lost temporarily and domination of the sea. Under the Treaty of Versailles (Paris) in 1783, England recognized the independence of the colonies, France regained some possessions in the West Indies and West Africa. Florida, the island of Menorca in the Mediterranean were returned to Spain, Holland was forced to cede Ceylon to the British.
Many contemporaries considered the colonies falling away as the beginning of the decline of England as the dominant maritime and trading power. In fact, the recognition of the real situation, the irreversibility of the results of the revolution in North America paved the way for the restoration of the international position of England, which was based on the country's rapid economic development as a result of the industrial revolution that had begun. And French absolutism turned out to be completely incapable of taking advantage of the external political situation that was exceptionally favorable for him after the Paris world.
By the end of the XVIII century. In most of the Spanish and Portuguese possessions in America, revolutionary changes were also coming.
* * *
The development of international relations in the XVIII century. showed how fragile the world was. Conflicts between the European powers over trade and colonial hegemony were mostly resolved in wars. The rivalry of the European powers was won by the most advanced economically, the most modernized countries. It is not surprising that by the XVIII century. leadership in the colonial seizures passed to England.
The first example of the instability of the colonial system was shown by the North American British colonies, which moved from the struggle for political freedoms to the war for independence from the metropolis (the American revolution of 1775), which led to the formation of an independent state - the United States of America.
At the heart of international relations on the European continent were the French-English rivalry for domination over the colonies, the competition between Prussia and Austria for hegemony in Germany, the struggle of Russia for access to the Baltic and Black Seas. In the XVIII century. Russia's expansion has increased dramatically and at the same time its prestige in international politics. Most wars of the XVIII century. were coalition, but the coalition was not strong.
At the same time, reactionary features began to take shape in the foreign policy of a number of European states, which were most clearly manifested in the liquidation of Polish statehood and in relation to the French bourgeois revolution.
Questions for self-test
1. 1. How were the successes in colonial policy related to the internal development of Western countries?
2. 2. Tell us about the main directions of foreign policy of European countries in the XVIII century.
3. 3. What are the results of the foreign policy of Peter I, Catherine II?
4. 4. Tell us about the causes, nature, features of the war of independence in the English colonies of North America.


Comments
To leave a comment
The World History
Terms: The World History