Lecture
Pedagogy belongs to the humanities whose field of research is related to the study of human relations. For a long period of its existence, it was associated with many sciences that influenced its formation and development.
Among the first, there were connections between pedagogy and philosophy, especially with such areas as ethics and aesthetics. Ethics reveals the path of moral formation of man. Aesthetics gives an idea of the principles of value attitude to the world. Philosophy is the methodological basis of pedagogy. From the system of philosophical views (existential, pragmatic, neopositivistic, materialistic, etc.) depends on the direction of pedagogical search, especially the content and organization of the educational process.
The relationship of pedagogy with psychology is traditional. The results of psychological research, embodied in the laws of human mental development, allow teachers to organize the processes of training and education, based on these laws and ensuring the formation of it as a subject of activity and individuality.
Modern pedagogy is characterized by connections with various natural and human sciences, primarily with the sciences that study man: biology (anatomy and human physiology), anthropology, and medicine. No less significant for the development of pedagogy are its ties with the sciences that study man in society, in the system of social relations. Therefore, it was not by chance that quite stable interactions were established between pedagogy, sociology, economics, political science and other social sciences. However, the influence of philosophy, psychology and anthropology remains dominant. They determine the development of pedagogical science.
The forms and types of relations of pedagogy with other sciences are diverse:
• using pedagogics of basic ideas, theoretical propositions, generalizing conclusions of other sciences (for example, using the activity approach to teaching and educating a person);
• application of methods of other sciences (mathematical modeling and design, questioning and sociological survey);
• the use in pedagogy of specific research results obtained by various sciences (basic psychological neoplasms in the process of human development or physiology data on working capacity at different age periods);
• participation of pedagogy in comprehensive studies of common problems (transition to learning from the age of six, organization of training for sick or weakened children).
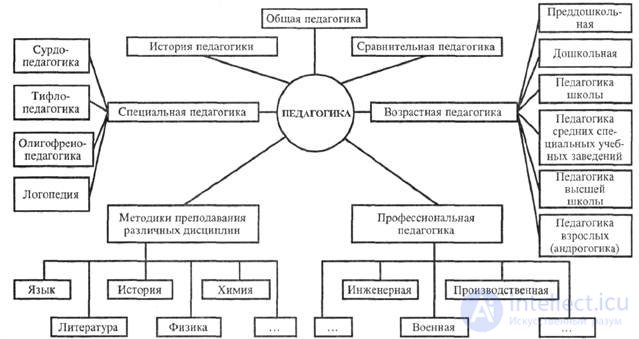
The development of relations of pedagogy with other sciences leads to the emergence of new branches of pedagogy. In recent years, such branches as the philosophy of education, comparative pedagogy, social pedagogy, and others have stood out. Today, pedagogy includes a complex system of pedagogical sciences that include: general pedagogy, which studies the basic laws of education; age pedagogy - pre-school, school, adult pedagogy (andragogy), exploring the age aspects of training and education; correctional pedagogy with its branches: deaf-and-dumb pedagogy, typhlopedagogic, oligophrenopedagogic, speech therapy; private techniques - subject didactics, exploring the specifics of the application of the general laws of education to the teaching of individual academic disciplines; the history of pedagogy and education, which studies the development of pedagogical ideas and educational practices in various historical eras; sectoral pedagogy (military, sports, industrial, etc.).
Comments
To leave a comment
Pedagogy and didactics
Terms: Pedagogy and didactics