Lecture
Data flow (eng. Stream ) in programming is an abstraction used to read or write files, sockets, etc. in a single manner.
Streams are a convenient unified software interface for reading or writing files (including special and, in particular, connected devices), sockets and transferring data between processes.
Support for threads is included in most programming languages and almost all modern (for 2008) operating systems.
When the process starts, it is provided with predefined standard streams.
The ability to redirect threads allows you to link various programs, and gives the system flexibility, which is part of the Unix philosophy.
Thread abstraction is especially important in the C programming language, where it represents the source of input and / or output of data, usually bytes, associated with a file, device, or other process. Work with threads has been moved to many other languages:
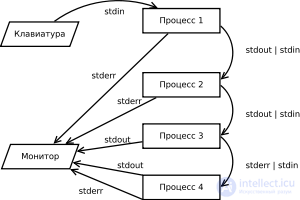
The UNIX command shell intensively uses thread abstraction to share several utilities together.
Comments
To leave a comment
Operating Systems and System Programming
Terms: Operating Systems and System Programming