Lecture
Vibration sensor (vibrometer) - a device that allows you to determine the parameters of vibration phenomena. Most often, vibrometers are used to determine:
Simply put, if a vibrating object is considered a simple oscillator, then the vibrometer allows you to obtain information about the basic parameters of its vibrations (frequency and amplitude), and, in some cases, obtain the spectral characteristic of the oscillatory process.

Figure 1. Schematic of the vibration sensor.
The general scheme of the vibration sensor contains two main units (Figure 1): a vibration transducer (1) and an electronic processing unit (2). The functional purpose of the first block is the conversion of mechanical vibrations into an electrical signal. There are several conversion mechanisms:
The conversion mechanism to a large extent determines both the characteristics of the device and its cost.
The second unit - the electronic processing unit - serves to "decrypt" the received signal. As a rule, an analog-to-digital converter is located at the input of such blocks, and the bulk of the operations on the signal are already digitally expanded, which extends the functionality of the post-processing process, improves noise immunity, and allows information to be output via an external interface.
When used in production, stationary vibrometers can be part of control systems as feedback sensors; for these purposes, some models of vibrometers have an analog output signal (usually voltage).
To obtain a comprehensive characteristic of the vibration process, a spectrum analyzer can be added to the measurement system. If the spectrum analyzer is multi-channel, it can serve as the basis for a distributed system of vibration diagnostics containing more than one vibration sensor.
Currently, most vibrometers belong to one of two types:
Let us consider in more detail each type of sensor.
The operation of an optical vibrometer, like ultrasonic displacement sensors, is based on the Doppler effect. An instrument typically contains a laser radiation source, a receiving optical circuit, and an electronic processing circuit (Figure 2). When reflecting radiation from a stationary object, the wavelength of the received beam does not differ from the true laser wavelength. If the object moves along the axis of radiation, the reflected wavelength is shifted by a certain amount (Doppler effect), the value and sign of which carry information about the speed and direction of movement of the object, and the interferometric scheme used in the receiving optical module allows this value to be determined. Thus, the oscillations of the reflecting surface modulate the frequency shift, and the electronic processing of this modulation signal allows you to obtain the parameters of vibrational vibrations.
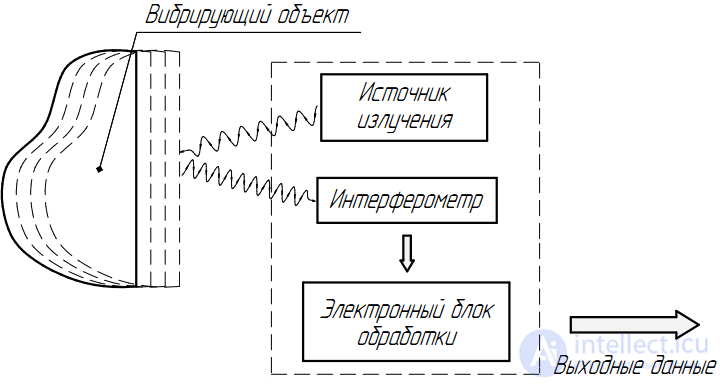
Figure 2. Schematic of an optical vibrometer.
Despite the fact that the composition of optical vibrometers includes a laser radiation source, such devices are quite safe, because due to the high sensitivity of the receiving optical system, very small optical power is sufficient for measurements.
One of the main advantages of optical vibrometers is that they can be used for non-contact diagnostics; when they are used in a stationary measuring complex, only one focus is needed on the measured surface. In addition, devices of this type have high accuracy and speed, since they are devoid of moving elements. The disadvantages include a rather high price.
As the name implies, the operation of this type of instrument is based on the piezoelectric effect — the phenomenon of the appearance of a potential difference on a piezocrystal during its mechanical deformation. Inside the vibrometer case, an inert body is suspended from elastic elements containing piezoelectric material (Figure 3). If the device’s body is attached to a vibrating surface, the elastic elements will register vibrations of an inert body, which is not attached directly to the body, and therefore tends to maintain its original position. In general, in this configuration, a piezoelectric vibrometer is nothing but an accelerometer, and it is often quite difficult to draw a line between these types of sensitive devices.
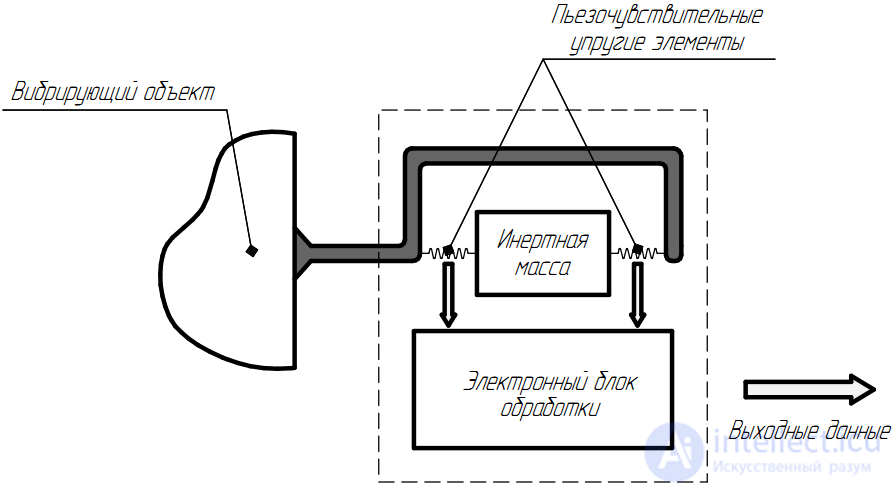
Figure 3. Diagram of a piezoelectric vibrometer.
An electric signal from a piezocrystal, as a rule, is fed to an analog-to-digital converter, and its processing is carried out in digital form. In general, as in the case of an optical vibrometer, the main purpose of the receiving sensitive unit is to convert vibration into an electrical signal, and the nature of its further processing is determined by the parameters of the digital electronic circuit.
The main disadvantage of this class of devices is the need for the sensitive part to come into contact with the measured object, which is not always appropriate in the production environment. In addition, piezoelectric devices have, as a rule, a narrower range of perceived frequencies, since they have a mechanical vibration transmission path, where the maximum frequency is determined by the inertia of the components.
The advantages of piezoelectric vibrometers include their relatively low cost, as well as a relatively simple device, which ensures reliability and resistance to external influences.
Comments
To leave a comment
Sensors
Terms: Sensors