Lecture
Among ordinary fractions there are two different types.
Consider fractions.
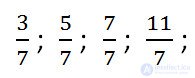
Note that in the first two fractions (3/7 and 5/7) the numerators are less than the denominators. Such fractions are called correct.
The correct fraction has a numerator less than the denominator. Therefore, the correct fraction is always less than one.
Consider the two remaining fractions.
The fraction 7/7 has a numerator equal to the denominator (such fractions are equal to one), and the fraction 11/7 has a numerator greater than the denominator. Such fractions are called incorrect.
A wrong fraction has a numerator equal to or greater than the denominator. Therefore, an improper fraction is either equal to one or greater than one.
Any wrong fraction is always more correct.
In the wrong fraction, you can select the whole part. Consider how this can be done.
To extract the whole part from an improper fraction:
Example. We extract the integer part of the irregular fraction 11/2.
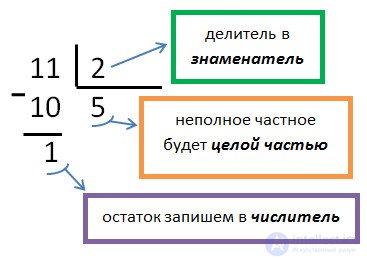
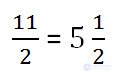
The resulting number above, containing the integer and fractional part, is called a mixed number .
We received a mixed number from an irregular fraction, but you can also perform the opposite action, that is, you can represent the mixed number as an improper fraction .
To represent a mixed number in the form of an improper fraction:
Example. Imagine a mixed number in the form of an improper fraction.
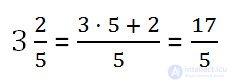
Any mixed number can be represented as the sum of the integer and fractional parts.
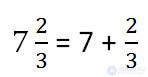
Any natural number can be written with a fraction with any natural denominator.
The quotient of dividing the numerator by the denominator of such a fraction will be equal to the given natural number.
Examples
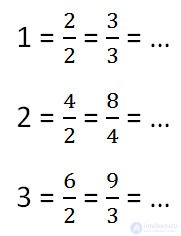
Comments
To leave a comment
Arithmetic
Terms: Arithmetic