Lecture
Back in 1969, a group of engineers at Bell Labs, a member of AT & T, decided to create an operating system that would be multitask (could perform several tasks at the same time), multi-user (at the same time several users could work) and mobile (could run on different platforms). This is how the UNIX project was born. Thus was born the programming language C. Creating the first and unix-system (and several subsequent versions), the specialists were not greedy and willingly shared the source codes with the universities, which contributed to the growing popularity of the new OS. Some universities based on UNIX source codes created their own operating systems (for example, BSD ). And here you should make an important conclusion for yourself that the UNIX operating system was created, as they say, by professionals for professionals. Linux , which also comes from UNIX, inherited all its positive aspects. This is a system that was not designed for home users and reliability and stability have always been a priority to the detriment of simplicity and convenience (unlike Windows , for example, which was originally developed for the home and its opposite tasks were priorities). You probably already know that Linux started developing Linus Ben Tort ( Linus Benedict Torvalds ) in 1991, when he was a student at the University of Helsinki. To be more precise, Torvalds wrote the Linux kernel (version 0.1 was published in the same 1991.). The kernel is the foundation of the operating system. It is, so to speak, the pivot around which everything else is built. It is also necessary to distinguish between the concepts of Linux and the distribution based on Linux . Look at Figure 1.
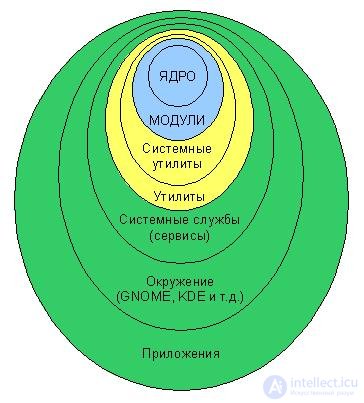
Picture 1
The figure shows schematically the main components of the Linux distribution. The kernel is a single file called vmlinuz-хххххххххх (where хххххххххх is the kernel version) located in the / boot directory. Although initially the core was completely monolithic in the future, some functions were transferred to separate modules. Modules are located in the / lib / modules directory. System utilities allow you to interact with certain functions of the kernel. Utilities are programs that allow you to perform some action in the operating system itself (creating files, copying, etc.). Actually, these 4 levels - the kernel, modules, system utilities and utilities - are Linux . But the system services, graphical shells and all sorts of software together with Linux- levels make up - distributive. For example, Ubuntu , Fedora , Knoppix , OpenSuse are all Linux-based distributions . The kernel is engaged in the development of a com *** and under the guidance of Linus Torvalds. Development and filling distributions involved other companies. For example, the Ubuntu distribution is developed by Canonical Ltd. This course is dedicated to the study of Linux , and not any specific distribution. Most of the commands and examples will work on most modern distributions. Therefore, almost without a difference on the basis of what distribution you will learn Linux . Having understood the volume of HOW Linux works and WHY it works like this and not the other way, you can quite easily cope with any distribution.
Comments
To leave a comment
LINUX operating system
Terms: LINUX operating system