Lecture
.

Peasant family. XIX century.
Family is a social institution, the basic unit of society [1] [2], characterized, in particular, by the following features [3] [4] [5] [2] [6]:
The family belongs to the most important social values [7]. According to some scientific theories, it was the form of the family that for many centuries could determine the general direction of evolution of macrosocial systems [8]. Each member of society, in addition to social status, ethnicity, property and financial status, from the moment of birth to the end of life has such a characteristic as the family and marital status.
At the stages of a person’s life cycle, his functions and status in the family consistently change. For an adult, a family is a source of satisfaction of a number of its needs and a small team that presents various and rather complex requirements to it. For a child, a family is an environment in which the conditions of its physical, mental, emotional and intellectual development take shape.
The content of the concept of "family" is transformed following the sociocultural change of society [9]. A family can also be understood as a parent couple or one parent with at least one child [10], as well as same-sex unions legalized in a number of countries [11].
A family is a community based on the marriage of spouses (father, mother) and their single children (own and adopted) spiritually connected with common life and mutual moral responsibility. The family is created on the basis of marriage, kinship, adoption, as well as on other grounds not prohibited by law and such that do not contradict the moral foundations of society.
Despite its general use, the concept of a family is quite multifaceted, and its clear scientific definition is rather difficult. In different societies and cultures, the definition of a family may vary in some way. In addition, often the definition also depends on the area in relation to which this definition is given. There are many definitions of the family. Each of them depends on the specific historical, ethnic and socio-economic conditions, as well as on the specific objectives of the study [12] [13].
According to the classical definition of one of the largest English sociologists Anthony Giddens, a family is understood as “a group of people connected by direct kinship, whose adult members take upon themselves the obligations to care for children.” In the context of this definition, kinship relations are considered to be relations arising from marriage (that is, recognized and approved by the society of the sexual union of two adults) or resulting from blood ties between individuals [14]. A family is a small group based on marriage or kinship, the members of which are connected by common life, mutual assistance, moral and legal responsibility [15] [9].
In law, a family is a legitimate social institution under the protection of the state. As a rule, a “full family” in a legal sense consists of a father, mother, and child (or children); “Incomplete family” - from a father with a child (or children) or a mother with a child (or children) [12]. In Russian family law, a family is defined as a circle of persons related by personal non-property and property rights and obligations arising from marriage, kinship, adoption [16].
The genealogical definition of a family represents it as a collection of people related by blood or property. This definition, on the one hand, is broader than the legal definition of a family, on the other hand, it excludes adoptive parents and children from the list of family members [17].
The psychological approach to the family (in particular, Klaus Schneewind (German Klaus Schneewind ) adheres to this approach) means by a family a certain set of individuals that satisfies four criteria [18]:
The social aspect in the definition of the concept of family dominated in socialist society, according to the position of Marxism that “the family gives us a miniature picture of the same opposites and contradictions in which society moves ” [19]. At different historical stages of development of family relations, territorial and economic aspects prevailed. For example, in France, “ the concept of a family included a group of persons locked up at night behind one lock ” [20], and Russian zemstvo statistics when conducting household censuses determined the family according to the number of eaters, based on the fact that “ according to the idea of peasants, the concept of family includes a circle of people who constantly eat at the same table or who eat from the same pot ”[21]. However, with all the importance of the socio-economic function of the family, it should be distinguished from the household, which can lead both an individual and a group of people not related by kinship relations. Similarly, living on the same living space can not be today decisive in the understanding of the family. At all times, the basis of it still remains a purely biological concept of a married couple, cohabiting with their descendants and elderly representatives of the older generation.
In Russian, there is an attitude towards the family and its members (from the first person) as to property (belonging) - my family, my wife, my children or emphasizes (from the side) the attitude to the family and its members - the Fyodor family, Fyodor's wife, children Fedor (and Mary).
Russian demographic science is interested in the family as a precondition for the reproduction of the population, as a unique social institution, a specific function of which is the birth of children, the reproduction of generations, of the population as a whole. Therefore, the Russian demography from the entire possible diversity of family structures of the population identifies and studies only those that are directly and directly connected with the reproduction of the population, which makes it sharply different from the demographic science of Western countries [22].
In 1992, in Russia, for the first time after World War II, the death rate exceeded the birth rate. Since 1993, there has been a steady decline in population, similar to the situation when the state is in a state of war. At the same time, the processes of progressive aging of the population are developing. For the first time, the number of Russians over 60 years old exceeded the number of minors under 15 years of age in 1999. And still exceeds. See. Interactive Russian population counter.
It is expected that after 2010 [23], a new demographic wave will start, when men and women who were born already in the 1990s will start getting married and acquiring children. that is, at the time when Russia had the lowest birth rate in the entire history of the country. As a result, there will be the smallest generation that enters the reproductive age. The proportion of women aged 20 to 29 by the beginning of 2025 will be almost halved. If the intensity of the birth rate among women of this age persists further, then for every percentage reduction in their number, the number of births in the country will also decrease. According to the All-Russian Census of 2002 [24], the number of families with three or more children does not exceed 6%. And for a positive reproduction of the population, it is necessary that, on average, in each family, three children are brought up. According to the “Summary of the results of the pilot survey“ Family and fertility ”, the average desired number of children, that is, the number of children that the respondents would like to have if all the favorable conditions are present, does not exceed three children. The desired number of children is, on average, somewhat higher only among respondents with a religious outlook. At the same time, the expected number of children is noticeably lower, that is, the number of children that respondents are ready to have: it does not even reach two.
The population policy in Russia, aimed at increasing the birth rate, is developing in the following areas:
The second direction is a priority from the assumption that “a change in attitudes towards an increase in the need for children can give a disproportionately greater result than an improvement in living conditions ” [25].

Holy Family with St. Anne and John the Baptist. Agnolo Bronzino painting, approx. 1530

Old Family (picture by Francisco Goya)
The Russian word “family” is of Slavic and Indo-European origin (cf. lit. Šeima), going back to the meaning of a territorial community [26] [27] (cf. lit. Zeme: Earth). In the Old Slavic and Old Russian languages, the word family meant both the family in general (all members of the family living together) and the servants, household members, serfs [28].
The scientific study of the forms of family life began in the 19th century and was connected with the works of I. Bachofen, L. Morgan [29], MM Kovalevsky. In particular, it was shown that the type of family to a high degree was dominated by the nature of the further evolution of the corresponding society [30].
Before World War II, the patriarchal family prevailed in Russia, which was characterized by the predominance of the man in the house and the subordination of all other family members to him. In the post-war years, from the end of the 40s to the 80s, the children-centrist family became dominant, in which the welfare of children and the preservation of marriage in the interests of children are very important. More recently, in recent decades, a married family [ source not specified 2386 days ], in which equal relations dominate, the stability of a marriage depends on the desires and the quality of relations between spouses. The economic independence of women, the improvement of their social status inevitably presupposes a different type of partner marriage . Many researchers have noted a change in the functions of the family in the direction of its greater psychologization and intimization. In the 20th century, there was a transition from a marriage of convenience or a duty to a marriage of love. On the one hand, as Kon I. S notes, this is a great achievement of humanity, but on the other hand, such a marriage presupposes a greater frequency of dissolution of marriages on psychological grounds, such as, for example, “dissimilarity of characters”, which leads to less stability of marriages. As Kohn notes, the main trend underlying all these processes is a change in value orientations , in the center of which now stands not the family group, but the individual [31].
The socio-psychological attitudes towards fertility have also changed. The judgments that “the duty of every woman to become a mother” and “the duty of every man to raise children” are more often accepted by the representatives of the older than the younger generations. Especially noticeable shifts in the attitudes of women. To the question “Should every woman become a mother?” Among those surveyed in the late 1990s. Petersburg women from 18 to 29 years old answered only 20% in the affirmative, and among 30-39-year-olds only 17%. This means that motherhood, which religious morality has always considered to be the main hypostasis of a woman, becomes only one of her social identities. In the ideas of Russians about the fair distribution of family functions and the duties of mother and father, traditionalist attitudes are struggling with egalitarian, accompanied by harsh mutual accusations of men and women.
Signs of family transformation began to manifest themselves in the developed countries of Europe as early as the mid-1960s, and in other European countries — from the late 1980s to the early 1990s. The list of the most important changes in the state of the family was summarized by Dirk van de Kaa [32]:
From the standpoint of population reproduction, a very important criterion for building a demographic typology of families is the stage of the family life cycle. The family cycle is determined by the following stages of parenthood:
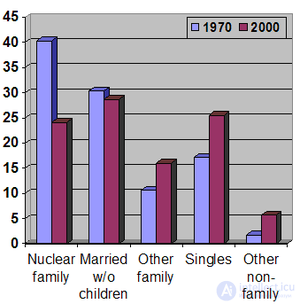
The evolution of family types in the United States from 1970 to 2000 [34]
The family structure, as well as the marriage one, is a moment indicator recorded during censuses or special population surveys. Therefore, to give an idea of the family structure of the population is possible only according to censuses or surveys. At the same time, the practice of demographic statistics distinguishes families as follows:
It is noteworthy that in Russia until 1992, only mothers who raised 5 or more children were considered large (for demographic achievements, awards were awarded: Medal “Motherhood Medal” II and I degrees - awarded to mothers who raised 5 and 6 children; Order “Maternal Glory” III , II, I degrees - awarded to mothers who raised 7, 8 and 9 children respectively, the Order “Mother Heroine” was awarded to mothers who raised 10 or more children). Today, officially, “having many children” starts from three children, that is, a medium-sized family is already considered a large family. Such a family in terms of the number of children today is the most optimal, comfortable for the state, and enjoying comprehensive social support in accordance with Presidential Decree No. 431 of May 5, 1992 “On Measures for Social Support of Large Families”.

The modern American family, including all relatives, of the middle class from the Midwest [35]
Modern Spanish family, including all relatives [36]
In the integrated study of family structure, they are considered in a complex combination. From a demographic point of view, several types of families and their organizations are distinguished.
Depending on the number of partners:
В зависимости от количества детей:
В зависимости от состава:
В зависимости от отношений между родителями и детьми:
Виды семей в зависимости от способов выбора семейного партнера:
В зависимости от места человека в семье:
В зависимости от проживания семьи:
Наследование по отцовской линии означает, что дети берут фамилию отца (в некоторых культурах и имя), и собственность обычно переходит по мужской линии. Такие семьи называются патрилинеальными . Наследование по женской линии означает матрилинеальность семьи.
Вопросами классификации современных семей занимался Торохтий В. С.[38]
Каждую из категорий семей характеризуют протекающие в ней социально-психологические явления и процессы, присущие ей брачно-семейные отношения, включающие психологические аспекты предметно-практической деятельности, круг общения и его содержание, особенности эмоциональных контактов членов семьи, социально-психологические цели семьи и индивидуально-психологические потребности её членов.
Об особенностях демографического развития семьи в России можно узнать из статьи «Демографическая ситуация в Российской Федерации».
| Наименование групп семей | Факторы, характеризующие данную группу |
|---|---|
| 1-я группа (оптимальная), | Высшее образование родителей. Высокий культурный уровень семьи. Высокая материальная обеспеченность. Хорошие жилищные условия. Здоровая в психологическом отношении атмосфера. Отсутствие вредных привычек. По состоянию здоровья — оптимальная. |
| 2-я группа (хорошая) | Высшее и среднее образование родителей. Высокий и удовлетворительный культурный уровень. Хорошие материально-бытовые условия. Благоприятные отношения в семье. Вредные привычки, кроме злоупотребления алкоголем. По состоянию здоровья — оптимальная. |
| 3-я группа (удовлетворительная) | Один из показателей является неудовлетворительным (культурный уровень, жилищные условия, взаимоотношения в семье). По состоянию здоровья — удовлетворительная. |
| 4-я группа (неудовлетворительная) | Наличие в семье двух и более неудовлетворительных из перечисленных показателей. Низкий уровень культуры. Неблагоприятный психологический климат в семье. Вредные привычки — злоупотребление алкоголем. По состоянию здоровья — неудовлетворительная. |
Социологи выделяют несколько функций семьи[39]:
Исследователи единодушны в том, что функции отражают исторический характер связи между семьёй и обществом, динамику семейных изменений на разных исторических этапах[40]. Современная семья утратила многие функции, цементировавшие её в прошлом: производственную, охранительную, образовательную и др.
Под функцией семьи следует понимать внешние проявления свойств какого-либо субъекта в данной системе отношений (семье), определённые действия по реализации потребностей. Функция отражает связь семейной группы с обществом, а также направленность её деятельности. Однако часть функций являются устойчивыми к изменениям, в этом смысле их можно назвать традиционными. К ним можно отнести следующие функции:
а) репродуктивная — в любой семье важнейшей является проблема деторождения. Цельность сексуальной потребности, обеспечивающей продолжение рода, и любви как высшего чувства делает невозможным отделение одного от другого. Супружеская любовь в значительной мере зависит от характера удовлетворения сексуальных потребностей, особенностей их регулирования и отношения супругов к проблеме деторождения, самим детям;
б) хозяйственно-экономическая — включает питание семьи, приобретение и содержание домашнего имущества, одежды, обуви, благоустройство жилища, создание домашнего уюта, организацию жизни и быта семьи, формирование и расходование домашнего бюджета;
в) регенеративная — (лат. regeneratio — возрождение, возобновление). Означает наследование статуса, фамилии, имущества, социального положения. Сюда же можно отнести и передачу каких-то фамильных драгоценностей[41];
вовсе необязательно буквально понимать под «драгоценностями» ювелирные украшения, их можно передать любому постороннему, а вот такую драгоценность, как альбом с фотографиями, чужому человеку не передашь — только своему, родному
d) educational - (socialization [42]). Consists of the need for paternity and motherhood, contact with children, their upbringing, self-realization in children [43];
Family and social education are interrelated, complement each other and can, within certain limits, even replace each other, but in general they are unequal and under no circumstances can become such. Family education is more emotional in nature than any other upbringing, because its “guide” is parental love for children, causing children to respond to parents;
e) the sphere of initial social control - moral regulation of the behavior of family members in various spheres of life, as well as regulation of responsibilities and obligations in relations between spouses, parents and children, representatives of the older and middle generations;
e) recreational - (lat. recreatio - recovery). It is associated with recreation, leisure activities, care for the health and well-being of family members.
g) spiritual communication - the development of personalities of family members, spiritual mutual enrichment;
h) social status - the provision of a certain social status to family members, the reproduction of social structure;
and) psychotherapeutic - allows family members to meet the needs for sympathy, respect, recognition, emotional support, psychological protection.
While the traditional functions began to weaken dramatically, this new, previously unknown, psychotherapeutic function emerged [41].
Marriage is successful or not, depending on the activation of this function, that is, at present, family existence largely depends on the stability of close emotional relationships.
Family Psychology
The family as a complex education becomes the object of attention of various sections of psychology: social, age, clinical, pedagogical, etc. The subject becomes the family as a social institution, a small group and an open self-organizing system.
In the scientific literature, synonymous with the concept of "psychological climate of the family" are "the psychological atmosphere of the family", "the emotional climate of the family", "the socio-psychological climate of the family." It should be noted that there is no strict definition of these concepts. For example, O. A. Dobrynina refers to the socio-psychological climate of a family as its generalized, integrative characteristic, which reflects the degree of satisfaction of spouses with the main aspects of the family’s activity, general tone and style of communication.
The psychological climate in the family determines the stability of family relations, has a decisive impact on the development of both children and adults. He is not something unchangeable, given once and for all. It is created by members of each family, and it depends on their efforts how favorable or unfavorable it will be and how long the marriage will last. So for a favorable psychological climate the following signs are characteristic: cohesion, the possibility of comprehensive development of the personality of each of its members, the high benevolent demands of family members to each other, a sense of security and emotional satisfaction, pride in belonging to their family, responsibility. In a family with a favorable psychological climate, each of its members treats the rest with love, respect and trust, parents - also with reverence, the weaker - with the willingness to help at any moment. Important indicators of a favorable psychological climate for a family are the desire of its members to spend their free time in the home circle, talk about all the topics of interest, do homework together, emphasize the dignity and good deeds of each. Such a climate contributes to harmony, reducing the severity of conflicts that arise, relieving stressful states, increasing the assessment of one’s own social significance and realizing the personal potential of each family member. The initial basis for a favorable family climate is matrimonial relations. Joint life requires the spouses to be willing to compromise, the ability to reckon with the needs of a partner, to give in to each other, to develop such qualities as mutual respect, trust, and mutual understanding.
When family members experience anxiety, emotional discomfort, alienation, in this case they talk about an unfavorable psychological climate in the family. All this prevents the family from performing one of its main functions - psychotherapeutic, relieving stress and fatigue, and also leads to depressions, quarrels, mental tension, deficit in positive emotions. If family members do not seek to change this situation for the better, then the very existence of the family becomes problematic.
An important factor affecting the psychological climate of a family is its composition, as in incomplete families with children, an unfavorable psychological climate is most often formed [44].
Psychological climate can be defined as a more or less stable emotional mood characteristic of a family, which is a consequence of family communication, that is, it arises as a result of the aggregate mood of family members, their emotional experiences and worries, relationships with each other, towards other people, towards work, to surrounding events. It is worth noting that the emotional atmosphere of the family is an important factor in the efficiency of the family’s vital functions, and its overall health, it determines the stability of the marriage.
Many Western researchers believe that in modern society, the family loses its traditional functions, becoming an institution of emotional contact, a kind of "psychological haven." Domestic scientists also emphasize the increasing role of emotional factors in the functioning of the family.
V.S. Torokhtiy says about the psychological health of the family and that this “integral indicator of the dynamics of vital functions for it, expressing the qualitative side of the sociopsychological processes proceeding in it and, in particular, the ability of the family to resist the undesirable effects of the social environment” not identical with the concept of “socio-psychological climate”, which is more applicable to groups (including small ones) of heterogeneous composition, often uniting their members on the basis of professional activity and they have ample opportunities to leave the group, etc. For a small group that has kinship ties that provide a stable and long-lasting psychological interdependence, where intimacy of interpersonal intimate experiences remains close to each other, where the similarity of not one, but one common family goals, and the flexibility of their priority and targeting is preserved, where integrity is the main condition for its existence - the term “psychological health of the family” is more acceptable.
Psychological health is a state of spiritual psychological well-being of the family, which provides adequate regulation of the behavior and activities of all family members, which are adequate to their living conditions. The main criteria for the psychological health of the family BC Torokhti considers the similarity of family values, functional and role consistency, social role adequacy in the family, emotional satisfaction, adaptability in microsocial relations, aspiration for family longevity. These criteria for the psychological health of the family create a general psychological portrait of the modern family and, above all, characterize the degree of its well-being.
The impact of family relations on the mental development of the individual
Family values
Family traditions are the usual norms in the family, behaviors, customs and attitudes that are passed down from generation to generation. Family traditions and rituals are, on the one hand, one of the important signs of a healthy (by definition V. Satir) or functional (by definition E. Eidemiller and other researchers) family, and, on the other hand, the presence of family traditions is one of the most important mechanisms for transferring the laws of intrafamily interaction to the next generations of a family: the distribution of roles in all spheres of family life, the rules of intrafamily communication, including ways to resolve conflicts and overcome emerging problems Family traditions and ceremonies are based on social, religious and historical traditions and ceremonies, but are creatively transformed and complemented by their own, therefore they are unique for each family.
V. Satir considered healthy [45] families in which:
In turn, the dysfunctional family, in the opinion of Russian psychotherapists Marik and Ev Hazin, is characterized by:
The system of traditional for the Russian national culture beliefs, in the opinion of senior schoolchildren, contains the conviction that “a man and a woman in a family must fulfill various roles”, “a man is a stronghold of a family, a source of well-being and a defender, one who solves problems”, “the main sphere the activities of women in the family - domestic work and raising children "," a woman must be patient, compliant and ready for self-sacrifice "," parents must take care of raising children ", and" children must respect their parents ". Negative attitude towards infidelity of spouses is noted as an important conviction: “husband and wife should be faithful to each other, love each other and support both in joy and in sorrow, in illness and in old age”.
Pupils attributed to traditional forms of behavior in the family that “the right to make a proposal to create a family belongs to a man (the groom)”; “Many family events (marriage, birth of children, care of family members) are covered by the church,” that is, there are wedding ceremonies, baptisms, funerals; "The decisive word in solving any issues belongs to the man." The greatest difficulty was caused by the question of the leading discussion of what are the national traditions in the upbringing of children. In addition, it turned out that even those schoolchildren who know about differences in religious practices associated with family life (wedding, child baptism) in different religious denominations, do not know what exactly these differences are. The main difference states “tougher subordination of the wife to the husband by Muslims”, “women in the Muslim family have less rights than in Orthodox families”. The majority of schoolchildren could not explain the meaning of those ceremonies that they indicated as national family traditions: the meaning of wedding ceremonies, baptisms and funerals.
“This is undoubtedly due to the fact that in 52% of families parents and representatives of older generations either do not adhere to folk traditions and customs at all (more than 5%) or follow traditions irregularly (47%). All this leads to the fact that the majority of schoolchildren (58.3%) are convinced that in their future family life they do not have to follow the customs and traditions of their people. ”[47].
Ethnocultural marriage and family traditions in one way or another were persecuted and supplanted by unified demands. Changing in accordance with the requirements of the environment of a higher order, the family maintains family traditions as one of the main ways of educating and continuing themselves. Family traditions bring together all relatives, makes them a family, and not just a community of blood relatives. Home customs and rituals can be a kind of vaccination against the separation of children from their parents, their mutual misunderstanding.
Comments
To leave a comment
Interpersonal relationships
Terms: Interpersonal relationships