Lecture
Qualimetry (from the Latin "qualis" - which is the quality and the Greek "metreo" - measure, measure) is a scientific discipline, within the framework of which the methodology and problems of a comprehensive, quantitative assessment of the quality of objects of any nature: animate or inanimate, objects or processes, products labor or products of nature that are material or spiritual in nature (of course, the object of application of Qualimetry methods can be any constructive and technological solution if its quality is to be subjected to qual metric analysis). Qualimetry is an area of practical and scientific. activities related to the development of theoretical foundations and methods for measuring and quantifying quality.
Qualimetry is an integral part of qualiology - the science of quality. The object of Qualimetry is the study of the principles and methods of quality assessment, and the subject is a set of quality properties of objects and processes with which a person contacts in their practical activities. Qualimetry is usually divided into theoretical, studying the problems of quality assessment in general, and applied, considering the issues of quality measurement in relation to specific objects. Qualimetry as a science is going through a period of formation, which explains the lack of consensus on a number of issues. Being largely a scientific discipline of interdisciplinary nature, Qualimetry on many issues intertwines with specific engineering disciplines: standardization, metrology, economics, production organization, law, psychology, etc., and an entire group of mathematical theories is included in its apparatus.
The ultimate goal of Qualimetry is the development and improvement of methods by which the quality of a particular object being evaluated can be expressed by one number characterizing the degree to which a given object meets a public or personal need. In addition, such techniques allow us to solve other problems of qualimetric analysis. From the point of view of accuracy and reliability of the obtained quality estimates, the methods used in Qualimetry are divided into exact (being the most time-consuming, but providing maximum accuracy and reliability achievable at the time of development), approximate and simplified (not requiring significant costs, but less accurate and reliable) .
Qualimetry has developed several approaches to quantitative quality assessment. The most common of them is based on the following principles:
1) quality is a combination of only those properties of an object that are associated with the result achieved with its help (but not with the costs incurred) and which manifest themselves in the process of consumption (operation, use) of the object in accordance with its purpose;
2) some complex and any simple properties can be measured using an absolute property index 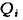 , (i = 1, n; n is the number of properties of the object being evaluated). The resulting Q values are expressed in units specific to each property. For measurements can be used metrological, expert, analytical methods;
, (i = 1, n; n is the number of properties of the object being evaluated). The resulting Q values are expressed in units specific to each property. For measurements can be used metrological, expert, analytical methods;
3) all properties that form quality form a hierarchical structure in the form of a property tree. The lower tier of this tree (the root of the tree) is the most complex property - the quality of the object, and the branches of the higher tier represent simple and quasi-simple properties;
4) for comparison of various properties measured in scales, different in scope and dimension, a relative dimensionless indicator is used 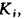 reflecting the degree of approximation of the absolute property index
reflecting the degree of approximation of the absolute property index 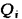 to reference
to reference  and rejection
and rejection  indicators characterizing the highest and lowest levels of social needs. Relative indicator is described by dependency.
indicators characterizing the highest and lowest levels of social needs. Relative indicator is described by dependency. 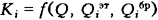 which, in the case of a simplified qualimetry method, can be represented by a normalizing function
which, in the case of a simplified qualimetry method, can be represented by a normalizing function
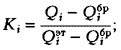
5) to compare the relative importance of all the properties included in the "property tree", use the dimensionless weight coefficients 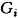 . For convenience, usually taken
. For convenience, usually taken 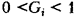 , but
, but 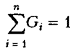 . The values of weight coefficients are determined with the involvement of varieties of expert and non-expert (analytical) methods;
. The values of weight coefficients are determined with the involvement of varieties of expert and non-expert (analytical) methods;
6) the quantitative assessment of quality is expressed using the indicator 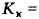
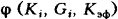 . Function
. Function  can be expressed by different polynomials, averages, etc. (see: Additive quality indicators). When using the simplified Qualimetry method, this function can very often be expressed by the formula
can be expressed by different polynomials, averages, etc. (see: Additive quality indicators). When using the simplified Qualimetry method, this function can very often be expressed by the formula 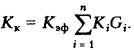
7) if, in addition to the quality of the object, it is necessary to take into account the costs of its production and consumption (use, operation) - the so-called total costs (of which the reduced costs used in the theory of economic efficiency) are used, then the integral quality indicator, the definition of values which is based on the same principles.
One of the main problems of QC, which is usually solved empirically, is the development of an algorithm for converting object parameters into its quality indicators and, in particular, a targeted search for the minimum set of properties (indicators) that form the object quality. The problem of choice is to identify certain groups of indicators that would satisfy the requirements of their necessity, sufficiency and independence.
To solve this problem, a functional-typological analysis can be used, based on the consideration of quality as a system. At the same time, external consumer qualities (properties) are distinguished, according to which they are judged on the suitability of products to meet certain needs in accordance with the purpose, and internal consumer qualities - physical, causing external qualities and characterizing the object (created and operated) as having the structure of interrelated physical properties of its components items.
The classification of quality indicators is similar to the classification of technical system indicators. Quality assessment is often carried out in order to solve the problem of optimizing the quality of an object, i.e. achieving the best ratio between the useful effect obtained from using the object and determining the degree of conformity of the object of assessment to a given standard.
Optimization of quality assessment is usually a multi-objective task (see: Technical level of products, Quality indicator of technical objects, Quality of technical objects).
Comments
To leave a comment
Qualimetry reliability and quality
Terms: Qualimetry reliability and quality