Lecture
Lecture questions:
1. Weight coefficients
2. Basic methods for determining weight coefficients
3. Calculation of weight indicators
The weight coefficient of the product quality indicator is a quantitative characteristic of the significance of this indicator.
telia among other indicators of quality.
Usually, when calculating the level of quality, weight proportional factors are used, provided that the sum of all values of weight coefficients is equal to one, i.e. 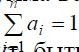
However, weighting factors can also be expressed in points or percentages. The choice of formulas for calculating weighting factors is chosen when the condition of viability is fulfilled.
To determine the values of weighting coefficients, analytical and expert methods are used, respectively, in accordance with GOST 24294-80 and GOST 23554-79.
2. Basic methods for determining weight coefficients
There are four methods for determining weight coefficients:
To determine the weighting coefficients use indicators of the properties of several similar products. If the number of investigated products is equal to or exceeds the number of selected quality indicators, then the method of registration is used to determine the numerical values of weight coefficients .
analysis of parametric quality indicators.
The method of determining weight coefficients by cost regression dependencies is based on the construction of dependencies between the costs of creation and operation and initial indicators of product properties.
This method is applicable under two conditions:
a) cost dependencies are defined for products that are produced for a long time and are in steady demand, i.e. is not scarce or "unmarketable";
b) the number of quality indicators included in the cost dependence is not large.
The method of limiting and nominal values is based on the use of known maximum permissible values of indicators of product properties that determine the requirements for a suitable product or its belonging to this category of quality.
This method is used when the limiting values of quality indicators are determined correctly and their reliability is confirmed by a long term use.
The method of equivalent ratios should be applied only in cases when it is possible to substantiate which relative change in the quantity of products.
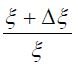
equivalent (provided that the overall effect of the use of the product is constant) the relative change in the corresponding quality indicator
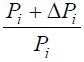
In other words, it is necessary, for example, to know by how many percent it is possible to reduce the number of units of manufactured products in order to satisfy the same needs if this quality indicator changes by one percent or by a given amount.
The weighting factors of property indicators determined by a particular method are usually contained in industry-specific regulatory and technical documents (most often in industry standards) for homogeneous groups or types of products.
If the number of single quality indicators reflected in industry standards does not coincide with the number of single indicators or groups of quality indicators of the product being assessed, as well as similar products, the values of weighting factors are recalculated.
With a smaller than in the standards, the number of single indicators or groups of indicators of properties recalculation of weight coefficients is made according to the formula:
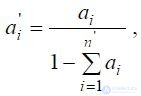
Where 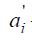 - the value of the weight coefficient of the i- th indicator (group) after recalculation;
- the value of the weight coefficient of the i- th indicator (group) after recalculation;
ai is the value of the weight coefficient of the i- th indicator according to the standard;
 - the sum of the weight coefficients of the relevant indicators;
- the sum of the weight coefficients of the relevant indicators;
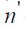 - the number of missing indicators.
- the number of missing indicators.
With more than in the standards, the number of indicators of the properties that make up the quality, recalculation is performed according to the formula:
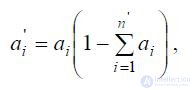
n` - the number of additional indicators of properties;
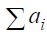 - the total value of the weight coefficients of the complemented indicators of properties.
- the total value of the weight coefficients of the complemented indicators of properties.
The methods described above for analytically determining the values of weight coefficients are based on the initial information and differ in the methods of calculations. However, when applied correctly, they give approximately the same results.
Methods of expert determination of the weighting coefficients of individual properties of the object being evaluated consist essentially in averaging the values of the coefficients given by several experts.
A. Method of regression analysis of parametric quality indicators
In this method, the linear dependence of the complex index on the selected properties for the corresponding number of products is initially recorded.
These dependencies make up the following system of equations:
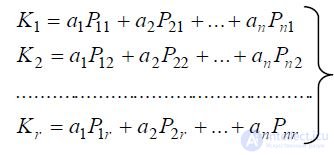
Where
Ki is the value of the complex indicator of the properties of the jth sample of the product ( j = 1, 2, ..., r ; r = n );
r is the number of complex indicators of product samples;
n is the number of indicators of product properties;
Pij is the value of the index of the property of the i- th quality of the j- th sample ( i = 1, 2, ... n );
ai is the weight coefficient of the i -th property index.
The weight coefficients ai are determined, by the mathematical least squares method of a similar system of equations, as its regression coefficients.
B. Method for determining weight coefficients by costing regression dependencies
If, for example, the cost dependence of a product on several indicators of its properties is known in the form:
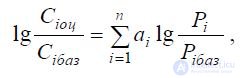
then ai are weight coefficients.
In this formula, the following notation:
Сi and Cibaz - cost (wholesale price) of the estimated product and the base sample, respectively;
Pi and Pibaz are indicators of the properties of the estimated product and the base sample, respectively;
ai - weighting coefficients determined by the least squares method;
n - the number of indicators of product quality
B. Limit and nominal value method
The parameter weight of the quality indicator, with a comprehensive assessment of product quality by the average weighted arithmetic index, is determined by the formula:
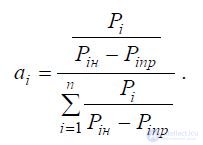
For the weighted average of the geometric index, the weight parameter is calculated by the formula:
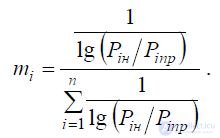
In the formulas given here
Pin - the nominal value of the indicator Pi;
Pipr - the maximum permissible value of the index Pi
G. Method of Equivalent Relations
Weight coefficients, determined by the method of equivalent ratios, calculated by the formula:

D. Method of expert determination of weight coefficients
The weight coefficient of the i- th product property is determined by the following formula:

where K i is the weight coefficient of the i- th property of the product;
Ai - the measured value of the i-th importance of the properties of the product;
 - the total value of the i-th importance of product properties
- the total value of the i-th importance of product properties
An example of the calculations of weights is presented in table 6
Table 6 The results of the expert survey to determine the weight properties of products
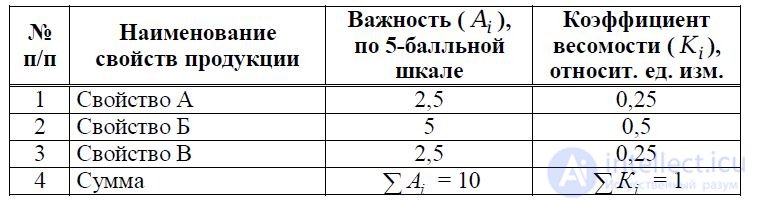
As a result of the calculation, a significant proportion of the weight coefficient falls on property B. The weight coefficient of properties A and B was distributed in equal parts.
Comments
To leave a comment
Qualimetry reliability and quality
Terms: Qualimetry reliability and quality