Lecture
Information architecture (. English Information Part architecture , often shortened to "Agency") - a combination of schemes for the organization, indexing and navigation, implemented in the information system.
Information architecture deals with the principles of organizing and navigating information to help people find and process the data they need more successfully.
Louis Rosenfeld [1]
Examples of
Web development is the process of creating a website or web application. The main stages of the process are web design, page layout, client and server side programming, and web server support.
Web design (from the English. Web design ) - a branch of web development and a kind of design, whose tasks include designing user web interfaces for sites or web applications. Web designers design the logical structure of web pages, think over the most convenient solutions for presenting information, and also decorate a web project. As a result of the intersection of two branches of human endeavor, a competent web designer must be familiar with the latest web technologies and possess the appropriate artistic qualities. Most of the specialists working in the field of design usually concentrate in such a creative education as a design studio.
Web design is a type of graphic design aimed at the development and design of objects of the information environment of the Internet, designed to provide them with high consumer properties and aesthetic qualities. Such an interpretation separates web design from web programming, emphasizes the specifics of the subject activity of a web designer, and positions web design as a type of graphic design [1].
Currently, web design services are provided by both specialized companies and individuals (web designers or webmasters who are freelancers).
Web designer is a relatively young profession, and professional education in the field of web design is not yet widespread in Russia. In connection with the increase in demand for representation on the Web, the demand for website design is growing, and the number of web designers is increasing.
Web design is one of the main nominations in the competitive program of the Youth Delphic Games in Russia.
Currently, the term web design is understood precisely to design the structure of a web resource, to ensure the convenience of using the resource for users. Recently, an important part of the resource design has been bringing the resource into compliance with the W3C standards, which ensures the availability of content for people with disabilities and users of portable devices (see usability - "usability"), as well as cross-platform (in this case - ie. n. cross-browser) layout of the resource. Also directly with the design of sites related to Internet marketing (Internet marketing), that is, promotion and advertising of the created resource, search engine optimization.
The project manager is responsible for drawing up technical specifications for specialists. Working with a customer begins with filling out a brief, in which the customer expresses his wishes regarding the visual presentation and structure of the site, points out errors in the old version of the site, gives examples of competitors' sites. Based on the brief, the manager draws up a technical assignment, taking into account the capabilities of software and design tools. The stage ends after the approval of the technical task by the customer. It is important to note right away that the stages of website design depend on many factors, such as the size of the site, functionality, tasks that the future resource should perform, and much more. However, there are several stages that are mandatory in the planning of any project.
Work begins with creating a design, usually in a graphics editor. The designer creates one or several design options in accordance with the terms of reference. At the same time, the design of the main page is created separately, and the designs of standard pages (for example: articles, news, product catalog). Actually "page design" is a graphic file, a layered drawing, consisting of the smallest picture-layers of elements of the general picture.
At the same time, the designer must take into account the limitations of the html standards (do not create a design that then cannot be implemented using standard html tools). The exception is Flash design.
The number of sketches and the procedure for their submission are discussed with the project manager. Also, the project manager controls the timing. In large web studios, an art director is involved in the process, who controls the quality of the graphics. The stage also ends with the approval of the sketch by the customer.
The approved design is transferred to the html-layout designer, who "cuts" the graphic image into separate images, from which the html-page is subsequently added. The result is code that can be viewed with a browser. Typical pages will later be used as templates.
Then the finished HTML files are passed to the programmer. Site programming can be carried out both "from scratch" and on the basis of CMS - content management system. CMS is often referred to as a "engine" by web developers.
In the case of the CMS, I must say that the "CMS" itself, in a sense, is a ready-made site, consisting of replaceable parts. The "programmer" - in this case, it would be correct to call him simply a CMS specialist - must replace the standard template that came with the CMS with the original template. This is the original template he has to create from the original "web design".
When programming a site, a specialist is assigned deadline milestones.
The web site design should look adequate in different browsers, especially Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome and Opera browsers.
Internet Explorer (version 6) interpreted HTML standards in its own way (echoes of the old struggle for leadership with Netscape). This obsolete browser posed a lot of problems for web designers. Many developers even suggested abandoning the layout for IE 6, however, the presence of this browser in the standard delivery of Windows XP, and hence its presence on many user computers, forced web designers to test their projects in it. As of summer 2012, IE 6 is used by 6% of users, mainly at the expense of China, where it is used by 21% of users [2].
The testing process can include a wide variety of checks: the appearance of the page with large fonts, with different browser window sizes, in the absence of a flash player, and many others. Found errors are sent for correction until they are eliminated.
The project manager controls the timing. Also at this stage, a designer is involved in the work so that he conducts architectural supervision.
Site files are placed on the provider's server and make the necessary settings. At this stage, the site is still closed to visitors.
The site is filled with content - texts, images, files for downloading, etc. Sometimes the texts are compiled by a studio specialist, sometimes the content is handled by a responsible person on the part of the customer. This is solved at the stage of drawing up the technical task. If the content is compiled by a representative of the studio, then this happens and is approved in parallel with other stages of the project.
Associated with some changes to the site itself. It starts with defining the semantic core. Here the keywords are determined that will attract the most interested visitors, for which it is easier to win the competition. Then these words are entered on the site. Texts, links, other tags are adapted so that search engines can successfully find them by keywords.
It usually comes down to building the structure of incoming links. This is actually promotion. External SEO optimization has nothing to do with website development. Since SEO-optimization is a kind of shamanism - it is like magic, classified into "white" and "black" - such, after which the site gets to the top in two weeks, and then to the ban. True white hat SEO is a time consuming and time consuming process, the cost of which can be several times higher than the cost of creating a website.
The customer or his authorized representative looks at the finished project and, if everything suits them, they sign the documents on the delivery of the project.
Also, at this stage, the customer's representative is trained to work in the administrator's area of the site.
A unique design is more expensive, but it also involves drawing from scratch, a completely unique development for a specific order. Depending on the professionalism and / or policy of the company, the web designer either develops the idea and concept of the design completely independently, or receives a number of requirements (color, style, etc.), expectations and ideas from the customer or the creative director (art director) and tries to stick to this direction when developing a layout. Most customers mistakenly equate a web designer and a webmaster, entrusting him with the publication of the site.
Sometimes a designer can offer a design solution based on templates (his own or even someone else's), this speeds up the work and will cost the customer less. Some designers even specialize in making design layouts for sale as ready-made templates, which can then be bought and used by less experienced designers or webmasters to make generic websites (essentially no unique designs). Sometimes a small re-layout and adaptation of such a template for a specific order is called web design development.
The final product of the web designer's work is a design layout: a picture representing the expected future appearance of the site's pages, approximately 960x640 px (pixels) - a size corresponding to the average standard associated with the need for further binding to different monitor screen resolutions. This picture is multi-layered, where, at the discretion of the designer, almost every detail is a separate layer attached to other picture layers, due to which revision, replacement, rearrangement and other tasks can be easily performed. Depending on the idea and goals, the layout can include photographs, complex collages, illustrations, text layers, unique icons. For the main page and internal pages, sometimes separate layouts are drawn with additions or changes in accordance with the topic of the page.
The image can initially be vector or raster, made in Adobe Illustrator, Adobe Photoshop, GIMP or another visual editor (for example, Scribus or Inkscape), but for a layout designer, the image is usually converted to a raster format.
For demonstration to the client, the image is usually translated into a simple one-layer and familiar image format.
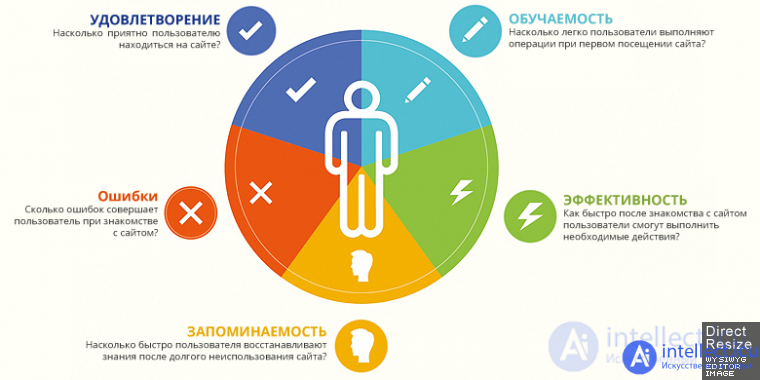
Ease of use , Usability (English usability - literally "the ability to use ", "the ability to be used ", " utility ") is a concept in microergonomics, an ergonomic characteristic [1] of the degree of convenience of an object for use by users when achieving certain goals in a certain context [2 ]. The term has a connection with the concept of " ergonomics ", but unlike the latter, it is less associated with technical aesthetics, with appearance and is more tied to the utility of the object used .
Usability is a scientific and applied discipline dedicated to improving the efficiency, productivity and usability of tools of activity. Usability is distinguished from ergonomics by the interest in the efficiency of the user (consumer), and not the human-machine system as a whole [3].
International standard ISO 9241-11 defines usability as
the degree to which a product can be used by specific users in a specific context of use to achieve specific goals with adequate efficiency, productivity and satisfaction
Moreover, the relative importance of all three aspects is determined by this very context.
Like many foreign terms that have recently come into use in the "post-Soviet space", the word "usability" is often used without taking into account its meaning in the original English and without regard to international standards of engineering terminology. As a rule, this happens due to the fact that the key moment of "certainty" for the context is ignored. Therefore, it often happens that "intuitiveness" for developers is not that for end users.
When developing user interfaces, the word usability denotes the general concept of their convenience when using software, consistency and simplicity in the arrangement of controls. However, at the same time, there is often a substitution of concepts - utilitarian aesthetic. Then the usefulness of a particular solution for the user, clearly not clearly defined for purposes and not justified in details , is taken for granted, arising from the originality of the appearance.
The term "usability" can be regarded as a synonym for the word "ergonomics" with the difference that the latter determines the minimum of specific physical efforts when using a thing, and the former determines the final total degree of convenience, a measure of intellectual effort required to obtain useful qualities of this thing, and the speed of achieving a positive result when managing it. Therefore, in relation to such products as consumer electronics or communications, the concept of "ergonomics" is often used in relation to the shape, arrangement of nodes and weight, for example, and "usability" - in relation to the clarity of controls and modes of operation, to the number and necessity of functions.
In a broader sense, the term "usability" is used as ease of use (for example, for mechanical devices and tools (such as a doorknob or a knocker), the ergonomics of the form will increase the usability of the thing (that is, "usability", "friendliness and ease of use", "Practicality" and generally "applicability").
Usability matters a lot for ecommerce conversion rates. However, usability does not only mean improved visual guidance or improved site hierarchy. It also means more contact with a potential buyer through a professionally made, serious design, presenting the right information when it is needed.
Layout of web pages - the process of formation (layout) of web pages in a text or WYSIWYG editor, the next stage after web design; as well as the result of this process, that is, the actual web page.
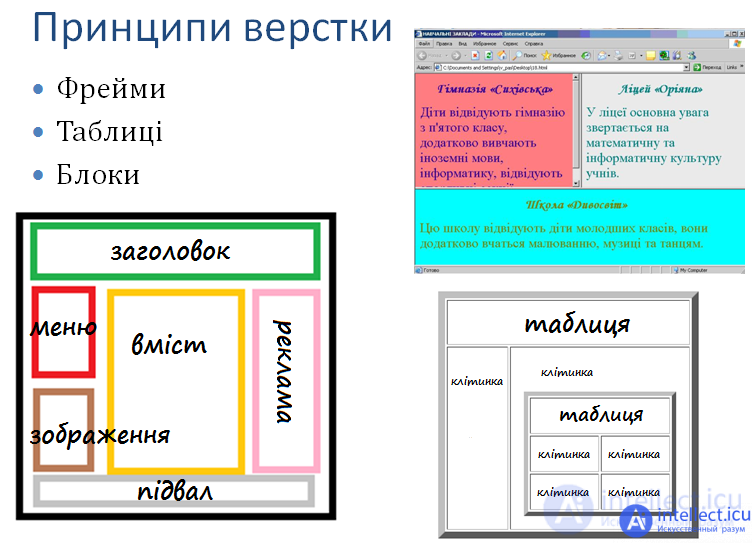
Table layout
Tabular layout was previously the main layout method, but it is still widely used in a variety of cases. Tables are used to create frames, define modular grids, create colored backgrounds, align elements, and so on.
Layers were used in the Netscape browser (layer tag), and were structural elements that can be placed on a web page by stacking them on top of each other with pixel precision . At the same time, the scripts allowed changing the layer parameters dynamically.
Block layout
Layout using blocks (div tag) and style sheets (CSS) describing them. Implements the concept of semantic layout.
Frame layout
Until recently, tables and frames were the main layout tools (frames, due to some problems [1], are a thing of the past: for example, the HTML 5 standard no longer includes support for frames [2]). Nowadays, blockchain is used much more widely. However, table layout is much simpler than block layout.
According to the principles of using HTML markup tools, there are logical markup and presentation (physical) markup.
For example, italic text can be obtained using both a tag and a tag .
In the first case, italic is set explicitly, and in the second, logical stress is made on the text, which is usually displayed in italics.
In other words, in the first approach, they are guided by the appearance, and in the second, by the logical purpose.
The advantage of the second approach is the independence of the layout from the type of devices used and the design of web pages.
If you stick to logical layout, then you can use the same layout for screen, print and mobile devices, adjusting the appearance using separate style files.
All sites, according to the layout, can be divided into three fundamental groups:
Fixed type of layout - design (tabular or block), in which the width of the column / image is set in pixels, that is, it is specified exactly.
Rubber layout type - a design in which the column / picture width is set as a percentage of the current screen resolution.
Responsive layout / type of layout - a design that adjusts (adapts) to the size of the screen, including the rebuilding of blocks from one place to another, or their replacement with blocks displayed only at a certain resolution. Responsive layout has replaced the idea of creating special mobile versions of the site, "living" on separate subdomains (for example, m.wikipedia.org).
Fixed design
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
Rubber design
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
Adaptive layout
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
That is, each type of design has its pluses and minuses, and the choice depends on the problem being solved. At the same time, a mixed design can be used - some columns of a tabular design should be set in percentages and others in pixels. [3]
Browsers deliberately treat a table as a single object, which prevents the contents of the table from being displayed until the entire contents of the table are downloaded to the local computer. [4] When using a table as a skeleton for placing the elements of a web page, its original advantage turns into a disadvantage, as it results in a delay in the output of the content. You should also take into account the growing volume of web pages with the active use of tables, especially in the case of their nesting into each other. All this leads to the fact that the table layout causes unnecessary delays in the output of information in the browser.
The problem arises with multiple nesting of tables, which is typical for achieving certain effects on a web page. The increase in the number of tables increases the chance of layout errors, increases the size of documents and slows down the download speed of files. The use of visual editors, such as Adobe Dreamweaver or Microsoft FrontPage, to create and edit documents makes it easier to work with tables, but due to the abundance of their parameters, developers are not immune to errors and unnecessary work associated with individual editing of each table.
In addition, the use of tables for design purposes does not correspond to the concept of semantic layout, which implies the use of elements (tags) in accordance with their sense, semantic meaning. Element and accompanying (,
, etc.) are intended to mark up tabular information (i.e., one in which there is a semantic relationship between elements belonging to the same column or one row). The W3C, as the developer of the HTML language, calls for the use of HTML for logical markup of information, and the design (including the positioning of various blocks) should be described separately from (X) HTML markup (using CSS, for example).
"Spacers"
When using tables, a well-known technique has become the use of spacers - transparent images one pixel high. The image itself is not displayed on the web page, but it can be scaled anywhere. It turns out an invisible stick of a certain width or height, which prevents the table cells from getting closer than a given distance. Spacers were especially useful for the Netscape browser, which did not show the background of the cell if nothing was placed in it. To get rid of this feature, a small transparent GIF picture was placed in the cell.
Techniques like these not only complicate the development of universal web pages, but also lead to slower document loading times. In this case, the browser has to load elements that are not visible to the user and, in fact, he does not need, but they are included in the overall traffic of the site.
Layers are structural elements that you can place on a web page by stacking them on top of each other with pixel precision. In HTML 4 and XHTML, a layer is a web page element created with a div tag and styled. [5]
The following principles are adhered to.
Layers can be placed in the browser window with pixel precision. The position of the layer is specified by two coordinates relative to any corner of the browser window, parent element, or document.
Scripts allow you to change layer parameters dynamically. This makes it possible to create different effects on the page, such as drop-down menus, games, expanding banners, floating windows, and more.
It is convenient to set and customize layer properties through styles. The possibilities of CSS expand the range of design delights. Using style sheets allows you to get compact and efficient code using simple methods.
More modern versions of browsers have become stricter in adhering to standards and contain tools for working with layers.
The layer can be moved, hidden and shown without reloading the entire page. With just a few instructions, you can create different effects like dropdown menus, tooltips, moving elements and more. Although adding such tricks increases the amount of code, it does not require reloading and updating the document and occurs without unnecessary delays on the part of the browser. In addition, the expressiveness and attractiveness of the site is greatly enhanced by the use of similar techniques with layers.
Layers can be stacked on top of each other, which makes it easier to place elements on a web page and provides more options for layout.
Layers are rendered faster than tables. Faster speed is achieved due to the compact code and the fact that the content of the layer is displayed as it is loaded. True, this can lead to "jumps" of page elements as they are loaded.
Do not assume that using layers is a panacea for all ills. Unfortunately, the standards for working with layers are not yet fully established and browsers implement certain features in different ways. Because of this, the main difficulty of layering is to create universal code that would work the same way and without errors in different browsers ("cross-browser") and at different screen resolutions. We have to delve into the intricacies of browser behavior when using different style elements.
Often, web specialists combine several specialties at once.
Also, web developers of the conditions are divided into a backend frontend and a full stack.
- Frontend is absolutely everything that the user observes on the screen of his PC. This includes the design of the resource, and the forms, and buttons, and the user's personal account on the site, etc. Front-end programmers are also involved in the layout and programming of these elements.
- Backend - this is the name of everything that, in one way or another, is connected with the server, with calculations on the server, as well as with the storage of information on it. For example, if you are looking for information in a search engine, the search results are generated by the server. These are all tasks for backend developers.
The frontend and backend have their own technologies and their own programming languages, and to work with them you need to know these languages. And if a programmer is well versed in both directions, if he easily performs tasks related to both the frontend and the backend, then this programmer is called a full-stack developer.
So a fullstack programmer is a universal specialist who is able to make up the site design, and customize the functioning of forms and buttons, and write the server side, plus he can configure the server itself. Such a programmer creates a web service alone, replacing 3-4 more narrow specialists.
Of course, it would be quite difficult for a full-stack developer to master all the necessary technologies as deeply as narrow specialists. However, today you can find quite a few projects that require universal developers with a good knowledge of a large number of technologies. So the profession of a full stack programmer is in high demand today.
There are two types of layout designers - some work in the web industry and create websites and web content, others work in the advertising and printing industry and prepare printed products for printing.
Layout of web pages is done by layout designers. In general, the task of the layout designer includes:
The layout designer uses the following software:
And also sometimes resorts to help:
The use of WYSIWYG editors and automatic layout programs is often frowned upon [6] [7] due to the poor quality of the resulting code. However, they are often more convenient for users to use than manual coding, and do not require deep knowledge of HTML, and therefore are widely used.
The job responsibilities of the html layout designer include:
The validity of the HTML layout is its compliance with the standards of The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The absence of errors in the layout of the document is one of the main indicators of the layout quality. Automatic check of the layout for errors can be carried out both with the help of the online service W3C, and various programs "validators". Different versions of the HTML specification assume different syntax, so a layout test for validity must take into account its Document Type.

Programmers in the office
A programmer is a specialist who writes and corrects programs for computers [1] (any computing devices), that is, programming.
Programming as an occupation can be the main professional activity of a specialist, or be used as an auxiliary activity for solving other professional problems, or be used in a non-professional sphere (as a tool for solving problems or for the sake of enjoying the programming process). The term "programmer" does not necessarily imply professional education or professional activity.
As the main professional activity, programming is used in the technical and scientific fields.
In engineering, the average technical qualification of a technician-programmer (formerly a "programmer-laboratory assistant") and the highest technical qualification of a software engineer are distinguished. The subject of activity of specialists with appropriate qualifications (technicians and engineers) is the design, development and production of software as an industrial product that satisfies the given functional, structural and technological requirements (the result of the activity is software). In Russia, the training of software engineers is carried out according to the training profile "Software for computer technology and automated systems" of the direction "Informatics and computer technology" [2].
There is training of mathematicians-programmers in the direction "Mathematical support and administration of information systems" [3].
At the end of the 2000s, a new direction of training programmers "Software Engineering" appeared in Russia [4]. The area of professional activity of graduates in this direction is the industrial production of software. This direction of training differs from the training of software engineers in the specialty "Software for computer technology and automated systems" in that general engineering disciplines are replaced by disciplines from the new field of knowledge of software engineering. The objects of professional activity of software engineers are not programs and software systems, but methods and tools for developing a software product, as well as processes of the life cycle of a software product.
The subject of activity of programmers in science is the solution of problems using the methods of applied mathematics and implementation on a computer (the result of the activity is the solution of the problem obtained using the program).
In Russia, training of specialists in this area is carried out in the following areas:
In Ukraine, the following codes of specialties in universities
|
12 |
Information |
121 |
Software engineering |
|
|
122 |
Computer Science and Information Technology |
|
|
|
123 |
Computer engineering |
|
|
|
124 |
System analysis |
|
|
|
125 |
Cybersecurity |
As an auxiliary activity, programming is currently used in a wide range of professions.
Due to the significant spread in modern society of computer technology and, accordingly, programming as a type of activity, the need for professional programmers in developed countries and third world countries is now much greater than the possibilities of higher education for training in the relevant specialties, while the qualification requirements in business in most cases, much narrower than training in a specialty at a university (see, for example, [5]). In this regard, the self-education of programmers and professional activities in the field of programming are very widespread without receiving formal education in the relevant specialty, and specialists who have received programming specialties,you need to constantly improve your knowledge and skills and quickly master new technologies.
As indicated above, from the point of view of correct terminology, a person may have (for example) the occupation "programmer", qualification "software engineer", specialty "software for computers and automated systems" and the position of "leading specialist". Colloquially, however, the word "programmer" is often used to refer to all of these concepts.
System administrators and other IT professionals are sometimes called programmers by mistake.
At present, as before, the classification of programmers into application and system is widely used. An application programmer is a programmer whose programs are designed to solve an applied problem that satisfies the needs of the end user and, according to the concept of classification, lies outside the computer sphere. A system programmer is a programmer whose programs are designed to ensure the operation of a computer and are used by other computer specialists.
The emergence of programming as a profession and, especially, as a professional activity is difficult to date unambiguously.
Often the first programmable device is considered to be a jacquard loom, built in 1804 by Joseph Marie Jacquard, which revolutionized the weaving industry by providing the ability to program patterns on fabrics using punched cards.
The first programmable computing device, the Analytical Engine, was developed by Charles Babbage (but was unable to build it). On July 19, 1843, Countess Ada Augusta Lovelace, daughter of the great English poet George Byron, is believed to have written the first program for the Analytical Engine in human history. This program solved the Bernoulli equation, which expresses the energy conservation law for a moving fluid.
In her first and only scientific work, Ada Lovelace addressed a large number of issues. A number of the general provisions expressed by her (the principle of saving working memory cells, the connection of recurrent formulas with cyclic computation processes) have retained their fundamental significance for modern programming. Babbage's material and Lovelace's commentary outlined concepts such as subroutine and subroutine library, instruction modification, and index register, which were not introduced until the 1950s.
However, none of the programs written by Ada Lovelace were ever launched.
Ada Augusta, Countess of Lovelace, is considered an honorary first programmer (although, of course, writing one program by modern standards cannot be considered an occupation or professional activity). History has kept its name in the name of the universal programming language "Ada".
The first working programmable computer (1941), the first programs for it, as well as (with certain reservations) the first high-level programming language Planckulkühl was created by the German engineer Konrad Zuse.
The names of people who first began to professionally perform the work of programming itself (apart from adjusting computer hardware) has not been preserved in history, since at first programming was viewed as a minor adjustment operation.
In 2009, the Programmer's Day was officially approved in Russia, which is celebrated annually on September 13 (in a leap year - September 12) - that is, the Programmer's Day is celebrated on the 256th day of the year. This number is not accidental: it is obtained from raising two to the eighth power. This is the number of numbers that can be expressed with one eight-bit byte.
A tester is a specialist who tests software (software). It is his responsibility to search for possible errors and failures in the operation of the program. The tester simulates various situations that may arise during the use of the program so that the developers can correct the errors found.
The tester also creates and uses a variety of input data, provided and not provided by the authors of the program. His activity usually implies at least three patterns of behavior:
The relationship between QA, QC and testing can be schematically represented as follows:
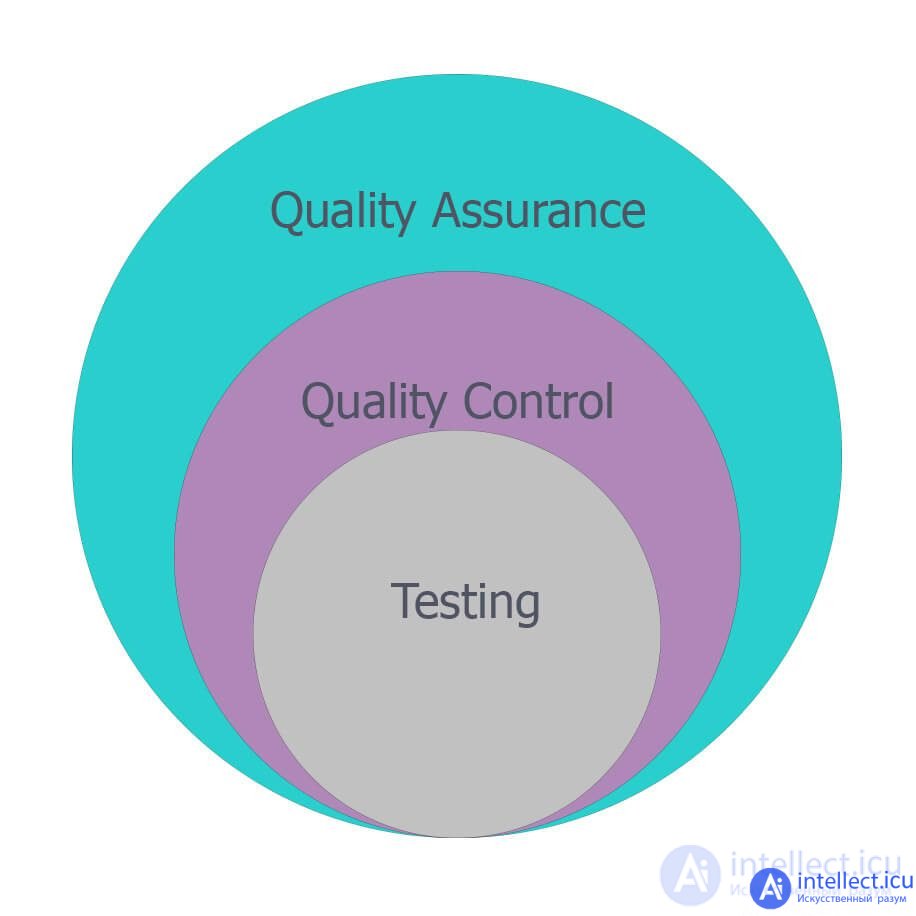
QA (Quality Assurance) - product quality assurance is, in fact, the whole complex of processes that ensure quality, the most extensive concept. QA is integrated into all stages of development: from project description to testing, release and even post-release maintenance.
QA specialists create and implement various tactics to improve quality at all stages of production: preparation and setting of standards, quality analysis, selection of tools, error prevention and continuous process improvement.
QC (Quality Control) - product quality control is part of the QA complex, which is responsible for analyzing test results, finding errors and eliminating them. QC is focused on validating a specific product and includes various processes such as code reviews, technical reviews, design reviews, testing, and more.
Testing is already a direct process of checking the results of work for compliance with the established requirements. A tester is a specialist who is involved in such verification. It tests components of a product or the entire product for design errors or inaccuracies. Testing is one of the key processes in a quality assurance system.
Specialization of testers can be divided into areas: testing security, performance, usability; and also by methods of writing tests: manual and automated testing.
In the case of creating programs with different levels of protection and access rights for the user, the number of possible models of behavior ("boss", "subordinate") increases significantly.
Alpha tester - a user of a program that is under development (the "Alpha version", as a rule, is not fully functional), who has undertaken any form of obligation to fully or partially test the program, as well as, possibly, on special conditions for copying it and use.
Beta Tester - a program user who has committed himself to testing the program ("Beta version"), including the officially published versions and the so-called "release candidates" of the program.
In different cases, the relationship of alpha and beta testers with developers may or may not be formalized. A number of users are volunteering to beta test the software.
Some argue that the specificity of the profession lies in the apparent monotony and monotony of the labor process; for others, testing is creative research work (as opposed to standardized development). One of the features of the profession is the ability to work remotely, and the distance often does not matter (the tester may be located in a different city or country in relation to the developer and customer). This allows us to consider this profession as one of the possible steps for gaining experience and accumulating knowledge in remote software development for the purpose of further work as a programmer.
The necessary qualities are logical thinking, good memory, the ability to learn and adapt to existing tasks, quickly switch from one type of task to another. Patience, perseverance and the ability to work in a team (in XP-testing) are equally important.
In addition, a tester acts both as a user and as an expert, and therefore must have a certain mindset: be able to reproduce the behavior of a product user and analyze the behavior of the system, the input parameters and the results obtained from the point of view of the engineer.
The main requirements for an applicant, as a rule, are:
At the same time, the requirements for the level of necessary skills and specialization vary depending on the software under test.
Not to be confused with CEO.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is a set of measures to improve the site's position in the search engine results for certain user queries in order to promote the site. Usually, the higher the position of the site in the search results, the more interested visitors go to it from the search engines. When analyzing the effectiveness of search engine optimization, the cost of the target visitor is estimated, taking into account the time taken to bring the site to the specified positions and site conversions.
According to the RAEC, the search engine optimization market in 2012 was equal to 10.24 billion rubles. Forecast for 2013 - market growth by 19% [1].
Search engines take into account many parameters of a site when calculating its relevance (degree of compliance with the entered query):
All factors affecting the position of a site in the search engine results can be divided into external and internal. Internal optimization (relating exclusively to the internal system of the site) - refers to the work aimed at improving the overall quality of the site, the benefits that it brings to the visitor. This can include work on the structure of the project, on facilitating the perception of content and directly on the quality of this content. The value of the total number of such factors in most sources fluctuates around 200. The functional approach to search engine optimization, aimed at fitting certain factors to their target values, has become a thing of the past due to the complication of search engine algorithms - the cost of "balancing" dozens of factors is many times higher than the cost of creating initially a quality resource.
External factors are divided into static and dynamic:
External search engine optimization methods:
The person who does the job of optimizing websites is called an optimizer.
There are various SEO services that make it easier for SEOs and give site owners the opportunity to promote them on their own.
Factors that lower a site's ranking include:
Along with the emergence and development of search engines in the mid-1990s, search engine optimization appeared. At that time, search engines placed a lot of importance on text on the page, keywords in meta tags, and other internal factors that could be easily manipulated by site owners. This led to the fact that in the results of many search engines the first few pages were occupied by sites that were completely devoted to advertising, which sharply reduced the quality of search engines' work. With the advent of PageRank technology, more weight was given to external factors, which helped Google to become the leader in search on a global scale, making it difficult to optimize with just text on the site.
However, optimization is evolving along with the search engines, and in today's search results, you can see more and more commercial sites with artificially inflated popularity, especially for commercially attractive queries (transactional queries).
Optimization methods can be divided into three classes according to their color (white, gray and black), however, recent events in the world of search engines make it clear that this division is very conditional - any manipulation of certain site parameters can be regarded by a search engine as an extremely undesirable effect on its results. Thus, any attempt to manipulate search results is expressly prohibited in the license to use the Yandex search engine. "White" SEOs and marketers use Yandex recommendations for creating "good" sites [2]. Thus, they promote the site without breaking the rules of search engines.
White optimization - optimizing work on a resource without the use of methods of promoting a resource officially prohibited by each search engine - without affecting the search algorithms of sites. This includes work on the site itself, namely on internal navigation and content, and work with the external environment of the site, that is, promoting the optimized site through reviews, press releases, registration in social bookmarks, affiliate programs, etc. links to the site. It should be noted that Yandex warns that if any optimization method is not officially prohibited, it does not mean that it can be used.
Gray search engine optimization can be attributed to the addition of a large number of keywords to the text of the page, often to the detriment of human readability, for example: "Butter oil, because it contains oil derivatives of oil fats." At the same time, optimization consists first in the selection of key queries for a specific web page, determining the size of the target "SEO text" and the required frequency of keywords in it, and then in formulating sentences and phrases containing key queries a certain number of phrases in different cases , singular and plural, with different forms of verbs. These parameters can then be adjusted according to the results of search engine results. At the same time, the task of an SEO copywriter is to write the original text in such a way thatso that such optimization was as less noticeable as possible to the "living" reader (and in particular to the assessor of the search engine). The inclusion of a key query in HTML tags title, h1, alt, and the meta keywords attribute is also widely used.
Another example of gray-scale optimization is doorway without a redirect, when when you get to the doorway there is no automatic redirection to the promoted site.
Gray optimization differs from black optimization in that it is not officially prohibited, but its use can still be regarded as an unnatural overestimation of the site's popularity. Some search engines, such as Google, may temporarily or permanently block such a site. That is, the final decision on whether the promotion methods are legal or not is made by a specialist - a moderator of a search engine, not a program.
Black optimization includes all methods that are contrary to the rules of search engines. Among them, the following can be distinguished: the use of doorways (pages and resources created specifically for search engine robots, often with a large number of keywords on the page), a technique called cloaking (the user is given one easy-to-read page, and the search robot is given another, optimized for any requests), the use of hidden text on site pages, the use of "single-pixel links".
Not to be confused with copyright - copyright, copyright.
Copywriting (English copywriting from copy - manuscript, text material + write - to write) - professional activity in writing advertising and presentation texts. Such can be considered all texts that directly or indirectly advertise or popularize a product, company, service, person or idea.
Specialists who are engaged in copywriting are called copywriters. .
In English, the word "copywriting" is a neologism and is not represented in dictionaries. A "copywriter" is defined as a "writer of advertising or publicity copy".
In Runet, copywriting is sometimes understood as creating texts for the needs of SEO or writing articles of a non-advertising nature .
Copywriting has nothing to do with the term "copyright", which also came from the English language, which has a completely different semantic meaning.
The activity called copywriting has been around for a very long time. It arose along with trade, since the seller's replicas are already the result of copywriting.
The texts invented by copywriters of the Soviet era were and remain very popular, many of them have turned into catch phrases ("Smoking - harm to health", "Chatterbox is a godsend for a spy", "Building firmly - handing over ahead of schedule", etc.). Many advertising slogans are also known to this day: “Trekhgornoe beer will drive out the hypocrite and moonshine”, “There have never been any better nipples. I am ready to suck until old age "," Nowhere but in Mosselprom "," Keep your money in a savings bank ", etc.
It is in demand in direct advertising - the one that calls here and now to take the desired action: order, call, click. Such texts encourage the user to immediately buy a product or use a service.
As part of an advertising agency, a copywriter works in tandem with an art director. This symbiosis is called a creative couple.
John Caples (1900-1990) is considered one of the pioneers of copywriting in direct marketing. His book Tested Advertising Methods was first published in the US in 1932 and has gone through numerous reprints due to its enduring relevance. It was recently published in Russian.
Joseph Sugerman, another famous direct marketing ad executive of the late 20th century, is recognized as one of America's most effective and prolific copywriters. His book The Art of Creating Advertising Messages. The Adweek Copywriting Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Advertising and Marketing Copy from One of America's Top Copywriters has also been reprinted several times in Russia.
As an element of branding, it works for a delayed sale - fixing the brand image in the mind of the consumer or simply creating the desired image of a product, service, company, person, idea.
Sometimes
продолжение следует...
Часть 1 1.7. Professions for creating and maintaining websites
Часть 2 Copywriting and rewriting - 1.7. Professions for creating and maintaining
Comments
To leave a comment
Fundamentals of Internet and Web Technologies
Terms: Fundamentals of Internet and Web Technologies