Lecture
Taking into account (5.2) and (5.3) the torque of the body
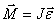 | (5.8) |
or

This expression is an analogue of Newton's second law for rotational motion, from which it follows that angular acceleration 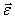 a solid body when rotating around a fixed axis is directly proportional to the torque and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia relative to this axis. From this expression it follows that the moment of inertia U is a measure of its inertia in the rotational motion around a fixed axis. In the case of translational motion, a measure of inertia, as is known, is body mass.
a solid body when rotating around a fixed axis is directly proportional to the torque and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia relative to this axis. From this expression it follows that the moment of inertia U is a measure of its inertia in the rotational motion around a fixed axis. In the case of translational motion, a measure of inertia, as is known, is body mass.
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics